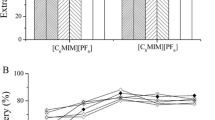
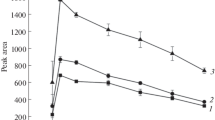
Abstract
A vortex-assisted dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction (VA-DLLME) procedure using hydrophobic deep eutectic solvent–based ferrofluid (HDES-FF) as an extractant was established. The developed sample preparation method coupled with high-performance liquid chromatography–diode array detector (HPLC–DAD) was applied to the pretreatment and determination of myclobutanil (MYC) in fruit juice. Hydrophobic deep eutectic solvent, synthesized by n-decanoic acid and dl-menthol, was as a carrier and combined with magnetic nanoparticles (Fe3O4@OA) to form HDES-FF as an extractant with high extraction capacity. The synthesized materials were characterized by Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR) spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction (XRD), and vibrating sample magnetometer (VSM). Parameters affecting extraction efficiency were optimized using single-factor experiments and Box-Behnken design via response surface methodology (BBD-RSM). Parallel tests were performed three times under the optimal conditions predicted by the model, yielding an actual mean recovery of 94.77% with RSD of 2.7% (n = 3) and an enrichment factor of 41.8 ± 0.98 (mean value ± SD, n = 3). Under the optimal conditions, the linear range was 1.0–100.0 µg·mL−1; the limit of detection (LOD) and limit of quantification (LOQ) were 0.25 and 0.80 µg·mL−1, respectively. The average spiked recoveries in the samples ranged from 98.2 to 100.5% with intra-day relative standard deviations (RSDs) of 1.2–3.5% (n = 3) and inter-day RSDs of 1.1–3.8% (n = 3). Finally, the method was successfully applied to the determination of MYC antimicrobial agent in different fruit juice samples. The proposed HDES-FF-VA-DLLME/HPLC–DAD method was verified to widely apply to the extraction of triazole fungicides.
Graphical Abstract





Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Data available on request from the authors.
References
Garcia-Muñoz P, Dachtler W, Altmayer B, Schulz R, Robert D, Seitz F et al (2020) Reaction pathways, kinetics and toxicity assessment during the photocatalytic degradation of glyphosate and myclobutanil pesticides: influence of the aqueous matrix. Chem Eng J 384:123315. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.123315
Fonseca FS, Carrão DB, de Albuquerque NCP, Nardini V, Dias LG, da Silva RM et al (2019) Myclobutanil enantioselective risk assessment in humans through in vitro CYP450 reactions: metabolism and inhibition studies. Food Chem Toxicol 128:202–211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2019.04.009
Allen JW, Wolf DC, George MH, Hester SD, Sun G, Thai S-F et al (2006) Toxicity profiles in mice treated with hepatotumorigenic and non-hepatotumorigenic triazole conazole fungicides: propiconazole, triadimefon, and myclobutanil. Toxicol Pathol 34(7):853–862. https://doi.org/10.1080/01926230601047816
Sun M, Liu D, Qiu X, Zhou Q, Shen Z, Wang P et al (2014) Acute toxicity, bioactivity, and enantioselective behavior with tissue distribution in rabbits of myclobutanil enantiomers. Chirality 26(12):784–789
Lin C, Zhang L, Zhang H, Wang Q, Zhu J, Wang J et al (2018) Enantioselective degradation of myclobutanil and famoxadone in grape. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25(3):2718–2725. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0539-4
EU Pesticides Database - MRLs (2020) https://ec.europa.eu/food/plant/pesticides/eu-pesticides-database/start/screen/mrls. Accessed 2020
National Standard for Food Safety Maximum Residue Limits of Pesticides in Food (2021). (GB 2763–2021, 496): National Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China; Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs of the People’s Republic of China; State Administration of Market Administration.
Wang H, Yang X, Hu L, Gao H, Lu R, Zhang S et al (2016) Detection of triazole pesticides in environmental water and juice samples using dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction with solidified sedimentary ionic liquids. New J Chem 40(5):4696–4704. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5NJ03376D
Morin-Crini N, Rocchi S, Jeanvoine A, Garcia C, Millon L, Crini G (2018) Analysis of triazole fungicides in aqueous solutions and their removal on modified activated carbons. Arab J Sci Eng 43(7):3493–3501. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-017-2913-4
Farajzadeh MA, Feriduni B, Mogaddam MR (2015) Determination of triazole pesticide residues in edible oils using air-assisted liquid-liquid microextraction followed by gas chromatography with flame ionization detection. J Sep Sci 38(6):1002–1009. https://doi.org/10.1002/jssc.201400818
Tian HZ, Xu CQ, Shi ZM, Fu HL, Li XW (2021) Enantioseparation and determination of triazole fungicides in fruit juice by aqueous biphasic system coupled with HPLC-MS/MS. J Sep Sci 44(18):3407–3417. https://doi.org/10.1002/jssc.202100370
Abdallah OI, Alrasheed AM, Al-Mundarij AA, Omar AF, Alhewairini SS, Al-Jamhan KA (2021) Levels of residues and dietary risk assessment of the fungicides myclobutanil, penconazole, tebuconazole, and triadimenol in squash. Biomed Chromatogr 35(8):e5126. https://doi.org/10.1002/bmc.5126
Li Y, Dong F, Liu X, Xu J, Li J, Kong Z et al (2012) Simultaneous enantioselective determination of triazole fungicides in soil and water by chiral liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 1224:51–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2011.12.044
Zhang H, Wang X, Qian M, Wang X, Xu H, Xu M et al (2011) Residue analysis and degradation studies of fenbuconazole and myclobutanil in strawberry by chiral high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J Agric Food Chem 59(22):12012–12017
Pelajić M, Peček G, Mutavdžić Pavlović D, Vitali Čepo D (2016) Novel multiresidue method for determination of pesticides in red wine using gas chromatography–mass spectrometry and solid phase extraction. Food Chem 200:98–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2016.01.018
Xiong YB, Lu ZH, Wang DD, Yang MO, Guo HM, Yang ZH (2020) Application of polydopamine functionalized magnetic graphene in triazole fungicides residue analysis. J Chromatogr A 1614:460725. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2019.460725
Wang P, Zhao Y, Wang X, Yu GW, Wang J, Li ZG et al (2018) Microwave-assisted-demulsification dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction for the determination of triazole fungicides in water by gas chromatography with mass spectrometry. J Sep Sci 41(24):4498–4505. https://doi.org/10.1002/jssc.201800860
Zeng H, Xie X, Huang Y, Chen J, Liu Y, Zhang Y et al (2019) Enantioseparation and determination of triazole fungicides in vegetables and fruits by aqueous two-phase extraction coupled with online heart-cutting two-dimensional liquid chromatography. Food Chem 301:125265. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.125265
Qiao L, Sun R, Yu C, Tao Y, Yan Y (2021) Novel hydrophobic deep eutectic solvents for ultrasound-assisted dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction of trace non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in water and milk samples. Microchem J 170:106686. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2021.106686
Ying P, Guilong L, Hanyang Z et al (2016) Dispersive solid-phase extraction followed by vortex-assisted dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction based on the solidification of a floating organic droplet for the determination of benzoylurea insecticides in soil and sewage sludge. J Sep Sci 39(7):1258–1265
Xue J, Yang L, Chen X, Bai XH, Hu S (2021) Vortex-assisted dispersive liquid-phase microextraction for the analysis of main active compounds from Zi-Cao-Cheng-Qi decoction based on a hydrophobic deep eutectic solvent. J Sep Sci 44(24):4376–4383. https://doi.org/10.1002/jssc.202100270
Abbott AP, Capper G, Davies DL, Rasheed RK, Tambyrajah V (2003).Novel solvent properties of choline chloride/urea mixtures. Chem Commu (1) 70–71. https://doi.org/10.1039/B210714G
Majidi SM, Hadjmohammadi MR (2019) Alcohol-based deep eutectic solvent as a carrier of SiO2@Fe3O4 for the development of magnetic dispersive micro-solid-phase extraction method: application for the preconcentration and determination of morin in apple and grape juices, diluted and acidic extract of dried onion and green tea infusion samples. J Sep Sci 42(17):2842–2850. https://doi.org/10.1002/jssc.201900234
Osch D, Zubeir LF, Bruinhorst A, Rocha M, Kroon MC (2015) Hydrophobic deep eutectic solvents: water-immiscible extractants. Green Chem 17(9):4518–4521
van Osch DJGP, Dietz CHJT, Warrag SEE, Kroon MC (2020) The curious case of hydrophobic deep eutectic solvents: a story on the discovery, design, and applications. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 8(29):10591–10612. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.0c00559
Shishov A, Volodina N, Nechaeva D, Gagarinova S, Bulatov A (2018) Deep eutectic solvents as a new kind of dispersive solvent for dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction. RSC Adv 8(67):38146–38149. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8ra07300g
Nalle F, Wahid R, Wulandari I, Sabarudin A (2019) Synthesis and characterization of magnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles using oleic acid as stabilizing agent. Rasayan J Chem 12:14–21
Socoliuc V, Avdeev MV, Kuncser V, Turcu R, Tombácz E, Vékás L (2022) Ferrofluids and bio-ferrofluids: looking back and stepping forward. Nanoscale 14(13):4786–4886. https://doi.org/10.1039/D1NR05841J
Shaaban H, Mostafa A, Alqarni AM, Alsultan R, Shehab ZA, Aljarrash Z et al (2023) Dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction utilizing menthol-based deep eutectic solvent for simultaneous determination of sulfonamides residues in powdered milk-based infant formulas. J Food Compos Anal 117:105137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfca.2023.105137
Shi D, Yang H, Ji S, Jiang S, Liu X, Zhang D (2015) Preparation and characterization of core-shell structure Fe3O4@C magnetic nanoparticles. Procedia Eng 102:1555–1562. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeng.2015.01.291
Tian F, Zhou J-F, Shao C-L, Wu H-B, Hao L (2020) Effective recovery of oil slick using the prepared high hydrophobic and oleophilic Fe3O4 magnetorheological fluid. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochem Eng Aspects 591:124531. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2020.124531
Van TN, Quang TD, Xuan QC, Kim H, Ahn D, Nguyen TM et al (2023) Applying response surface methodology to optimize partial nitrification in sequence batch reactor treating salinity wastewater. Sci Total Environ 862:160802. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.160802
Epshtein NA (2020) System suitability requirements for liquid chromatography methods: controlled parameters and their recommended values (review). Pharm Chem J 54(5):518–525. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11094-020-02231-w
Paul N, Naik PK, Ribeiro BD, Gooh Pattader PS, Marrucho IM, Banerjee T (2020) Molecular dynamics insights and water stability of hydrophobic deep eutectic solvents aided extraction of nitenpyram from an aqueous environment. J Phys Chem B 124(34):7405–7420. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcb.0c03647
Funding
This work was supported by the Youqing Lift Program of Shenyang Pharmaceutical University (YQ202206) and the Middle-aged Backbone Personnel Training Program of Shenyang Pharmaceutical University (ZQN2016011).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Yue Na: methodology, validation, investigation, formal analysis, writing original draft, preparing revision; Xun Gao: methodology, supervision, resources, writing—review and editing; Jiawei Hong: data curation, software; Xunyong Zhou: methodology, writing—review and editing, revision; Ning Liang: methodology, supervision, resources, writing—review and editing; and Longshan Zhao: methodology, supervision, resources, writing—review and editing.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Na, Y., Gao, X., Hong, J. et al. Vortex-assisted dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction based on the hydrophobic deep eutectic solvent–based ferrofluid for extraction and detection of myclobutanil. Microchim Acta 190, 352 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-023-05884-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-023-05884-y