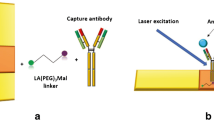
Abstract
The modification of EGFR aptamer (Apt 1) and HER2 aptamer (Apt 2) with gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) is reported to obtain probe I (Apt 1-AuNPs) and probe II (Apt 2-AuNPs). Taking Eca109, KYSE510, and KYSE150 cells as models, the sandwich scattering system of probe I-cell-probe II was formed by the recognition of tumor markers by the aptamer modified probe, and the resonance Rayleigh scattering (RRS) spectra were investigated. The results showed that the scattering system can be used to quantitatively detect the Eca109 cell lines in the range 5.0×10 to 5.0×105 cells·mL−1 with a detection limit of 15 cells· mL−1.The system can also detect the KYSE510 cell lines in a linear range of 5.0×10 to 5.0×105 cells·mL−1 with a detection limit of 18 cells·mL−1 and the KYSE150 cell lines in a linear range of 3.0×10 to 5.0×105 cells·mL−1 with a detection limit of 12 cells·mL−1. To demonstrate the potential application of the RRS method for real sample analysis, cells were spiked into blank serum samples at concentrations from 1.0×102 to 1.0×105 cells·mL−1. The recovery was between 97.0% and 102.3%, and the RSD was between 1.1% and 4.9%, confirming the feasibility of the proposed method for ESCC cell determination.
Graphical abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang C, Wang J, Chen Z, Gao Y, He J (2017) Immunohistochemical prognostic markers of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: a systematic review. Chin J Cancer 36(1):1–17. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40880-017-0232-5
Yang L, Yan X, Chen J, Zhan Q, Hua Y, Xu S, Li Z, Wang Z, Dong Y, Zuo D (2021) Hexokinase 2 discerns a novel circulating tumor cell population associated with poor prognosis in lung cancer patients. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 118(11):e2012228118. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2012228118
Chen J, Xu J, Wan T, Deng H, Li D (2021) High-sensitive detection of small-cell lung cancer cells based on terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated extension polymerization aptamer probe. ACS Biomater Sci Eng 7(3):1169–1180. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsbiomaterials.0c01633
Fukuyama S, Kumamoto S, Nagano S, Hitotsuya S, Yasuda K, Kitamura Y, Iwatsuki M, Baba H, Ihara T, Nakanishi Y (2021) Detection of cancer cells in whole blood using a dynamic deformable microfilter and a nucleic acid aptamer. Talanta 228:122239. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2021.122239
Hoshi K, Messina MS, Ohata J, Chung CY-S, Chang CJ (2022) A puromycin-dependent activity-based sensing probe for histochemical staining of hydrogen peroxide in cells and animal tissues. Nat Protoc 17(7):1691–1710. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41596-022-00694-7
Geng H, Feng C, Sun Z, Fan X, Xie Y, Gu J, Fan L, Liu G, Li C, Thorne RF (2023) Chloride intracellular channel 1 promotes esophageal squamous cell carcinoma proliferation via mTOR signalling. Transl Oncol 27:101560. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tranon.2022.101560
Chen X, Wang J, Song L, Yu Y, Shi M, Jiang W, Liu X, He X (2022) Downregulation of fibulin-4 inhibits autophagy and promotes the sensitivity of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells to apatinib by activating the Akt-mTOR signaling pathway. Thorac Cancer 13(18):2592–2605. https://doi.org/10.1111/1759-7714.14595
Kuai J-H, Wang Q, Zhang A-J, Zhang J-Y, Chen Z-F, Wu K-K, Hu X-Z (2018) Epidermal growth factor receptor-targeted immune magnetic liposomes capture circulating colorectal tumor cells efficiently. World J Gastroenterol 24(3):351–359. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v24.i3.351
Zhang X, Jiang X, Wang W, Luo S, Guan S, Li W, Situ B, Li B, Zhang Y, Zheng L (2023) A simple and sensitive electrochemical biosensor for circulating tumor cell determination based on dual-toehold accelerated catalytic hairpin assembly. Mikrochim Acta 190(2):65. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-023-05649-7
Xu Y, Zhang D, Lin J, Wu X, Xu X, Akakuru OU, Zhang H, Zhang Z, Xie Y, Wu A (2022) Ultrahigh SERS activity of the TiO2@Ag nanostructure leveraged for accurately detecting CTCs in peripheral blood. Biomater Sci 10(7):1812–1820. https://doi.org/10.1039/d1bm01821c
Fereidouni F, Todd A, Li Y, Chang C-W, Luong K, Rosenberg A, Lee Y-J, Chan JW, Borowsky A, Matsukuma K (2019) Dual-mode emission and transmission microscopy for virtual histochemistry using hematoxylin- and eosin-stained tissue sections. Biomed Opt Express 10(12):6516–6530. https://doi.org/10.1364/boe.10.006516
Tan WCC, Nerurkar SN, Cai HY, Ng HHM, Wu D, Wee YTF, Lim JCT, Yeong J, Lim TKH (2020) Overview of multiplex immunohistochemistry/ immunofluorescence techniques in the era of cancer immunotherapy. Cancer Commun 40(4):135–153. https://doi.org/10.1002/cac2.12023
Shu X, Sansare S, Jin D, Zeng X, Tong K-Y, Pandey R, Zhou R (2021) Artificial-intelligence-enabled reagent-free imaging hematology analyzer. Adv Intell Syst 3(8):2000277. https://doi.org/10.1002/aisy.202000277
Yang Y, Huang Y, Li C (2019) A reusable electrochemical sensor for one-step biosensing in complex media using triplex-forming oligonucleotide coupled DNA nanostructure. Anal Chim Acta 1055:90–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2018.12.031
Zhang Q, Xu G, Guo N, Wang T, Song P, Xia L (2021) In-situ synthesis of methyl cellulose film decorated with silver nanoparticles as a flexible surface-enhanced Raman substrate for the rapid detection of pesticide residues in fruits and vegetables. Materials 14(19):5750. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14195750
Wang W, He S, Dong G, Sheng C (2022) Nucleic-acid-based targeted degradation in drug discovery. J Med Chem 65(15):10217–10232. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.2c00875
Fan R, Tao X, Zhai X, Zhu Y, Li Y, Chen Y, Dong D, Yang S, Lv L (2023) Application of aptamer-drug delivery system in the therapy of breast cancer. Biomed Pharmacother 161:114444. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2023.114444
Li J, Ren X, Zhao J, Lou X (2021) PD-L1 aptamer isolation via Modular-SELEX and its applications in cancer cell detection and tumor tissue section imaging. Analyst 146(9):2910–2918. https://doi.org/10.1039/d1an00182e
Zhang W, Zhou R, Yang Y, Peng S, Xiao D, Kong T, Cai X, Zhu B (2021) Aptamer-mediated synthesis of multifunctional nano-hydroxyapatite for active tumour bioimaging and treatment. Cell Prolif 54(9):e13105. https://doi.org/10.1111/cpr.13105
Li J, Wang J, Zhang X, Chang H, Wei W (2018) Highly selective detection of epidermal growth factor receptor by multifunctional gold-nanoparticle-based resonance Rayleigh scattering method. Sens. Actuators B Chem 273:1300–1306. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2018.07.046
Li J, Yang Y, Wang J, Zhang B, Chang H, Wei W (2018) Resonance Rayleigh scattering detection of the epidermal growth factor receptor based on an aptamer-functionalized gold-nanoparticle probe. Anal Methods 10(24):2910–2916. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8ay00860d
Fasting C, Schalley CA, Weber M, Seitz O, Hecht S, Koksch B, Dernedde J, Graf C, Knapp E-W, Haag R (2012) Multivalency as a chemical organization and action principle. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 51(42):10472–10498. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201201114
Wang Y, Liu X, Wu L, Ding L, Effah CY, Wu Y, Xiong Y, He L (2022) Construction and bioapplications of aptamer-based dual recognition strategy. Biosens Bioelectron 195:113661. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2021.113661
Hedner C, Borg D, Nodin B, Karnevi E, Jirstrom K, Eberhard J (2018) Expression and prognostic significance of human epidermal growth factor receptors 1, 2 and 3 in oesophageal and gastric adenocarcinomas preneoadjuvant and postneoadjuvant treatment. J Clin Pathol 71(5):451–462. https://doi.org/10.1136/jclinpath-2017-204774
Delektorskaia VV, Chemeris GI, Kononets PV, Grigorchuk AI (2010) Immunohistochemical study of epidermal growth factor receptor expression in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Arkh Patol 72(5):3–6
Wang X, Niu H, Fan Q, Lu P, Ma C, Liu W, Liu Y, Li W, Hu S, Ling Y (2016) Predictive value of EGFR overexpression and gene amplification on icotinib efficacy in patients with advanced esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Oncotarget 7(17):24744–24751. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.8271
Zhan N, Dong W-G, Tang Y-F, Wang Z-S, C-l X (2012) Analysis of HER2 gene amplification and protein expression in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Med Oncol 29(2):933–940. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-011-9850-y
Hou W, Qin X, Zhu X, Fei M, Liu P, Liu L, Moon H, Zhang P, Greshock J, Bachman KE (2013) Lapatinib inhibits the growth of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and synergistically interacts with 5-fluorouracil in patient-derived xenograft models. Oncol Rep 30(2):707–714. https://doi.org/10.3892/or.2013.2500
Turkevich J, Stevenson PC, Hillier J (1951) A study of the nucleation and growth processes in the synthesis of colloidal gold. Discuss Faraday Soc 11:55–75. https://doi.org/10.1039/df9511100055
Haiss W, Thanh NTK, Aveyard J, Fernig DG (2007) Determination of size and concentration of gold nanoparticles from UV-Vis spectra. Anal Chem 79(11):4215–4221. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac0702084
Anker JN, Hall WP, Lyandres O, Shah NC, Zhao J, Van Duyne RP (2008) Biosensing with plasmonic nanosensors. Nat Mater 7(6):442–453. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmat2162
D'Agata R, Palladino P, Spoto G (2017) Streptavidin-coated gold nanoparticles: critical role of oligonucleotides on stability and fractal aggregation. Beilstein J Nanotechnol 8:1–11. https://doi.org/10.3762/bjnano.8.1
Gulicovski JJ, Cerovic LS, Milonjic SK, Popovic IG (2008) Adsorption of itaconic acid from aqueous solutions onto alumina. J Serb Chem Soc 73(8-9):825–834. https://doi.org/10.2298/jsc0809825g
Jiang Y, Zhao H, Zhu N, Lin Y, Yu P, Mao L (2008) A simple assay for direct colorimetric visualization of trinitrotoluene at picomolar levels using gold nanoparticles. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 47(45):8601–8604. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.200804066
Häussling L, Michel B, Ringsdorf H, Rohrer H (1991) Direct observation of streptavidin specifically adsorbed on biotin-functionalized self-assembled monolayers with the scanning tunneling microscope. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 30:569–572. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.199105691
Weber PC, Ohlendorf DH, Wendoloski JJ, Salemme FR (1989) Structural origins of high-affinity biotin binding to streptavidin. Science 243(4887):85–88. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.2911722
Yeo ELL, Chua AJS, Parthasarathy K, Yeo HY, Ng ML, Kah JCY (2015) Understanding aggregation-based assays: nature of protein corona and number of epitopes on antigen matters. RSC Adv 5:14982–14993. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4ra12089b
El-Sayed IH, Huang XH, El-Sayed MA (2005) Surface plasmon resonance scattering and absorption of anti-EGFR antibody conjugated gold nanoparticles in cancer diagnostics: applications in oral cancer. Nano Lett 5(5):829–834. https://doi.org/10.1021/nl050074e
Huang Y-F, Lin Y-W, Lin Z-H, Chang H-T (2009) Aptamer-modified gold nanoparticles for targeting breast cancer cells through light scattering. J Nanopart Res 11(4):775–783. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-008-9424-x
Giljohann DA, Seferos DS, Patel PC, Millstone JE, Rosi NL, Mirkin CA (2007) Oligonucleotide loading determines cellular uptake of DNA-modified gold nanoparticles. Nano Lett 7(12):3818–3821. https://doi.org/10.1021/nl072471q
Funding
Great thanks for the support from the Fundamental Research Program of Shanxi Province (No. 20210302124325), Research Project of Health Commission of Shanxi Province (No. 2022112), Scientific and Technologial Innovation Programs of Higher Education Institutions in Shanxi (No. 2019L0660), and the Doctoral Scientific Research Foundation of Changzhi Medical College (No.BS201916).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing of interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, J., Wang, J., Ma, D. et al. Highly sensitive and specific resonance Rayleigh scattering detection of esophageal cancer cells via dual-aptamer target binding strategy. Microchim Acta 190, 248 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-023-05828-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-023-05828-6