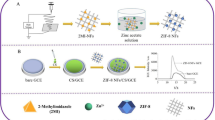
Abstract
Electrospun nanofibers containing CdTe@ZnNi-metal–organic frameworks (CdTe@ZnNi-MOF NFs) were used for the first time in luminol-O2 electrochemiluminescence (ECL) system to construct ECL sensor for chlorpyrifos (CPF) detection. Firstly, CdTe@ZnNi-MOF NFs obtained by blending method was used to modify the surface of a glassy carbon electrode, and then, the proposed solid-state ECL sensor was constructed by dropping luminol onto the surface of nanofiber benefiting from chitosan (CTS) viscosity. CdTe@ZnNi-MOF NFs with its large surface area and porosity can be used not only as luminol carrier but also as co-reaction promoter of the ECL system. The ECL sensor obtained satisfactory results in weakly alkaline solution under the synergistic action of CdTe@ZnNi-MOF NFs and luminol. The constructed ECL sensor can effectively detect CPF in the range 1.0 × 10−14–1.0 × 10−9 M, and the detection limit was 6.23 × 10−17 M (3σ/m). The constructed sensor was simple and sensitive, and can be used for the determination of CPF in vegetable samples. It not only broadened the application of MOFs in the field of ECL but also provided a new idea for expanding the application of the luminol-O2 system.
Graphical Abstract





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kamyabi MA, Moharramnezhad M (2022) Single-step microwave synthesis of a novel ternary nanocomposite as an efficient luminophore and boron nitride quantum dots as a new coreactant for a cathodic ECL monitoring of chlorpyrifos. Anal Methods 14:750–762. https://doi.org/10.1039/d1ay01687c
Fang H, Yu YL, Wang XG, Chu XQ, Pan XD, Yang XE (2008) Effects of repeated applications of chlorpyrifos on its persistence and soil microbial functional diversity and development of its degradation capability. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 81:397–400. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-008-9514-6
McClelland SJ, Bendis RJ, Relyea RA, Woodley SK (2018) Insecticide-induced changes in amphibian brains: how sublethal concentrations of chlorpyrifos directly affect neurodevelopment. Environ Toxicol Chem 37(10):2692–2698. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.4240
McClain ES, Miller DR, Cliffel DE (2019) Communication—microfluidic electrochemical acetylcholine detection in the presence of chlorpyrifos. J Electrochem Soc 166(16):G178–G181. https://doi.org/10.1149/2.0711916jes
Kumar P, Singh SP, Shrikant K, Madhukar D (2011) Analysis of buff alo liver samples for the presence of chlorpyrifos residues by using high performance liquid chromatography. Turk J Vet Anim Sci 35:2. https://doi.org/10.3906/vet-0809-7
Wani AA, Dar AA, Jan I, Sofi KA, Sofi JA, Dar IH (2019) Method validation and simultaneous quantification of eight organochlorines/organophosphates in apple by gas chromatography. J SCI FOOD AGR 99(7):3687–3692. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.9599
Li XJ, Gan PS, Peng RF, Huang C, Yu H (2010) Determination of 23 organophosphorous pesticides in surface water using SPME followed by GC-MS. Jour Chromatogr Sci 48:183–187. https://doi.org/10.1093/chromsci/48.3.183
Sahu B, Kurrey B, Khalkho BR, Deb MK (2022) α-Cyclodextrin functionalized silver nanoparticles as colorimetric sensor for micro extraction and trace level detection of chlorpyrifos pesticide in fruits and vegetables. Colloid Surface A 654:129947. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2022.129947
Xie HZ, Bei F, Hou JY, Ai SY (2018) A highly sensitive dual-signaling assay via inner filter effect between g-C3N4 and gold nanoparticles for organophosphorus pesticides. Sens Actuators B-Chem 255:2232–2239. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2017.09.024
Xu WZ, Wang QQ, Huang WH, Yang WM (2018) Construction of a novel electrochemical sensor based on molecularly imprinted polymers for the selective determination of chlorpyrifos in real samples. J Sep Sci 40(24):4839–4846. https://doi.org/10.1002/jssc.201701004
Kamyabi MA, Moharramnezhad M (2020) An ultra-sensitive electrochemiluminescence platformbased on ZnONPs/Ni-foam and K2S2O8 for detection of chlorpyrifos. J Electroanal Chem 865:114120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2020.114120
Wang XF, Liu HW, Qi HL, Gao Q, Zhang CX (2020) Highly efficient electrochemiluminescence of ruthenium complex-functionalized CdS quantum dots and their analytical application. J Mater Chem B 8(16):3598–3605. https://doi.org/10.1039/C9TB02463H
Lu J, Shan XY, Wu Q, Sun Z, Zhang X, Zhao YJ, Tian L (2022) Solid-state electrochemiluminescence sensor based on zeolitic imidazolate framework-67 electrospinning nanofbers for chlorpyrifos detection. Microchim Acta 189:298. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-022-05398-z
Ma XM, Kang Q, Li MM, Fu L, Zou GZ, Shen DZ (2022) Sensitive, signal-modulation strategy for discrimination of ECL spectra and investigation of mutual interactions of emitters. Anal Chem 94(8):3637–3644. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.1c05217
Liu GJ, Guan XH, Li BX, Zhou H, Kong N, Wang HY (2022) Hemin-graphene oxide-gold nanoflower-assisted enhanced electrochemiluminescence immunosensor for determination of prostate-specific antigen. Microchim Acta 189:297. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-022-05387-2
Du JF, Chen JS, Liu XP, Mao CJ, Jin BK (2022) Coupled electrochemiluminescent and resonance energy transfer determination of microRNA-141 using functionalized Mxene composite. Microchim Acta 189:264. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-022-05359-6
Zhou Y, Zhuo Y, Liao N, Chai YQ, Yuan R (2014) Ultrasensitive immunoassay based on a pseudobienzyme amplifying system of choline oxidase and luminol-reduced Pt@Au hybrid nanoflowers. Chem Commun 50(93):14627–14630. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4CC05269B
Wang YF, ShaKE HFH, Xiong X, Jia NQ (2018) A sandwich-type electrochemiluminescence aptasensor for insulin detection based on the nano-C60/BSA@luminol nanocomposite and ferrocene derivative. Electrochim Acta 290:90–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2018.08.080
Sha HF, Wang YF, Zhang Y, Ke H, Xiong X, Jia NQ (2018) Enzyme-free ECL immunesensor based on PbS nanocrystals for highly sensitive detection of alpha fetoprotein. Sens Actuators B-Chem 277:157–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2018.09.006
Wu FF, Zhou Y, Zhang H, Yuan R, Chai YQ (2018) Electrochemiluminescence peptide-based biosensor with hetero nanostructures as coreaction accelerator for the ultrasensitive determination of tryptase. Anal Chem 90:2263–2270. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.7b04631ujik
Zhang X, Tian L, Wu KX, Sun Z, Wu Q, Shan XY, Zhao YJ, Chen RZ, Lu J (2022) High sensitivity electrochemiluminescence sensor based on the synergy of ZIF-7 and CdTe for determination of glucose. Microchem J 177:107254. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2022.107254
Zhao YJ, Tian L, Wu SQ, Zhang X, Sun Z, Hu Y, Wang Y, Chen RZ, Lu J (2021) Ultrasensitive electrochemiluminescence biosensor for permethrin based on iron oxide nanomaterials and Au nanoparticles. Microchem J 168:106487. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2021.106487
Sheng DH, Ying XT, Li R, Cheng SY, Zhang C, Dong W, Pan XH (2022) Polydopamine-mediated modification of ZIF-8 onto magnetic nanoparticles for enhanced tetracycline adsorption from wastewater. Chemosphere 308:136249. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.136249
Seal N, Neogi S (2022) Lewis acid-base integrated robust metal-organic framework and reconfigurable composite for solvent-free Biginelli condensation and tandem catalysis with size selectivity. Mater today Chem 26:101064. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtchem.2022.101064
Lawson S, Siemers A, Kostlenick J, Al-Naddaf Q, Newport K, Rownaghi AA, Rezaei F (2021) Mixing Mg-MOF-74 with Zn-MOF-74: a facile pathway of controlling the pharmacokinetic release rate of curcumin. ACS Appl Bio Mater 4(9):6874–6880. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsabm.1c00585
Yao LY, Yang F, Hu GB, Yang Y, Huang W, Liang WB, Yuan R, Xiao DR (2020) Restriction of intramolecular motions (RIM) by metal-organic frameworks for electrochemiluminescence enhancement: 2D Zr12-adb nanoplate as a novel ECL tag for the construction of biosensing platform. Biosens Bioelectron 155:112099. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2020.112099
Wang XY, Wang X, Hu CY, GUo W, Wu XJ, Chen GX, Dai WJ, Zhen SJ, Huang CZ, Li YF (2022) Controlled synthesis of zinc-metal organic framework microflower with high efficiency electrochemiluminescence for miR-21 detection. Biosens Bioelectron 213:114443. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2022.114443
Phromsiri N, Abiodun SL, Manipuntee C, Leeladee P, Greytak AB, Insin N (2023) Fluorescent responses of CdSe and Si QDs toward Copper (II) ion and the mixed-QDs probe for Cu2+ ion sensing. J Mol Struct 1271:134050. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2022.134050
Tian L, Wu KX, Hu Y, Wang Y, Zhao YJ, Chen RZ, Lu J (2020) A molecularly imprinted electrochemiluminescence nanoprobe based on complexes consisting of CdTe and multiwall carbon nanotube for sensitive determination of clenbuterol. Microchim Acta 187(6):358. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-020-04319-2
Yang X, Yu YQ, Peng LZ, Lei YM, Chai YQ, Yuan R, Zhuo Y (2018) Strong electrochemiluminescence from MOF accelerator enriched quantum dots for enhanced sensing of trace cTnI. Anal Chem 90:3995–4002. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.7b05137
Wang XY, Wang YJ, Shan YQ, Jiang M, Li JL (2016) Sensitive determination of bisphenol A using a novel solid-state electrochemiluminescence quenching sensor. Int J Environ An Ch 96:1480–1490. https://doi.org/10.1080/03067319.2016.1271879
Wang XY, Wang YJ, Jiang M, Shan YQ, Wang XB (2017) On-site determination of bisphenol A in river water by a novel solid-state electrochemiluminescence quenching sensor. Environ Chem 14:115–122. https://doi.org/10.1071/EN16137
Wang XY, Wang YJ, Jiang M, Shan YQ, Jin X, Gong M, Wang XB (2018) Functional electrospun nanofibers-based electrochemiluminescence immunosensor for detection of the TSP 53 using RuAg/SiO2 NPs as signal enhancers. Anal Biochem 548:15–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ab.2018.02.006
Lu J, Sun Z, Zhang X, Shan X, Wu Q, Zhao Y, Tian L (2022) Electrospun nanofibers modified with Ni-MOF for electrochemiluminescent determination of glucose. Microchem J 180:107623. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2022.107623
Sun Z, Lu J, Zhang X, Shan X, Wu Q, Zhao Y, Tian L (2022) Electrospun nanofbers modifed with zeolitic imidazolate framework-8 for electrochemiluminescent determination of terbutaline. Microchim Acta 189:99. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-022-05207-7
Ehzari H, Safari M, Samimi M, Shamsipur M, Gholivand MB (2022) A highly sensitive electrochemical biosensor for chlorpyrifos pesticide detection using the adsorbent nanomatrix contain the human serum albumin and the Pd: CdTe quantum dots. Microchem J 179:107424. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2022.107424
Talan A, Mishra A, Eremin SA, Narang J, Kumar A, Gandhi S (2018) Ultrasensitive electrochemical immuno-sensing platform based on gold nanoparticles triggering chlorpyrifos detection in fruits and vegetables. Biosens Bioelectron 105:14–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2018.01.013
Wang G, Tan X, Zhou Q, Liu Y, Wang M, Yang L (2014) Synthesis of highly dipersed zinc oxide nanoparticles on carboxylic graphene for development a sensitive acetylcholines terase biosensor. Sens Actuators B-Chem 190:730–736. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2013.09.042
Roushani M, Nezhadali A, Jalilian Z (2018) An electrochemical chlorpyrifos aptasensor based on the use of a glassy carbon electrode modified with an electropolymerized aptamer-imprinted polymer and gold nanorods. Microchim Acta 185:551. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-3083-0
Chen PP, Liu Z, Liu JH, Liu HB, Bian WW, Tian D, Xia FQ, Zhou CL (2020) A novel electrochemiluminescence aptasensor based CdTe QDs@NH2-MIL-88(Fe) for signal amplification. Electrochim Acta 354:136644. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2020.136644
Kamyabi MA, Moharramnezhad M (2020) An ultra-sensitive electrochemiluminescence platform based on ZnONPs/Ni-foam and K2S2O8 for detection of chlorpyrifos. J Electroanal Chem 86:114120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2020.114120
Liu JH, Chen PP, Xia FQ, Liu Z, Liu HB, Yi JL, Zhou CL (2020) Sensitive electrochemiluminescence aptasensor for chlorpyrifos detection based on resonance energy transfer between MoS2/CdS nanospheres and Ag/CQDs. Sens Actuators B-Chem 315:128098. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2020.128098
Funding
We received financial support from the Graduate Innovation Project of ChangChun Normal University (No.2022–014).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Zhuo Sun: supervision, visualization, conceptualization, formal analysis, investigation, writing — original draft. Juan Lu: methodology, data curation, visualization, conceptualization, formal analysis, investigation, writing — original draft, writing — review and editing. Xin Zhang: methodology, data curation, formal analysis, investigation, writing — review and editing. Xiangyu Shan: funding acquisition, project administration, supervision, conceptualization, investigation. Qian Wu: project administration, funding acquisition, resources, ssupervision, formal analysis. Chao Li: project administration, formal analysis, supervision, visualization, conceptualization. Huiling Li: formal analysis, project administration, visualization, supervision, conceptualization. Shuning Yang: formal analysis, project administration, visualization, conceptualization. Li Tian: resources, supervision, project administration, funding acquisition, conceptualization, formal analysis.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, Z., Lu, J., Zhang, X. et al. Electrospun nanofibers containing CdTe@ZnNi-MOF for electrochemiluminescent determination of chlorpyrifos. Microchim Acta 189, 473 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-022-05574-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-022-05574-1