Abstract
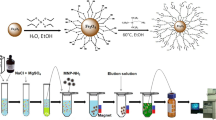
Sulfonic acid-functionalized covalent organic frameworks (COF-SO3) as a coating of stir bar sorptive extraction (SBSE) for capturing three fluoroquinolones from milk have been developed. The COF-SO3 material was characterized by X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscopy, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, and infrared spectroscopy. Milk without any typical treatments like protein precipitation and defatting was only diluted five times with water for test. Combined with high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), a SBSE-HPLC method was established for detecting fluoroquinolones in milk samples. The corresponding wide linear ranges (4.00–500.0 µg L−1), low detection limits (1.20–2.62 µg L−1), good test repeatability (RSD < 5.2%), and acceptable enrichment factors (56.2–61.5) were implemented for three fluoroquinolones. The analytical method was applied to determine trace targets and provided satisfactory results. Furthermore, the research displayed satisfied reproducibility for bar-to-bar (RSD < 6.5%) and batch-to-batch (RSD < 8.6%) tests.
Graphical abstract




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lian L, Zhang X, Hao J, Lv J, Wang X, Zhu B, Lou D (2018) Magnetic solid-phase extraction of fluoroquinolones from water samples using titanium-based metal-organic framework functionalized magnetic microspheres. J Chromatog A 1579:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2018.10.019
Mathur P, Sanyal D, Callahan DL, Conlan XA, Pfeffer FM (2021) Treatment technologies to mitigate the harmful effects of recalcitrant fluoroquinolone antibiotics on the environment and human health. Environ Pollut 291:118233. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2021.118233
Pan XC (2007) Research progress of detection method for FQs residue. J Anhui Agr Sci 22:38–41. https://doi.org/10.16377/j.cnki.issn1007-7731.2016.13.013
Wegener HC, Aarestrup FM, Gerner-Smidt P, Bager F (1999) Transfer of antibiotic resistant bacteria from animals to man. Acta Vet Scand 92:51–57. https://doi.org/10.1556/AVet.47.1999.4.7
Zhang D (2016) Research progress on detection of FQs residues in edible animal products. Anhui Agr Sci Bull 22:38–41. https://doi.org/10.16377/j.cnki.issn1007-7731.2016.13.013
Yu H, Jia Y, Wu R, Chen X, Chan TWD (2019) Determination of fluoroquinolones in food samples by magnetic solid-phase extraction based on a magnetic molecular sieve nanocomposite prior to high-performance liquid chromatography and tandem mass spectrometry. Anal Bioanal Chem 411:2817–2826. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-019-01726-0
Karageorgou E, Manousi N, Samanidou V, Kabir A, Furton KG (2016) Fabric phase sorptive extraction for the fast isolation of sulfonamides residues from raw milk followed by high performance liquid chromatography with ultraviolet detection. Food Chem 196:428–436. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2015.09.060
Xu H, Mi HY, Guan MM, Shan HY, Fei Q, Huan YF, Zhang ZQ, Feng GD (2017) Residue analysis of tetracyclines in milk by HPLC coupled with hollow fiber membranes-based dynamic liquid-liquid micro-extraction. Food Chem 232:198–202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2017.04.021
Mo ZL, Pang YH, Yu LH, Shen XF (2021) Membrane-protected covalent organic framework fiber for direct immersion solid-phase microextraction of 17beta-estradiol in milk. Food Chem 359:129816. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.129816
Cui JY, Zhang QY (2019) Development of new stir bar sorptive extraction technology. Contemp Chem Ind 48:111–114. https://doi.org/10.13840/j.cnki.cn21-1457/tq.2019.01.029
David F, Ochiai N, Sandra P (2019) Two decades of stir bar sorptive extraction: a retrospective and future outlook. TrAC-Trend Anal Chem 112:102–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2018.12.006
Hasan CK, Ghiasvand A, Lewis TW, Nesterenko PN, Paull B (2020) Recent advances in stir-bar sorptive extraction: coatings, technical improvements, and applications. Anal Chim Acta 1139:222–240. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2020.08.021
Ayazi Z, Matin A A (2016) Development of carbon nanotube-polyamide nanocomposite-based stir bar sorptive extraction coupled to HPLC-UV applying response surface methodology for the analysis of bisphenol A in aqueous samples. J Chromatogr Sci 1841–1850. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27601043.
Cong H, Man H, B B, Chen, H, (2015) Simultaneous determination of polar and apolar compounds in environmental samples by a polyaniline/hydroxyl multi-walled carbon nanotubes composite-coated stir bar sorptive extraction coupled with high performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr A 1394:36–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2015.03.046
Khoobi A, Salavati-Niasari M, Ghani M, Ghoreishi SM, Gholami A (2019) Multivariate optimization methods for in-situ growth of LDH/ZIF-8 nanocrystals on anodized aluminium substrate as a nanosorbent for stir bar sorptive extraction in biological and food samples. Food Chem 288:39–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.02.118
Metekua BE, Huang JK, Zeng JB, Aslam S, Zhang Y, Zhang X, Cui BW, Wen CY, Yan ZF (2021) Magnetic rod-based metal-organic framework metal composite as multifunctional nanostirrer with adsorptive, peroxidase-like and catalytic properties. Chinese Chem Lett 32:3245–3251.
Zatrochová S, Martínez‑Pérez‑Cejuela H, Catalá‑Icardo M, Simó‑Alfonso EF, Lhotská I, Šatínský D, Herrero‑Martínez JM (2022) Development of hybrid monoliths incorporating metal-organic frameworks for stir bar sorptive extraction coupled with liquid chromatography for determination of estrogen endocrine disruptors in water and human urine samples. Microchim Acta 189:92. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-022-05208-6
Xu H, Gao J, Jiang D (2015) Stable, crystalline, porous, covalent organic frameworks as a platform for chiral organocatalysts. Nat Chem 7:905–912. https://doi.org/10.1038/nchem.2352
Côté AP, Benin AI, Ockwig NW, O’Keeffe M, Matzger AJ, Yaghi OM (2005) Porous, crystalline, covalent organic frameworks. Science 310:1166–1170. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1120411
Vallez-Gomis V, Grau J, Benede JL, Giokas DL, Chisvert A, Salvador A (2021) Fundamentals and applications of stir bar sorptive dispersive microextraction: a tutorial review. Anal Chim Acta 1153:338271. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2021.338271
Kandambeth S, Dey K, Banerjee R (2019) Covalent organic frameworks: chemistry beyond the structure. J Am Chem Soc 141:1807–1822. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.8b10334
Tan W, Wu X, Liu W, Ye F, Zhao S (2021) Synchronous construction of hierarchical porosity and thiol functionalization in COFs for selective extraction of cationic dyes in water samples. ACS Appl Mater Inter 13:4352–4363. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.0c18902
Du ML, Yang C, Qian HL, Yan XP (2022) Hydroxyl-functionalized three-dimensional covalent organic framework for selective and rapid extraction of organophosphorus pesticides. J Chromatogr A 1673:463071. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2022.463071
Lu Q, Ma Y, Li H, Guan X, Yusran Y, Xue M, Valtchev V (2018) Postsynthetic functionalization of three-dimensional covalent organic frameworks for selective extraction of lanthanide ions. Angew Chem 57:6042–6048. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201712246
Wang XM, Ji H, Wang FB, Cui XL, Liu YA, Du XZ, Lu XQ (2021) NiFe2O4-based magnetic covalent organic framework nanocomposites for the efficient adsorption of brominated flame retardants from water. Microchim Acta 188:161. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-021-04809-x
Chen T, Li B, Huang W, Lin C, Li G, Ren H, Ma H (2021) Highly crystalline ionic covalent organic framework membrane for nanofiltration and charge-controlled organic pollutants removal. Sep Purif Technol 256:117787. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2020.117787
Ma W, Zheng Q, He Y, Li G, Guo W, Lin Z, Zhang L (2019) Size-controllable synthesis of uniform spherical covalent organic frameworks at room temperature for highly efficient and selective enrichment of hydrophobic peptides. J Am Chem Soc 141:18271–18277. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.9b09189
Klongklaew P, Kanatharana P, Bunkoed O (2020) Development of doubly porous composite adsorbent for the extraction of fluoroquinolones from food samples. Food Chem 309:125685. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.125685
Bagheri N, Lawati H, Sharji N, Hassanzadeh J (2020) Magnetic zinc based 2D-metal organic framework as an efficient adsorbent for simultaneous determination of fluoroquinolones using 3D printed microchip and liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. Talanta 224:121796. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2020.121796
Zhang M, Chen J, Zhao F, Zeng B (2020) Determination of fluoroquinolones in foods using ionic liquid modified Fe3O4/MWCNTs as the adsorbent for magnetic solid phase extraction coupled with HPLC. Anal Methods 12:4457–4465. https://doi.org/10.1039/d0ay01045f
Ma W, Row KH (2021) Hydrophilic deep eutectic solvents modified phenolic resin as tailored adsorbent for the extraction and determination of levofloxacin and ciprofloxacin from milk. Anal Bioanal Chem 413:4329–4339. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-021-03389-2
Sun X, Wang J, Li Y, Yang J, Jin J, Shah SM, Chen J (2014) Novel dummy molecularly imprinted polymers for matrix solid-phase dispersion extraction of eight fluoroquinolones from fish samples. J Chromatogr A 1359:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2014.07.007
Xu J, Li C, Li X, Xiao YX (2021) Hydrophobic magnetic nanoparticle assisted catanionic surfactant supramolecular solvent microextraction of multiresidue antibiotics in water samples. Anal Methods 13:264–3273. https://doi.org/10.1039/D1AY00525A
Funding
This research work was financially supported by the Major Science and Technology Innovation Project of Shandong Province (2019JZZY020903) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC, Nos. 21777054 and 21405061).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, J., Feng, J., Sun, M. et al. Sulfonic acid-functionalized covalent organic frameworks as the coating for stir bar sorptive extraction of fluoroquinolones in milk samples. Microchim Acta 190, 5 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-022-05534-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-022-05534-9