Abstract
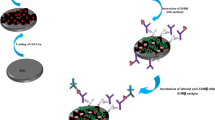
A competitive fluorescent immunoassay is described for the ultrasensitive determination of amyloid beta peptide1-42 (Aβ1-42), a biomarker for early diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease. N, S-doped graphene quantum dots (N, S-GQDs) were freely assembled on the surface of Ag@SiO2 nanoparticles to obtain a composite (Ag@SiO2@N, S-GQD nanocomposite), which was successfully prepared and characterized. By theoretical study, the optical properties of nanocomposites are improved compared with GQDs, due to the advantages of combining N, S co-doping and metal-enhanced fluorescence (MEF) effect of Ag NPs. In addition, Aβ1-42 was modified by Ag@SiO2@N, S-GQDs to prepare a probe with high photoluminescence properties (Ag@SiO2@N, S-GQDs-Aβ1-42). In the presence of Aβ1-42, a competitive reaction towards anti-Aβ1-42 fixed on the ELISA plate was proceeded between Aβ1-42 and Ag@SiO2@N, S-GQDs-Aβ1-42 by specific capture of antigen-antibody. The emission peak of Ag@SiO2@N, S-GQDs-Aβ1-42 (400 nm emission) was used for the quantitative determination of Aβ1-42. Under the optimal conditions, the fluorescent immunoassay exhibited a linear range of 0.32 pg·mL−1–5 ng·mL−1 with a detection limit of 0.098 pg·mL−1. The results show that the immunoassay has good analytical ability and can provide a new method for the clinical determination of Aβ1-42.
Graphical Abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rabbito A, Dulewicz M, Kulczynska-Przybik A, Mroczko B (2020) Biochemical markers in Alzheime’s disease. Int J Mol Sci 21:1989
Atri A (2019) The Alzheimer’s disease clinical spectrum: diagnosis and management. Med Clin North Am 103:263–293
Abbasi HY, Tehrani Z, Devadoss A, Ali MM, Moradi-Bachiller S, Albani D, Guy OJ (2021) Graphene based electrochemical immunosensor for the ultra-sensitive label free detection of Alzheimer’s beta amyloid peptides Aβ(1–42). Nanoscale Adv 3:2295–2304
Yeung CHC, Lau KWD, Au Yeung SL, Schooling CM (2021) Amyloid, tau and risk of Alzheimer’s disease: a Mendelian randomization study. Eur J Epidemiol 36:81–88
Qiang W, Yau WM, Lu JX, Collinge J, Tycko R (2017) Structural variation in amyloid-beta fibrils from Alzheimer’s disease clinical subtypes. Nature 541:217–221
Palmqvist S, Insel PS, Stomrud E, Janelidze S, Zetterberg H, Brix B, Eichenlaub U, Dage JL, Chai X, Blennow K, Mattsson N, Hansson O (2019) Cerebrospinal fluid and plasma biomarker trajectories with increasing amyloid deposition in Alzheimer’s disease. EMBO Mol Med 11:e11170
Pottiez G, Yang L, Stewart T, Song N, Aro P, Galasko DR, Quinn JF, Peskind ER, Shi M, Zhang J (2017) Mass-spectrometry-based method to quantify in parallel tau and amyloid beta 1-42 in CSF for the diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease. J Proteome Res 16:1228–1238
Devi R, Gogoi S, Dutta HS, Bordoloi M, Sanghi SK, Khan R (2020) Au/NiFe2O4 nanoparticle decorated graphene oxide nanosheets for electrochemical immunosensing of amyloid beta peptide. Nanoscale Adv 2:239–248
Mehta PD, Patrick BA, Miller DL, Coyle PK, Wisniewski T (2020) A sensitive and cost-effective chemiluminescence ELISA for measurement of amyloid-beta 1-42 peptide in human plasma. J Alzheimers Dis 78:1237–1244
Hansen EO, Dias NS, Burgos ICB, Costa MV, Carvalho AT, Teixeira AL, Barbosa IG, Santos LAV, Rosa DVF, Ribeiro AJF, Viana BM, Bicalho MAC (2021) Millipore xMap(R) Luminex (HATMAG-68K): an accurate and cost-effective method for evaluating Alzheimer’s biomarkers in cerebrospinal fluid. Front Psychiatry 12:716686
Rezabakhsh A, Rahbarghazi R, Fathi F (2020) Surface plasmon resonance biosensors for detection of Alzheimer’s biomarkers; an effective step in early and accurate diagnosis. Biosens Bioelectron 167:112511
Yu D, Yin Q, Wang J, Yang J, Chen Z, Gao Z, Huang Q, Li S (2021) SERS-based immunoassay enhanced with silver probe for selective separation and detection of Alzheimer’s disease biomarkers. Int J Nanomedicine 16:1901–1911
Ghafary Z, Hallaj R, Salimi A, Mafakheri S (2021) Ultrasensitive fluorescence immunosensor based on mesoporous silica and magnetic nanoparticles: capture and release strategy. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 257:119749
Safarian SM, Kusov PA, Kosolobov SS, Borzenkova OV, Khakimov AV, Kotelevtsev YV, Drachev VP (2021) Surface-specific washing-free immunosensor for time-resolved cortisol monitoring. Talanta 225:122070
Lin Q, Wu J, Liu L, Wu W, Fang X, Kong J (2021) Sandwich/competitive immuno-sensors on micro-interface for SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibodies. Anal Chim Acta 1187:339144
Li M, Chen T, Gooding JJ, Liu J (2019) Review of carbon and graphene quantum dots for sensing. ACS Sens 4:1732–1748
Chhabra VA, Kaur R, Kumar N, Deep A, Rajesh C, Kim KH (2018) Synthesis and spectroscopic studies of functionalized graphene quantum dots with diverse fluorescence characteristics. RSC Adv 8:11446–11454
Sohal N, Maity B, Basu S (2021) Recent advances in heteroatom-doped graphene quantum dots for sensing applications. RSC Adv 11:25586–25615
Yang M, Lian Z, Si C, Li B (2020) Revealing the role of nitrogen dopants in tuning the electronic and optical properties of graphene quantum dots via a TD-DFT study. Phys Chem Chem Phys 22:28230–28237
Kadian S, Manik G, Ashish K, Singh M, Chauhan RP (2019) Effect of sulfur doping on fluorescence and quantum yield of graphene quantum dots: an experimental and theoretical investigation. Nanotechnology 30:435704
Ouyang Z, Lei Y, Luo L, Jiang Z, Hu J, Lin Y (2020) S, N co-doped graphene quantum dots decorated CdSe for enhanced photoelectric properties. Nanotechnology 31:095710
Peng J, Wang S, Zhang PH, Jiang LP, Shi JJ, Zhu JJ (2013) Fabrication of graphene quantum dots and hexagonal boron nitride nanocomposites for fluorescent cell imaging. J Biomed Nanotechnol 9:1679–1685
Jeong Y, Kook YM, Lee K, Koh WG (2018) Metal enhanced fluorescence (MEF) for biosensors: General approaches and a review of recent developments. Biosens Bioelectron 111:102–116
Cui Q, He F, Li L, Mohwald H (2014) Controllable metal-enhanced fluorescence in organized films and colloidal system. Adv Colloid Interface Sci 207:164–177
Li F, Sun L, Luo Y, Li M, Xu Y, Hu G, Li X, Wang L (2018) Effect of thiophene S on the enhanced ORR electrocatalytic performance of sulfur-doped graphene quantum dot/reduced graphene oxide nanocomposites. RSC Adv 8:19635–19641
Kong X, Yu Q, Zhang X, Du X, Gong H, Jiang H (2012) Synthesis and application of surface enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) tags of Ag@SiO2 core/shell nanoparticles in protein detection. J Mater Chem 22:7767–7774
Xia C, Hai X, Chen X-W, Wang J-H (2017) Simultaneously fabrication of free and solidified N, S-doped graphene quantum dots via a facile solvent-free synthesis route for fluorescent detection. Talanta 168:269–278
Yan Y, Meng L, Zhang W, Zheng Y, Wang S, Ren B, Yang Z, Yan X (2017) High-throughput single-particle analysis of metal-enhanced fluorescence in free solution using Ag@SiO2 core–shell nanoparticles. ACS Sens 2:1369–1376
Nair RV, Thomas RT, Mohamed AP, Pillai S (2020) Fluorescent turn-off sensor based on sulphur-doped graphene quantum dots in colloidal and film forms for the ultrasensitive detection of carbamate pesticides. Microchem J 157:104971
Fan T, Zhang G, Jian L, Murtaza I, Meng H, Liu Y, Min Y (2019) Facile synthesis of defect-rich nitrogen and sulfur co-doped graphene quantum dots as metal-free electrocatalyst for the oxygen reduction reaction. J Alloys Compd 792:844–850
Han Q, Li G, Wang D, He E, Dong J, Gao W, Li J, Liu T, Zhang Z, Zheng H (2014) Synthesis of Ag-SiO2 composite nanospheres and their catalytic activity. Sci China Chem 57:881–887
Brinkmann M, Hayden J, Letz M, Reichel S, Click C, Mannstadt W, Schreder B, Wolff S, Ritter S, Davis MJ (2012) Optical materials and their properties, second edn. Springer, New York
Shen C, Ge S, Pang Y, Xi F, Liu J, Dong X, Chen P (2017) Facile and scalable preparation of highly luminescent N,S co-doped graphene quantum dots and their application for parallel detection of multiple metal ions. J Mater Chem B 5:6593–6600
Funding
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant no. 81201197).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, Q., Zheng, M., Li, M. et al. Competitive fluorescent immunoassay for the ultrasensitive determination of amyloid beta peptide1-42 based on Ag@SiO2@N, S-GQD nanocomposites. Microchim Acta 190, 194 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-023-05774-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-023-05774-3