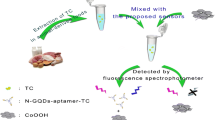
Abstract
A distinctive fluorescent nanoprobe with the function of doxycycline identification was designed by encapsulating histidine and serine-functionalized graphene quantum dots (His-GQDs-Ser) into the luminescent metal-organic frameworks (MOF). The synthesized nanoprobe displayed the merits of prominent selectivity, wide detection range, and high sensitivity. The interaction of doxycycline and the fabricated fluorescent nanoprobe contributed to the phenomenon of the suppression of the fluorescence of the His-GQDs-Ser and enhancement of the MOF fluorescence. Linear relation between the concentration of doxycycline and the ratio fluorescence intensity of the nanoprobe was observed, which evidenced the brilliant capability in the ranges 0.003–6.25 μM and 6.25–25 μM with a detection limit of 1.8 nM. Additionally, the practicability of the probe was verified in analysis of spiked milk sample, and the satisfactory recoveries of doxycycline varied from 97.39 to 103.61%, with relative standard deviations in the range 0.62–1.42%. A proportional fluorescence sensor for doxycycline detection in standard solution was constructed, which provides a potential for the development of other fluorescence detection systems.
Graphical Abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anna G, Iwona S-B, Ewelina N-K, Malgorzata G-S (2022) Risk to public health regarding doxycycline residues in chicken claws. J Agric Food Chem 70:2495–2500. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.1c07480
Małgorzata G-S, Anna G, Ewelina N-K, Andrzej P (2020) Doxycycline transfer from substrate to white button mushroom (Agaricus bisporus) and assessment of the potential consumer exposure. Food Chem 324:126867. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.126867
Liu F, Wang M, He Y, Song G, Zhao J (2022) Smartphone-assisted ratiometric fluorescence sensing platform for the detection of doxycycline based on BCNO QDs and calcium ion. Microchimica Acta 189:113. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-022-05224-6
Tian X, Fan Z (2021) Novel ratiometric probe based on the use of rare earth-carbon dots nanocomposite for the visual determination of doxycycline. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 260:119925. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2021.119925
Xu N, Li M, Chou W, Lin Z (2020) A physiologically based pharmacokinetic model of doxycycline for predicting tissue residues and withdrawal intervals in grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella). Food Chem Toxicol 137:111127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2020.111127
Sun X, He X, Zhang Y, Chen L (2009) Determination of tetracyclines in food samples by molecularly imprinted monolithic column coupling with high performance liquid chromatography. Talanta 79:926–934. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2009.05.033
Reverte S, Borrull F, Pocurull E, RMD M (2003) Determination of antibiotic compounds in water by solid-phase extraction-high-performance liquid chromatography-(electrospray) mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 1010:225–232. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0021-9673(03)01064-1
Han S, Zhang X, Sun H, Wei J, Wang H, Wang S, Jin J, Zhang Z (2021) Electrochemical behavior and voltammetric determination of chloramphenicol and doxycycline using a glassy carbon electrode modified with single-walled carbon nanohorns. Electroanal. 33:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1002/elan.202100354
Meng L, Lan C, Liu Z, Xu N, Wu Y (2019) A novel ratiometric fluorescence probe for highly sensitive and specific detection of chlorotetracycline among tetracycline antibiotics. Anal Chim Acta 1089:144–151. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2019.08.065
Wang Y, Sun Y, Dai H, Ni P, Jiang S, Lu W, Li Z (2016) Li Z (2016) A colorimetric biosensor using Fe3O4 nanoparticles for highly sensitive and selective detection of tetracyclines. Sens Actuators B Chem 236:621–626. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2016.06.029
Charoenraks T, Palaharn S, Grudpan K, Siangproh W, Chailapakul O (2004) Flow injection analysis of doxycycline or chlortetracycline in pharmaceutical formulations with pulsed amperometric detection. Talanta 5:1247–1252. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2004.04.036
Tashkhourian J, Absalan G, Jafari M, Zare S (2016) A rapid and sensitive assay for determination of doxycycline using thioglycolic acid-capped cadmium telluride quantum dot. Spectrochim Acta A 152:119–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2015.07.063
Feng X, Ashley J, Zhou T, Sun Y (2018) Fluorometric determination of doxycycline based on the use of carbon quantum dots incorporated into a molecularly imprinted polymer. Microchimica Acta 185:500. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-2999-8
Hanjun S, Li W, Weili W, Xiaogang Q (2013) Recent advances in graphene quantum dots for sensing. Mater Today 16:433–442. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mattod.2013.10.020
Yuan L, Liu L, Bai Y, Qin J, Chen M, Feng F (2022) A novel ratiometric fluorescent probe for detection of L-glutamic acid based on dual-emission carbon dots. Talanta 245:123416. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2022.123416
Bourzac K (2013) Quantum dots go on display. Nature 493:283. https://doi.org/10.1038/493283a
Narayanan R, Das A, Deepa M, Srivastava AK (2013) Energy relay from an unconventional yellow dye to CdS/CdSe quantum dots for enhanced solar cell performance. ChemPhysChem 14:4010–4021. https://doi.org/10.1002/cphc.201300605
Zhang L, Wang D, Huang H, Liu L, Zhou Y, Xia X, Deng K, Liu X (2016) Preparation of gold-carbon dots and ratiometric fluorescence cellular imaging. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8:6646–6655. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.5b12084
Yu L, Chen H, Yue J, Chen X, Sun M, Hou J, Alamry KA, Marwani HM, Wang X, Wang S (2020) Europium metal-organic framework for selective and sensitive detection of doxycycline based on fluorescence enhancement. Talanta 207:120297. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2019.120297
Lee S, Oh S, Oh M (2020) Atypical hybrid metal–organic frameworks (MOFs): a combinative process for MOF-on-MOF growth, etching, and structure transformation. Angew Chem Int Ed. 1; 59:1327–1333. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201912986
Xu H, Zhou S, Xiao L, Wang H, Li S, Yuan Q (2015) Fabrication of a nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dot from MOF-derived porous carbon and its application for highly selective fluorescence detection of Fe3+. J Mater Chem C 3:291–297. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4TC01991A
Marshall CR, Dvorak JP, Twight LP et al (2022) Size-dependent properties of solution-processable conductive MOF nanocrystals. J Am Chem Soc 5(144):5784–5794. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.1c10800
Katayama Y, Kalaj M, Barcus KS (2020) Self-assembly of metal-organic framework (MOF) nanoparticle monolayers and free-standing multilayers. J Am Chem Soc 1(141):20000–20003. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.9b10966
Li H, Shi L, Li C, Fu X, Huang Q, Zhang B (2020) Metal-organic framework based on α-cyclodextrin gives high ethylene gas adsorption capacity and storage stability. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 12:34095–34104. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.0c08594
Qiu S, Xue M, Zhu G (2014) Metal-organic framework membranes: from synthesis to separation application. Chem Soc Rev 16:6116–6140. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4CS00159A
Wang C, An B, Lin W (2019) Metal-organic frameworks in solid-gas phase catalysis. ACS Catalysis 9:130–146. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsctal.8b04055
Arabi M, Ostovan A, Wang Y, Mei R, Longwen F, Li J, Wang X, Chen L (2022) Chiral molecular imprinting-based SERS detection strategy for absolute enantiomeric discrimination. Nat Commun 13:5757. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-33448-w
Arabi M, Ostovan A, Wang Y, Li J, Li B, Wang X, Chen L (2022) Greenificated molecularly imprinted materials for advanced applications. Adv Mater 42:2203154. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202203154
Arabi M, Ostovan A, Li J, Wang X, Zhang Z, Choo J, Chen L (2021) Molecular imprinting: green perspectives and strategies. Adv Mater 30:2100543. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202100543
Arabi M, Ostovan A, Wang Y, Mei R, Fu L, Wang X, Ma J, Chen L (2021) Label-free SERS detection of Raman-Inactive protein biomarkers by Raman reporter indicator: toward ultrasensitivity and universality. Biosens Bioelectron 174:112825. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2020.112825
Li R, Jiang Y, Wang Q, Yang Y, Li N, Sun X, Li Z (2021) Serine and histidine-functionalized graphene quantum dot with unique double fluorescence emission as a fluorescent probe for highly sensitive detection of carbendazim. Sens Actuators B Chem 343:130099. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2021.130099
Lian X, Yan B (2016) A lanthanide metal-organic framework (MOF-76) for adsorbing dyes and fluorescence detecting aromatic pollutants. RSC Adv 6:11570. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5ra23681a
Wang H, Liu D, Wei M, Qi W, Li X, Niu Y (2021) A stable and highly luminescent 3D Eu(III)-organic framework for the detection of colchicine in aqueous environment. Environ Res 11:208. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2021.112652
Shang L, Dong S (2009) Design of fluorescent assays for cyanide and hydrogen peroxide based on the inner filter effect of metal nanoparticles. Anal Chem 81:1465–1470. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac802281x
Zheng M, Xie Z, Qu D, Li D, Du P, Jing X, Sun Z (2013) On-off-on fluorescent carbon dot nanosensor for recognition of chromium (VI) and ascorbic acid based on the inner filter effect. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 5:13242–13247. https://doi.org/10.1021/am4042355
Elhaleem A, Shymaa M, Elsebaei F, Shalan S, Belal F (2022) Utilization of N, S-doped carbon dots as a fluorescent nanosensor for determination of cromolyn based on inner filter effect: application to aqueous humour. Luminescence 5:713–721. https://doi.org/10.1002/bio.4212
Xiaowei M, Minxing W, Zhang B, Liu X, Shaomei X, Huang Y, Wang X, Song D, Ma P, Sun Y (2021) A sensitive “off-on”carbon dots-Ag nanoparticles fluorescent probe for cysteamine detection via the inner filter effect. Talanta 121463. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2020.121463
Xingliang D, Zhenxing Z, Yizheng J, Yuan N, Hujia C, Xiaoyong L, Liwei C, Jianpu W, Xiaogang P (2014) Solution-processed, high-performance light-emitting diodes based on quantum dots. Nature 515:96–99. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature13829
Guo Y, Zhao W (2020) Hydrothermal synthesis of highly fluorescent nitrogen-doped carbon quantum dots with good biocompatibility and the application for sensing ellagic acid. Spectrochimica Acta Part A: molecular and biomolecular spectroscopy. 240:118580. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2020.118580
Aghamali A, Khosravi M, Hamishehkar H, Modirshahla N, Behnajady MA (2018) Preparation of novel high performance recoverable and natural sunlight-driven nanocomposite photocatalyst of Fe3O4/C/TiO2/N-CQDs. Mater Sci Semicond Process 87:142–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mssp.2018.07.018
Xu J, Shen X, Jia L, Zhou T et al (2017) A novel visual ratiometric fluorescent sensing platform for highly-sensitive visual detection of tetracyclines by a lanthanide-functionalized palygorskite nanomaterial. J Hazard Mater 342:158–165. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2017.08.020
Wei W, He J, Wang Y, Kong M (2019) Ratiometric method based on silicon nanodots and Eu3+ system for highly-sensitive detection of tetracyclines. Talanta. 204:491–498. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2019.06.036
Ding L, Cao Y, Li H, Wang F, Guo DY, Yang W, Pan Q (2022) A ratiometric fluorescence-scattering sensor for rapid, sensitive and selective detection of doxycycline in animal foodstuffs. Food Chem 373:131669. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.131669
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YiXiu Han: methodology, investigation, formal analysis, writing—original draft.
YingXiang Du: conceptualization, supervision, writing—review and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
ESM 1
(DOCX 895 kb)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Han, Y., Li, P. & Du, Y. Encapsulating functionalized graphene quantum dot into metal-organic framework as a ratiometric fluorescent nanoprobe for doxycycline sensing. Microchim Acta 190, 234 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-023-05815-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-023-05815-x