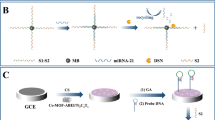
Abstract
Based on a dual signal amplification strategy of novel accordion-like Bi2O3-decorated Ti3C2 (Ti3C2@Bi2O3) nanocomposites and hybridization chain reaction (HCR), an ultra-sensitive electrochemical biosensor was constructed for miRNA-21 detection. By etching Ti3AlC2 with HF, Ti3C2 with an accordion-like structure was first obtained and subsequently covered by Bi2O3 nanoparticles (NPs), forming Ti3C2@Bi2O3. A layer of Au NPs was electrodeposited on the glassy carbon electrode coated with Ti3C2@Bi2O3, which not only significantly improved the electron transport capacity of the electrode but also greatly increased its surface active area. Upon the immobilization of the thiolated capture probe (SH-CP) on the electrode, the target miRNA-21 specifically hybridized with SH-CP and thus opened its hairpin structure, triggering HCR to form a long double strand with the primers H1 and H2. A large number of the electrochemical indicator molecules were thus embedded inside the long double strands to produce the desirable electrochemical signal at a potential of − 0.19 V (vs. Ag/AgCl). Such dual signal amplification strategy successfully endowed the biosensor with ultra-high sensitivity for miRNA-21 detection in a wide linear range from 1 fM to 100 pM with a detection limit as low as 0.16 fM. The excellent detection of miRNA-21 in human blood plasma displayed a broad prospect in clinical diagnosis.
Graphical Abstract
An ultra-sensitive electrochemical biosensor was successfully constructed for miRNA-21 detection in human blood plasma based on the dual signal amplification strategy of novel accordion-like Bi2O3 decorated Ti3C2 (Ti3C2@Bi2O3) nanocomposites and hybridization chain reaction.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yang X, Wu Y, Zhang B, Ni B (2018) Noncoding RNAs in multiple sclerosis. Clin Epigenet 10. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13148-018-0586-9
Li MX, Zhao W, Wang H, Li XL, Xu CH, Chen HY et al (2018) Dynamic single molecular rulers: toward quantitative detection of microRNA-21 in living cells. Anal Chem 90(24):14255–14259. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.8b03322
He L, Hannon GJ (2004) MicroRNAs: small RNAs with a big role in gene regulation. Nat Rev Genet 5(7):522–531. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg1379
Nassar FJ, Nasr R, Talhouk R (2017) MicroRNAs as biomarkers for early breast cancer diagnosis, prognosis and therapy prediction. Pharmacol Ther 172:34–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharmthera.2016.11.012
Shu XL, Fan CB, Long B, Zhou X, Wang Y (2016) The anti-cancer effects of cisplatin on hepatic cancer are associated with modulation of miRNA-21 and miRNA-122 expression. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 20(21):4459–4465
Herbst RS, Morgensztern D, Boshoff C (2018) The biology and management of non-small cell lung cancer. Nature 553(7689):446–454. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature25183
Li M, Wang Y, Liu X, Zhang Z, Wang L, Li Y (2020) miR-629 targets FOXO3 to promote cell apoptosis in gastric cancer. Exp Ther Med 19(1):294–300. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2019.8168
Li J, Wu Z, Zheng D, Sun Y, Wang S, Yan Y (2019) Bioinformatics analysis of the regulatory lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA network and drug prediction in patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Mol Med Rep 20(1):549–558. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2019.10289
Elemeery MN, Badr AN, Mohamed MA, Ghareeb DA (2017) Validation of a serum microRNA panel as biomarkers for early diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma post-hepatitis C infection in Egyptian patients. World J Gastroenterol 23(21):3864–3875. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i21.3864
Varallyay E, Burgyan J, Havelda Z (2007) Detection of microRNAs by Northern blot analyses using LNA probes. Methods 43(2):140–145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymeth.2007.04.004
Lee W-H, Tsai M-J, Chang W-A, Wu L-Y, Wang H-Y, Chang K-F et al (2018) Deduction of novel genes potentially involved in hypoxic AC16 human cardiomyocytes using next-generation sequencing and bioinformatics approaches. Int J Mol Med 42(5):2489–2502. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijmm.2018.3851
Ahmed FE, Ahmed NC, Gouda MM, Vos PW, Bonnerup C (2018) RT-qPCR for fecal mature microRNA quantification and validation. Methods Mol Biol (Clifton, NJ) 1765:203–215. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-7765-9_13
Zhuang Y, Huang F, Xu Q, Zhang M, Lou X, Xia F (2016) Facile, fast-responsive, and photostable imaging of telomerase activity in living cells with a fluorescence turn-on manner. Anal Chem 88(6):3289–3294. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.5b04756
Xiao S, Wang X, Yang C, Jiang Y, Zhen S, Huang C et al (2022) Electrochemiluminescence resonance energy transfer system based on silver metal-organic frameworks as a double-amplified emitter for sensitive detection of miRNA-107. Anal Chem 94(2):1178–1186. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.1c04368
Tian R, Zheng XW (2016) Sensitive colorimetric detection of microrna based on target catalyzed double-arm hairpin DNA assembling. Anal Sci 32(7):751–755
Liu X, Huang R, Su R, Qi W, Wang L, He Z (2014) Grafting hyaluronic acid onto gold surface to achieve low protein fouling in surface plasmon resonance biosensors. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 6(15):13034–13042. https://doi.org/10.1021/am502921z
Cai W, Xie S, Tang Y, Chai Y, Yuan R, Zhang J (2017) A label-free electrochemical biosensor for microRNA detection based on catalytic hairpin assembly and in situ formation of molybdophosphate. Talanta 163:65–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2016.10.086
Negahdary M, Angnes L (2022) Application of electrochemical biosensors for the detection of microRNAs (miRNAs) related to cancer. Coordination Chem Rev 464. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2022.214565
Gao W, Dong H, Lei J, Ji H, Ju H (2011) Signal amplification of streptavidin–horseradish peroxidase functionalized carbon nanotubes for amperometric detection of attomolar DNA. Chem Commun 47(18). https://doi.org/10.1039/c1cc10840a
Ju H (2017) Signal amplification for highly sensitive immunosensing. J Anal Test 1(1). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41664-017-0008-6
Lei J, Ju H (2012) Signal amplification using functional nanomaterials for biosensing. Chem Soc Rev 41(6):2122–2134. https://doi.org/10.1039/c1cs15274b
Ju H (2012) Signal amplification for highly sensitive bioanalysis based on biosensors or biochips. J Biochips Tissue Chips 02(02). https://doi.org/10.4172/2153-0777.1000e114
Zhou QY, Ma RN, Hu CL, Sun F, Jia LP, Zhang W et al (2021) A novel ratiometric electrochemical biosensing strategy based on T7 exonuclease-assisted homogenous target recycling coupling hairpin assembly-triggered double-signal output for the multiple amplified detection of miRNA. Analyst 146(8):2705–2711. https://doi.org/10.1039/d1an00204j
Liu S, Yang Z, Chang Y, Chai Y, Yuan R (2018) An enzyme-free electrochemical biosensor combining target recycling with Fe3O4/CeO2@Au nanocatalysts for microRNA-21 detection. Biosens Bioelectron 119:170–175. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2018.08.006
Wang X, Liu G, Qi Y, Yuan Y, Gao J, Luo X et al (2019) Embedded Au nanoparticles-based ratiometric electrochemical sensing strategy for sensitive and reliable detection of copper ions. Anal Chem 91(18):12006–12013. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.9b02945
Heiat M, Negahdary M (2019) Sensitive diagnosis of alpha-fetoprotein by a label free nanoaptasensor designed by modified Au electrode with spindle-shaped gold nanostructure. Microchem J 148:456–466. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2019.05.004
Duan F, Guo C, Hu M, Song Y, Wang M, He L et al (2020) Construction of the 0D/2D heterojunction of Ti3C2Tx MXene nanosheets and iron phthalocyanine quantum dots for the impedimetric aptasensing of microRNA-155. Sensors Actuators B Chem 310. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2020.127844
Feng A, Yu Y, Mi L, Yu Y, Song L (2018) Comparative study on electrosorptive behavior of NH4HF2-etched Ti3C2 and HF-etched Ti3C2 for capacitive deionization. Ionics 25(2):727–735. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-018-2787-9
Song H, Wang Y, Ling Z, Zu D, Li Z, Shen Y et al (2020) Enhanced photocatalytic degradation of perfluorooctanoic acid by Ti(3)C(2) MXene-derived heterojunction photocatalyst: Application of intercalation strategy in DESs. Sci Total Environ 746:141009. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.141009
Đurđić S, Vukojević V, Vlahović F, Ognjanović M, Švorc Ľ, Kalcher K et al (2019) Application of bismuth (III) oxide decorated graphene nanoribbons for enzymatic glucose biosensing. J Electroanal Chem 850. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2019.113400
Liang L, Yang R, Han G, Feng Y, Zhao B, Zhang R et al (2020) Enhanced electromagnetic wave-absorbing performance of magnetic nanoparticles-anchored 2D Ti(3)C(2)T(x) MXene. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 12(2):2644–2654. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.9b18504
Liu LZ, Song C, Zhang Z, Yang J, Zhou LL, Zhang X et al (2015) Ultrasensitive electrochemical detection of microRNA-21 combining layered nanostructure of oxidized single-walled carbon nanotubes and nanodiamonds by hybridization chain reaction. Biosens Bioelectron 70:351–357. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2015.03.051
Ge Z, Lin M, Wang P, Pei H, Yan J, Shi J et al (2014) Hybridization chain reaction amplification of microRNA detection with a tetrahedral DNA nanostructure-based electrochemical biosensor. Anal Chem 86(4):2124–2130. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac4037262
Lu J, Wu L, Hu Y, Wang S, Guo Z (2018) Ultrasensitive Faraday cage-type electrochemiluminescence assay for femtomolar miRNA-141 via graphene oxide and hybridization chain reaction-assisted cascade amplification. Biosens Bioelectron 109:13–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2018.02.062
Oishi M (2015) Enzyme-free and isothermal detection of microRNA based on click-chemical ligation-assisted hybridization coupled with hybridization chain reaction signal amplification. Anal Bioanal Chem 407(14):4165–4172. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-015-8629-y
Mahmoudian-Sani M-R, Asadi-Samani M (2020) Modulation of microRNAs by Euphorbia microsciadia Boiss in MDA-MB-231 cell line: new possibilities in breast cancer therapy. Recent Pat Anti-Cancer Drug Discovery 15(2):174–184. https://doi.org/10.2174/1574892815666200630102944
Guo J, Yuan C, Yan Q, Duan Q, Li X, Yi G (2018) An electrochemical biosensor for microRNA-196a detection based on cyclic enzymatic signal amplification and template-free DNA extension reaction with the adsorption of methylene blue. Biosens Bioelectron 105:103–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2018.01.036
Song Y, Wang MY, Qian Q, Xu J, Zhou QG, Lv SJ et al (2021) Trace miRNA assay based on DNA nanostructures formed by hybridization chain reaction and gold-nanoparticle tags. ChemElectroChem 8(15):2778–2782. https://doi.org/10.1002/celc.202100466
Tian W, Li P, He W, Liu C, Li Z (2019) Rolling circle extension-actuated loop-mediated isothermal amplification (RCA-LAMP) for ultrasensitive detection of microRNAs. Biosens Bioelectron 128:17–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2018.12.041
Dong J, Yang H, Zhao J, Wen L, He C, Hu Z et al (2022) Sandwich-type microRNA biosensor based on graphene oxide incorporated 3D-flower-like MoS(2) and AuNPs coupling with HRP enzyme signal amplification. Mikrochim Acta 189(1):49. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-021-05141-0
Guo WJ, Wu Z, Yang XY, Pang DW, Zhang ZL (2019) Ultrasensitive electrochemical detection of microRNA-21 with wide linear dynamic range based on dual signal amplification. Biosens Bioelectron 131:267–273. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2019.02.026
Bao J, Hou CJ, Zhao YA, Geng XT, Samalo M, Yang HS et al (2019) An enzyme-free sensitive electrochemical microRNA-16 biosensor by applying a multiple signal amplification strategy based on Au/PPy-rGO nanocomposite as a substrate. Talanta 196:329–336. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2018.12.082
Zhou LL, Wang T, Bai Y, Li Y, Qiu JH, Yu W et al (2020) Dual-amplified strategy for ultrasensitive electrochemical biosensor based on click chemistry-mediated enzyme-assisted target recycling and functionalized fullerene nanoparticles in the detection of microRNA-141. Biosensors Bioelectronics 150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2019.111964
Lu J, Wang J, Hu X, Gyimah E, Yakubu S, Wang K et al (2019) Electrochemical biosensor based on tetrahedral DNA nanostructures and G-quadruplex-hemin conformation for the ultrasensitive detection of microRNA-21 in serum. Anal Chem 91(11):7353–7359. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.9b01133
Liang Z, Ou D, Sun D, Tong Y, Luo H, Chen Z (2019) Ultrasensitive biosensor for microRNA-155 using synergistically catalytic nanoprobe coupled with improved cascade strand displacement reaction. Biosens Bioelectron 146:111744. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2019.111744
Funding
This work was financially supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Shanghai (19ZR1434800), Shanghai Collaborative Innovation Center of Energy Therapy for Tumors, Clinical research project of Shanghai Municipal Health Commission (201940078), and Scientific research program of Shanghai Science and Technology Commission (21140903200). The authors greatly appreciated this support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ouyang, R., Jiang, L., Xie, X. et al. Ti3C2@Bi2O3 nanoaccordion for electrochemical determination of miRNA-21. Microchim Acta 190, 52 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-022-05624-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-022-05624-8