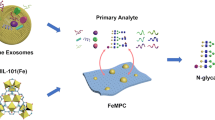
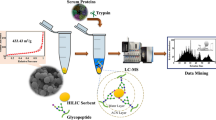
Abstract
Soft-template carbonized mesopores were developed for the purpose of enriching urinary exosomal glycans through organic–organic self-assembly using block copolymers and resol precursors. With a high surface area of 229 m2 g−1, a small pore size of 3.1 nm, and a significant amount of carbon that specifically interacts with oligosaccharides in glycans, this carbonized mesopore material exhibits high selectivity and low limits of detection (5 ng μL−1) towards glycans. Our analysis of complex urine samples from healthy volunteers and bladder carcinoma patients successfully profiled 48 and 56 exosomal glycans, respectively, and 16 of them were significantly changed. Moreover, one upregulated bisecting N-acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc)-type glycan with core fucose, two upregulated and two downregulated terminal-sialylated glycans were revealed to be linked to bladder carcinoma. This approach is of significant importance for understanding diseases that arise from protein glycosylation mutations, and it may contribute to the development of novel diagnostic and therapeutic strategies for bladder carcinoma.
Graphical Abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data available within the article or its supplementary materials.
References
Yang D, Zhang W, Zhang H, Zhang F, Chen L, Ma L, Larcher LM, Chen S, Liu N, Zhao Q, Tran PH (2020) Progress, opportunity, and perspective on exosome isolation - efforts for efficient exosome-based theranostics. Theranostics 10(8):3684–3707
Gurung S, Perocheau D, Touramanidou L, Baruteau J (2021) The exosome journey: from biogenesis to uptake and intracellular signalling. Cell Commun Signal 19(1):47
Yu D, Li Y, Wang M, Gu J, Xu W, Cai H, Fang X, Zhang X (2022) Exosomes as a new frontier of cancer liquid biopsy. Mol Cancer 21(1):56
Zhang Y, Liu Y, Liu H, Tang WH (2019) Exosomes: biogenesis, biologic function and clinical potential. Cell Biosci 9:19
Ludwig N, Whiteside TL, Reichert TE (2019) Challenges in exosome isolation and analysis in health and disease. Int J Mol Sci 20(19):4684
Wang ZD, Huang CW, Sun NR, Deng CH (2021) Advances in aptamer-based nanomaterials for separation and analysis of non-genetic biomarkers in biofluids. Sci China Chem 65(6):932–947
Dad HA, Gu TW, Zhu AQ, Huang LQ, Peng LH (2021) Plant exosome-like nanovesicles: emerging therapeutics and drug delivery nanoplatforms. Mol Ther 29(1):13–31
Guan S, Yu H, Yan G, Gao M, Sun W, Zhang X (2020) Characterization of urinary exosomes purified with size exclusion chromatography and ultracentrifugation. J Proteome Res 19(6):2217–2225
Wang J, Ma P, Kim DH, Liu BF, Demirci U (2021) Towards microfluidic-based exosome isolation and detection for tumor therapy. Nano Today 37:101066
Wei H, Chen Q, Lin L, Sha C, Li T, Liu Y, Yin X, Xu Y, Chen L, Gao W, Li Y, Zhu X (2021) Regulation of exosome production and cargo sorting. Int J Biol Sci 17(1):163–177
Qing G, Yan J, He X, Li X, Liang X (2020) Recent advances in hydrophilic interaction liquid interaction chromatography materials for glycopeptide enrichment and glycan separation. Trends Analyt Chem 124:115570
Kinoshita M, Yamada K (2022) Recent advances and trends in sample preparation and chemical modification for glycan analysis. J Pharmaceut Biomed 207(5):114424
Clerc F, Reiding KR, Jansen BC, Kammeijer GS, Bondt A (2016) Human plasma protein N-glycosylation. Glycoconj J 33(3):309–343
Kailemia MJ, Park D, Lebrilla CB (2017) Glycans and glycoproteins as specific biomarkers for cancer. Anal Bioanal Chem 409(2):395–410
Shimoda A, Sawada SI, Sasaki Y, Akiyoshi K (2019) Exosome surface glycans reflect osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells: profiling by an evanescent field fluorescence-assisted lectin array system. Sci Rep 9:11497
Liang Y, Eng WS, Colquhoun DR, Dinglasan RR, Graham DR, Mahal LK (2014) Complex N-linked glycans serve as a determinant for exosome/microvesicle cargo recruitment. J Biol Chem 289(47):32526–32537
Freitas D, Balmana M, Pocas J, Campos D, Osorio H, Konstantinidi A, Vakhrushev SY, Magalhaes A, Reis CA (2019) Different isolation approaches lead to diverse glycosylated extracellular vesicle populations. J Extracell Vesicles 8(1):1621131
Ruhaak LR, Xu G, Li Q, Goonatilleke E, Lebrilla CB (2018) Mass spectrometry approaches to glycomic and glycoproteomic analyses. Chem Rev 118(17):7886–7930
Sun NR, Yao JZ, Wang JW, Zhang XM, Li Y, Deng CH (2016) Magnetic nanoporous hybrid carbon from core–shell metal–organic frameworks for glycan extraction. RSC Adv 6(41):34434–34438
Wu Y, Chen H, Chen Y, Sun N, Deng C (2022) Metal organic frameworks as advanced extraction adsorbents for separation and analysis in proteomics and environmental research. Sci Chi Chem 65(4):650–677
Riley NM, Bertozzi CR, Pitteri SJ (2021) A pragmatic guide to enrichment strategies for mass spectrometry-based glycoproteomics. Mol Cell Proteomics 20:100029
Liu Y, Ma W, He Y, Chen Z, Lin Z (2020) Facile synthesis of hydrophilic magnetic mesoporous silica microspheres for selective enrichment of glycopeptides and glycans. Anal Lett 54(6):966–978
Lim B, Kydd L, Jaworski J (2019) A peptide-lectin fusion strategy for developing a glycan probe for use in various assay formats. Chemosensors (Basel) 7(4):55
Wang Y, Wang J, Li J, Ling Y, Jia Y, Yang Y, Liu X, Zhang X, Zhou Y (2020) Synergistic integration of FeNi magnetic nanoparticles with graphene-based porous carbon for efficient capture of N-linked glycans. Nanoscale 12(47):24188–24195
Xiong H, Gao T, Li K, Liu Y, Ma Y, Liu J, Qiao ZA, Song S, Dai S (2019) A polymer-oriented self-assembly strategy toward mesoporous metal oxides with ultrahigh surface areas. Adv Sci (6):1801543
Wu YL, Chen YJ, Chen HL, Yang CJ, Shen XZ, Deng CH, Sun NR, Wu H (2021) Probing serum N-glycan patterns for rapid and precise detection of Crohn's disease. Chem Comm 57(86):11362–11365
Yao J, Li L, Song H, Liu C, Chen X (2009) Synthesis of magnetically separable ordered mesoporous carbons from F127/[Ni(H2O)6](NO3)2/resorcinol-formaldehyde composites. Carbon 47(2):436–444
Zhai Y, Dou Y, Liu X, Tu B, Zhao D (2021) One-pot synthesis of magnetically separable ordered mesoporous carbon. Green Chem 23(2):1861–1870
Tang Y, Qiu M, Yang J, Shen F, Wang X, Qi X (2021) One-pot self-assembly synthesis of Ni-doped ordered mesoporous carbon for quantitative hydrogenation of furfural to furfuryl alcohol. Green Chemi 23(4):1861–1870
Park SS, Lee WK, Yoo JM, Ha CS (2019) Facile and one-pot synthesis of magnetic nanoparticles containing mesoporous carbon. Mol Crys Liq Cryst 685(1):55–63
Karolewicz B, Gajda M, Górniak A, Owczarek A, Mucha I (2017) Pluronic F127 as a suitable carrier for preparing the imatinib base solid dispersions and its potential in development of a modified release dosage forms. J Therm Anal Calorim 130(1):383–390
Meng Y, Gu D, Zhang F, Shi Y, Chen L, Feng D, Wu Z, Chen Z, Wan Y, Stein A, Zhao Q (2006) A family of highly ordered mesoporous polymer resin and carbon structures from organic-organic self-assembly. Chem Mater 18(4):4447–4464
Zhai Y, Dou Y, Liu X, Tu B, Zhao D (2009) One-pot synthesis of magnetically separable ordered mesoporous carbon. J Mater Chem 19(20):3292–3300
Asgari M, Vitale G, Sundararaj U (2021) Synthesis and characterization of a novel nickel pillared–clay catalyst: in-situ carbon nanotube–clay hybrid nanofiller from Ni-PILC. Appl Clay Sci 4:205
Wang Y, Su Y, Sun Q, Ma X, Ma X, Jiang Z (2006) Improved permeation performance of pluronic F127–polyethersulfone blend ultrafiltration membranes. J Membrane Sci 282(1):44–51
Zhuang X, Qian X, Lv J, Wan Y (2010) An alternative method to remove PEO–PPO–PEO template in organic–inorganic mesoporous nanocomposites by sulfuric acid extraction. Appl Surf Sci 256(17):5343–5348
Li N, Wang J, Yang X, Li L (2011) Novel nanogels as drug delivery systems for poorly soluble anticancer drugs. Colloids Surf B 83(2):237–244
Jayababu S, Inbasekaran M, Narayanasamy S (2022) Promising solar photodegradation of RY 86 by hydrophilic F127 (pluronic) aided nano cobalt ferrite and its biomedical applications. J Mol Liq 350:118530
Zhai Y, Dou Y, Liu X, Park SS, Ha CS, Zhao D (2011) Soft-template synthesis of ordered mesoporous carbon/nanoparticle nickel composites with a high surface area. Carbon 49(2):545–555
Wu Y, Zhang N, Wu H, Sun N, Deng C (2021) Magnetic porous carbon-dependent platform for the determination of N-glycans from urine exosomes. Mikrochim Acta 188(3):66
Lv J, Wang Z, Li F, Zhang Y, Lu H (2019) Reverse capture for selectively and sensitively revealing the N-glycome of serum exosomes. Chem Commun 55(95):14339–14342
Qin H, Zhao L, Li R, Wu R, Zou H (2011) Size-selective enrichment of N-linked glycans using highly ordered mesoporous carbon material and detection by MALDI-TOF MS. Anal Chem 83(20):7721–7728
Yang G, Tan Z, Lu W, Guo J, Yu H, Yu J, Sun C, Qi X, Li Z, Guan F (2015) Quantitative glycome analysis of N-glycan patterns in bladder cancer vs normal bladder cells using an integrated strategy. J Proteome Res 14(2):639–653
Li J, Zhao T, Li J, Shen J, Jia L, Zhu B, Dang L, Ma C, Liu D, Mu F, Hu L, Sun S (2022) Precision N-glycoproteomics reveals elevated LacdiNAc as a novel signature of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Mol Oncol 16(11):2135–2152
Sun N, Deng C, Li Y, Zhang X (2018) Highly selective enrichment of N-linked glycan by carbon-functionalized ordered graphene/mesoporous silica composites. Anal Chem 84(4):2246–2250
Niu H, Li X, Peng J, Zhang H, Zhao X, Zhou X, Yu D, Liu X, Wu R (2019) The efficient profiling of serum N-linked glycans by a highly porous 3d graphene composite. Analyst 144(17):5261–5270
Zhang X, Huang C, Jiang Y, Shen J, Geng P, Zhang W, Huang Q (2016) An electrochemical glycan biosensor based on a thionine-bridged multiwalled carbon nanotube/ gold nanoparticle composite-modified electrode. RSC Adv 6(114):112981–112987
Wang J, Weng L, Liu W, Zhang H, Gao M, Zhang X, Huang L (2022) Facile preparation of a novel chitosan-derived porous graphitized carbon biomaterial for highly efficient capture of N-glycans. Analyst 147(22):4954–4961
Mehmet KH, İzzet AV, Bekir SA (2019) A new titania glyco-purification tip for the fast enrichment and efficient analysis of glycopeptides and glycans by MALDI-TOF-MS. J Pharm Biomed Ana 174:191–197
Wang Y, Wang J, Gao M, Zhang X (2017) A novel carbon material with nanopores prepared using a metal–organic framework as precursor for highly selective enrichment of N-linked glycans. Anal Bioanal Chem 409(2):431–438
Li X, Xu G, Peng J, Liu S, Zhang H, Mao J, Niu H, Lv W, Zhao X, Wu R (2018) Highly porous metal-free graphitic carbon derived from metal-organic framework for profiling of N-linked glycans. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 10(14):11896–11906
Zhu B, Chen Z, Shen J, Xu Y, Lan R, Sun S (2022) Structural- and site-specific N-glycosylation characterization of COVID-19 virus spike with StrucGP. Anal Chem 94(36):12274–12279
Shen J, Jia L, Dang L, Su Y, Zhang J, Xu Y, Zhu B, Chen Z, Wu J, Lan R, Hao Z, Ma C, Zhao T, Gao N, Bai J, Zhi Y, Li J, Zhang J, Sun S (2021) StrucGP: de novo structural sequencing of site-specific N-glycan on glycoproteins using a modularization strategy. Nat Methods 18(8):921–929
Oikawa M, Hatakeyama S, Yoneyma T, Tobisawa Y, Narita T, Yamamoto H, Hashimoto Y, Koie T, Narita S, Sasaki A, Tsuchiya N (2018) Significance of serum N-glycan profiling as a diagnostic biomarker in urothelial carcinoma. Eur Urol Focus 4(2):405–411
Khoo KH (2021) Glycoproteomic software solutions spotlight glycans. Nat Methods 18(12):1457–1458
Yang G, Huang L, Zhang J, Yu H, Li Z, Guan F (2016) Global identification and differential distribution analysis of glycans in subcellular fractions of bladder cells. Int J Biol Sci 12(7):799–811
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by National Key R&D Program of China (2018YFA0507501), the National Science Foundation for Distinguished Young Scholars of China (21425518), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (22074019, 22004017), and Shanghai Sailing Pro-gram (20YF1405300).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The experiments in this work were carried out in compliance with the ethical standards. Meanwhile, it was conducted according to the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Ethics Committee of Fudan University. Besides, all volunteers and patients involved in the research gave consent.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Y., Wu, Y., Li, J. et al. Resol/triblock copolymer composite-guided smart fabrication of carbonized mesopores for efficiently decoding exosomal glycans. Microchim Acta 190, 319 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-023-05885-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-023-05885-x