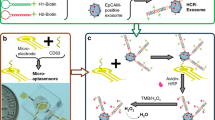
Abstract
A fluorescence aptasensor based on taking the advantage of the combination of magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs), terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase (TdT), and CRISPR/Cas12a was developed for the determination of nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC)-derived exosomes. The MNPs can eliminate background interference due to their magnetic separation capability. TdT can form an ultra-long polynucleotide tail which can bind with multiple crRNA, generating a signal amplification effect. The trans-cleavage activity of CRISPR/Cas12a can be specifically triggered via the crRNA binding with DNA, resulting in the bi-labeled DNA reporter with fluorophore and quencher being cleaved. The excitation wavelength of the fluorescence spectra was 490 nm. Fluorescence spectra with emission wavelengths ranging from 511 to 600 nm were collected. Under the optimization condition, the fabricated fluorescence aptasensor for NPC-derived exosome determination exhibited excellent sensitivity and specificity, with the linear range between 500 to 5 × 104 particles mL−1 and the limit of detection of 100 particles mL−1. It can be used for the determination of NPC-derived exosomes in clinical samples, which has a considerable clinical potential and prospect.
Graphical Abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data sets supporting the results of this article are included within the article and its additional files.
References
Guo R, Mao Y, Tang L, Chen L, Sun Y, Ma J (2019) The evolution of nasopharyngeal carcinoma staging. Brit J Radiol 92:20190244–20190244
Chen YP, Ismaila N, Chua M, Colevas AD, Haddad R, Huang SH, Wee J, Whitley AC, Yi JL, Yom SS, Chan A, Hu CS, Lang JY, Le QT, Lee A, Lee N, Lin JC, Ma B, Morgan TJ, Shah J, Sun Y, Ma J (2021) Chemotherapy in combination with radiotherapy for definitive-intent treatment of stage II-IVA nasopharyngeal carcinoma: CSCO and ASCO guideline. J Clin Oncol 39:840–859
Bossi P, Chan AT, Licitra L, Trama A, Orlandi E, Hui EP, Halamkova J, Mattheis S, Baujat B, Hardillo J, Smeele L, van Herpen C, Castro A, Machiels JP (2021) Nasopharyngeal carcinoma: ESMO-EURACAN clinical practice guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up(dagger). Ann Oncol 32:452–465
Chen H, Luo D, Shang B, Cao JJ, Wei J, Chen QH, Chen JS (2020) Immunoassay-type biosensor based on magnetic nanoparticle capture and the fluorescence signal formed by horseradish peroxidase catalysis for tumor-related exosome determination. Microchim Acta 187(5):282
Lu J, Liu QH, Wang F, Tan JJ, Deng YQ, Peng XH, Liu X, Zhang B, Xu X, Li XP (2018) Exosomal miR-9 inhibits angiogenesis by targeting MDK and regulating PDK/AKT pathway in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 37:147
Kalimuthu K, Kwon WY, Park KS (2019) A simple approach for rapid and cost-effective quantification of extracellular vesicles using a fluorescence polarization technique. J Bio Eng 13:31
Liao C, Liu H, Luo X (2021) The emerging roles of exosomal miRNAs in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Am J Cancer Res 11:2508–2520
Zhang H, Zhou Y, Luo D, Liu J, Yang E, Yang G, Feng G, Chen Q, Wu L (2021) Immunoassay-aptasensor for the determination of tumor-derived exosomes based on the combination of magnetic nanoparticles and hybridization chain reaction. Rsc Adv 11:4983–4990
Sun Z, Wang L, Wu S, Pan Y, Dong Y, Zhu S, Yang J, Yin Y, Li G (2020) An electrochemical biosensor designed by using Zr-based metal–organic frameworks for the detection of glioblastoma-derived exosomes with practical application. Anal Chem 92:3819–3826
Fu Y, Ma Q (2020) Recent developments in electrochemiluminescence nanosensors for cancer diagnosis applications. Nanoscale 12:13879–13898
Zhang H, Wang Z, Zhang Q, Wang F, Liu Y (2019) Ti3C2 MXenes nanosheets catalyzed highly efficient electrogenerated chemiluminescence biosensor for the detection of exosomes. Biosens Bioelectron 124–125:184–190
Liao GF, Liu X, Yang XF, Yang XH, Wang Q, Geng XH, Zou LY, Liu YQ, Li SY, Zheng Y, Wang KM (2020) Surface plasmon resonance assay for exosomes based on aptamer recognition and polydopamine-functionalized gold nanoparticles for signal amplification. Microchim Acta 187(4):251
Ramadan S, Lobo R, Zhang Y, Xu L, Shaforost O, Kwong HTD, Feng J, Yin T, Qiao M, Rajeshirke A, Jiao LR, Petrov PK, Dunlop IE, Titirici MM, Klein N (2021) Carbon-dot-enhanced graphene field-effect transistors for ultrasensitive detection of exosomes. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 13:7854–7864
Liu F, Vermesh O, Mani V, Ge TJ, Madsen SJ, Sabour A, Hsu EC, Gowrishankar G, Kanada M, Jokerst JV, Sierra RG, Chang E, Lau K, Sridhar K, Bermudez A, Pitteri SJ, Stoyanova T, Sinclair R, Nair VS, Gambhir SS, Demirci U (2017) The exosome total isolation chip. ACS Nano 11:10712–10723
Yang L, Jia J, Li S (2021) Advances in the application of exosomes identification using surface-enhanced raman spectroscopy for the early detection of cancers. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 9:808933
Xia Y, Chen T, Chen G, Weng Y, Zeng L, Liao Y, Chen W, Lan J, Zhang J, Chen J (2020) A nature-inspired colorimetric and fluorescent dual-modal biosensor for exosomes detection. Talanta 214:120851
Dong ZQ, Qin Q, Hu ZG, Zhang XL, Miao JH, Huang L, Chen P, Lu C, Pan MH (2020) CRISPR/Cas12a mediated genome editing enhances Bombyx mori resistance to BmNPV. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology 8:841
Wang M, Zhang R, Li J (2020) CRISPR/cas systems redefine nucleic acid detection: principles and methods. Biosens Bioelectron 165:112430
Zhang M, Wang H, Wang H, Wang F, Li Z (2021) CRISPR/Cas12a-assisted ligation-initiated loop-mediated isothermal amplification (CAL-LAMP) for highly specific detection of microRNAs. Anal Chem 93:7942–7948
Wang D, Wang J, Du Y, Ma J, Wang S, Tang A, Kong D (2020) CRISPR/Cas12a-based dual amplified biosensing system for sensitive and rapid detection of polynucleotide kinase/phosphatase. Biosens Bioelectron 168:112556–112564
Xiong Y, Zhang J, Yang Z, Mou Q, Ma Y, Xiong Y, Lu Y (2020) Functional DNA regulated CRISPR-Cas12a sensors for point-of-care diagnostics of non-nucleic-acid targets. J Am Chem Soc 142:207–213
Li SY, Cheng QX, Wang JM, Li XY, Zhang ZL, Gao S, Cao RB, Zhao GP, Wang J (2018) CRISPR-Cas12a-assisted nucleic acid detection. Cell Discov 4:20
Lang M, Luo D, Yang G, Mei Q, Feng G, Yang Y, Liu Z, Chen Q, Wu L (2020) An ultrasensitive electrochemical sensing platform for the detection of cTnI based on aptamer recognition and signal amplification assisted by TdT. RSC Adv 1:36396–43643
Li J, Tang L, Li T, Li K, Zhang Y, Ni W, Xiao MM, Zhao Y, Zhang ZY, Zhang GJ (2022) Tandem Cas13a/crRNA-mediated CRISPR-FET biosensor: a one-for-all check station for virus without amplification. ACS Sens 7:2680–2690
Zhang W, Jiang L, Diefenbach RJ, Campbell DH, Walsh BJ, Packer NH, Wang Y (2020) Enabling sensitive phenotypic profiling of cancer-derived small extracellular vesicles using surface-enhanced raman spectroscopy nanotags. ACS Sensors 5:764–771
Wang MH, Sun R, Zhou XM, Zhang MY, Lu JB, Yang Y, Zeng LS, Yang XZ, Shi L, Xiao RW, Wang HY, Mai SJ (2018) Epithelial cell adhesion molecule overexpression regulates epithelial-mesenchymal transition, stemness and metastasis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells via the PTEN/AKT/mTOR pathway. Cell Death Dis 9:2
Zhang W, Tian Z, Yang S, Rich J, Zhao S, Klingeborn M, Huang PH, Li Z, Stout A, Murphy Q, Patz E, Zhang S, Liu G, Huang TJ (2021) Electrochemical micro-aptasensors for exosome detection based on hybridization chain reaction amplification. Microsyst Nanoeng 7:63
Tjong V, Yu H, Hucknall A, Chilkoti A (2013) Direct fluorescence detection of RNA on microarrays by surface-initiated enzymatic polymerization. Anal Chem 85:426–433
Zhang X, Zheng C, Ding L, Wu Y, Xu H, Sun Y, Zeng Y, Liu X, Liu J (2021) CRISPR-Cas12a coupled with terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase mediated isothermal amplification for sensitive detection of polynucleotide kinase activity. Sens Actuators, B Chem 330:129317
Luo S, Wu Y, Pan W, Zhong G, Situ B, Li B, Ye X, Jiang X, Li W, Zhang Y, Zheng L, Wang Q (2023) An integrated magneto-fluorescent nanosensor for rapid and sensitive detection of tumor-derived exosomes. Sens Actuators B Chem 374:132792
Zhang Y, Fan J, Zhao J, Xu Z (2022) A biochip based on shell-isolated Au@MnO2 nanoparticle array-enhanced fluorescence effect for simple and sensitive exosome assay. Biosens Bioelectron 216:114373
Liao Z, Peng J, Chen S, Zhang P, Chen H, Feng D, Zhang T, Ye K, Deng Y, Dong Y, Geng L (2022) Sensitive fluorescent sensor for the fuzzy exosomes in serum based on the exosome imprinted polymer sandwiched with aggregation induced emission. Sens Actuators, B Chem 358:131182
Feng D, Ren M, Miao Y, Liao Z, Zhang T, Chen S, Ye K, Zhang P, Ma X, Ni J, Hu X, Li H, Peng J, Luo A, Geng L, Deng Y (2022) Dual selective sensor for exosomes in serum using magnetic imprinted polymer isolation sandwiched with aptamer/graphene oxide based FRET fluorescent ignition. Biosens Bioelectron 207:114112
Ding Z, Lu Y, Wei Y, Song D, Xu Z, Fang J (2022) DNA-Engineered iron-based metal-organic framework bio-interface for rapid visual determination of exosomes. J Colloid Interf Sci 612:424–433
Li Q, Wang Y, Ling L, Qiao L, Chen H, Ding C, Yu S (2021) Rapid and specific detection nanoplatform of serum exosomes for prostate cancer diagnosis. Microchim Acta 188:283
Sun Y, Wang C, Tang L, Zhang Y, Zhang GJ (2021) Magnetic-enhanced fluorescence sensing of tumor miRNA by combination of MNPs@PDA with duplex specific nuclease. Rsc Adv 11:2968–2975
Funding
These works were supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81803065), the Sanming Project of Medicine in Shenzhen (No. SZZYSM202106004), and the Science and Technology Planning Project of Shenzhen Municipality (JCYJ20210324143006017).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Peng Yi and Dan Luo are the co-first authors.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yi, P., Luo, D., Gao, Z. et al. Fluorescent aptasensor based on the MNPs-CRISPR/Cas12a-TdT for the determination of nasopharyngeal carcinoma-derived exosomes. Microchim Acta 190, 74 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-023-05657-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-023-05657-7