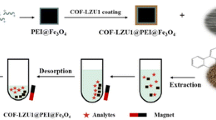
Abstract
Covalent organic framework (COF)–decorated magnetic nanoparticles (Fe3O4@DhaTab) with core–shell structure have been synthesized by one-pot method. The prepared Fe3O4@DhaTab was well characterized, and parameters of magnetic solid-phase extraction (MSPE) for parabens were also investigated in detail. Under optimized conditions, the adsorbent dosage was only 3 mg and extraction time was 10 min. The developed Fe3O4@DhaTab-based MSPE-HPLC analysis method offered good linearity (0.01–20 μg mL−1) with R2 (0.999) and low limits of detection (3.3–6.5 μg L−1) using UV detector at 254 nm. The proposed method was applied to determine four parabens in environmental water samples with recoveries in the range 64.0–105% and relative standard deviations of 0.16–7.8%. The adsorption mechanism was explored and indicated that porous DhaTab shell provided π-π, hydrophobic, and hydrogen bonding interactions in the MSPE process. The results revealed the potential of magnetic-functionalized COFs in determination of environmental contaminants.
Graphical abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nathaniel BB, Emmanuel I. U., Moses OA, Aemere O, Olumuyiwa OO. Martins O O, Olumide DO (2021) Toxicity and removal of parabens from water: a critical review. Sci Total Environ 792:148092. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.148092
Monica G, Miren LDA, Ettore C, Damià B (2016) Human exposure to endocrine disrupting compounds: their role in reproductive systems, metabolic syndrome and breast cancer. A review. Environmental Research 151:251–264. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2016.07.011
Camille H, Xavier D, Christophe R, Jean-Franc M (2015) Occurrence, fate and behavior of parabens in aquatic environments: a review, water research 68: 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2014.09.030.
Marina TG, Marciana S, Gabriel AAL, Cibele SB, Maira SC, Janete AAF, Foster WG, Kempinas WG (2017) Maternal exposure to butyl paraben impairs testicular structure and sperm quality on male rats. Environ Toxicol 32:1273–1289. https://doi.org/10.1002/tox.22323
Mohammad MA, Maryam T, Afsane C, Elham A, Majid H, Karim E, Roya K, Sedigheh K, Marjan M (2019) Paraben content in adjacent normal-malignant breast tissues from women with breast cancer. Biomed Environ Sci 32:893–904. https://doi.org/10.3967/bes2019.112
Nadeem R, Ki-Hyun K, Muhammad A, Waseem R, Richard JCB (2018) Recent developments in analytical quantitation approaches for parabens in human-associated samples. Trends Anal Chem 98:161–173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2017.11.009
Beate L, Sandra S, Bettina S, Linda S Rita S, Christiane P, Stefan R, Mario B, Michael B, Gabriele IS, Torsten S, Angela S, Isabell K, Ulrike ERK, Loreen T, Martin B, Beate IE, Kristin MJ, Thorsten R, Irina L, Tobias P (2020) Maternal paraben exposure triggers childhood overweight development. Nat Commun 11: 561. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-14202-1
Han JH, Cui YY, Yang CX (2021) Tailored amino/hydroxyl bifunctional microporous organic network for efficient stir bar sorptive extraction of parabens and flavors from cosmetic and food samples. J Chromatogr A 1655:462521. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2021.462521
Wei F, Monika M, Cheng H, Sang N, Guo LH (2021) Parabens as chemicals of emerging concern in the environment and humans: a review. Sci Total Environ 778:146150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.146150
João L, Rui CM, João G (2021) Paraben compounds-Part I: an overview of their characteristics, detection, and impacts. Appl Sci 11:2307. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11052307
Fernandez MF, Mustieles V, Suarez B, Reina-Perez I, Olivas-Martinez A, Vela-Soria F (2021) Determination of bisphenols, parabens, and benzophenones in placenta by dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction and gas chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Chemosphere 274:129707. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.129707
Cui YY, He X, Yang C-X, Yan X-P (2021) Application of microporous organic networks in separation science. Trends Anal Chem 139:116268. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2021.116268
He X, Cui YY, Yang C-X (2021) Thiol-yne click postsynthesis of a sulfonate group-enriched magnetic microporous organic network for efficient extraction of benzimidazole fungicides. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 13:39905–39914. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.1c11148
Jiang HL, Li N, Cui L, Wang X, Zhao RS (2019) Recent application of magnetic solid phase extraction for food safety analysis. Trends Anal Chem 120:115632. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2019.115632
He XQ, Cui YY, Zhang Y, Yang CX (2021) Fabrication of magnetic polydopamine@naphthyl microporous organic network nanosphere for efficient extraction of hydroxylated polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and p-nitrophenol from wastewater samples. J Chromatogr A 1651:462347. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2021.462347
Qian HL, Yang CX, Wang WL, Yang C, Yan XP (2018) Advances in covalent organic frameworks in separation science. J Chromatogr A 1542:1–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2018.02.023
Waller PJ, Gandara F, Yaghi OM (2015) Chemistry of covalent organic frameworks. Acc Chem Res 48:3053–3063. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.accounts.5b00369
Guo W, Wang W, Yang Y, Zhang S, Yang B, Ma W, He Y, Lin Z, Cai Z (2021) Facile fabrication of magnetic covalent organic frameworks and their application in selective enrichment of polychlorinated naphthalenes from fine particulate matter. Microchim Acta 188:91. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-021-04750-z
Jiang HL, Xue F, Sun J, Lin JM, Zhang C, Wang X, Zhao RS (2021) Ionic covalent organic frameworks for the magnetic solid-phase extraction of perfluorinated compounds in environmental water samples. Microchim Acta 188:47. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-021-04703-6
Qian HL, Wang Y, Yan XP (2022) Covalent organic frameworks for environmental analysis. Trends Anal Chem 147:116516. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2021.116516
Wang LL, Yang CX, Yan XP (2017) In situ growth of covalent organic framework shells on silica microspheres for application in liquid chromatography. ChemPlusChem 82:933–938. https://doi.org/10.1002/cplu.201700223
Zhang W, Liang F, Li C, Qiu LG, Yuan YP, Peng FM, Jiang X, Xie AJ, Shen YH, Zhu JF (2011) Microwave-enhanced synthesis of magnetic porous covalent triazine-based framework composites for fast separation of organic dye from aqueous solution. J Hazard Mater 186:984–990. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.11.093
Lu YY, Wang XL, Wang LL, Zhang W, Wei J, Lin JM, Zhao RS (2021) Room-temperature synthesis of amino-functionalized magnetic covalent organic frameworks for effcient extraction of perfluoroalkyl acids in environmental water samples. J Hazard Mater 407:124782. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.124782
Li S, Ma J, Wu G, Li J, Wang X, Chen L (2022) Magnetic covalent-organic frameworks for the simultaneous extraction of eleven emerging aromatic disinfection byproducts in water samples coupled with UHPLC–MS/MS determination. J Hazard Mater 424:127687. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.127687
Yusoff MM, Raoov M, Yahaya N, Salleh NM (2017) An ionic liquid loaded magnetically confned polymeric mesoporous adsorbent for extraction of parabens from environmental and cosmetic samples. RSC Adv 7:35832–35844. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7ra06682a
Klongklaew P, Bunkoed O (2021) The enrichment and extraction of parabens with polydopamine-coated microporous carrageenan hydrogel beads incorporating a hierarchical composite of metal-organic frameworks and magnetite nanoparticles. Microchem J 165:106103–106110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2021.106103
Du ZD, Cui YY, Yang CX, Yan XP (2020) Synthesis of magnetic amino-functionalized microporous organic network composites for magnetic solid phase extraction of endocrine disrupting chemicals from water, beverage bottle and juice samples. Talanta 206:120179. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2019.120179
Wang LL, Yang CX, Yan XP (2018) Exploring fluorescent covalent organic frameworks for selective sensing of Fe3+. Sci China Chem 61:1470–1474. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11426-018-9253-3
Wang LL, Fan M, Xing X, Liu YS, Sun SY (2021) Immobilization of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase on Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles and its application in histamine removal. Colloids Surf, B 205:111917–111923. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2021.111917
Yang XS, Wang LL, Liu YS, Yang CX, Zhao J, Ji SL, Liu QW, Hu ZH, Liu FJ, Wang P (2022) Fabrication of magnetic covalent organic framework for effective and selective solid-phase extraction of propylparaben from food samples. Food Chem 386:132843. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2022.132843
TahmasebiE YY, Mehdinia A, Rouhi F (2012) Polyaniline-coated Fe3O4 nanoparticles: an anion exchange magnetic sorbent for solid-phase extraction. J Sep Sci 35:2256–2265. https://doi.org/10.1002/jssc.201200345
Mehdinia A, Esfandiarnejad R, Jabbari A (2015) Magnetic nanocomposite of self doped polyaniline-graphene as a novel sorbent for solid-phase extraction. J Sep Sci 38:141–147. https://doi.org/10.1002/jssc.201400926
Casado-Carmona FA, Carmen M, Lucena R, Cardenas S, Valcarcel M (2016) Magnetic nanoparticles coated with ionic liquid for the extraction of endocrine disrupting compounds from waters. Microchem J 128:347–353. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2016.05.011
Feng J, He X, Liu X, Sun X, Li Y (2016) Preparation of magnetic graphene/mesoporous silica composites with phenyl-functionalized pore-walls as the restricted access matrix solid phase extraction adsorbent for the rapid extraction of parabens from water-based skin toners. J Chromatogr A 1465:20–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2016.08.052
Yusoff MM, Yahaya N, Saleh NM, Raoov M (2018) A study on the removal of propyl, butyl, and benzyl parabens via newly synthesised ionic liquid loaded magnetically confned polymeric mesoporous adsorbent. RSC Adv 8:25617–25635. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8ra03408g
Ghambari H, Reyes-Gallardo EM, Lucena R, Saraji M, Cardenas S (2017) Recycling polymer residues to synthesize magnetic nanocomposites for dispersive micro-solid phase extraction. Talanta 170:451–456. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2017.04.026
Shahvar A, Soltani R, Saraji M, Dinari M, Alijani S (2018) Covalent triazinebased framework for micro solid-phase extraction of parabens. J Chromatogr A 1565:48–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2018.06.033
Pastor-Belda M, Marin-Soler L, Campillo N, Vinas P, Hernandez-Cordoba M (2018) Magnetic carbon nanotube composite for the preconcentration of parabens from water and urine samples using dispersive solid phase extraction. J Chromatogr A 1564:102–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2018.06.025
Ning T, Yang HC, Shi CX, Yu J, Yu H, Chen P, Zhu SK (2022) An in vitro assessment for human skin exposure to parabens using magnetic solid phase extraction coupled with HPLC. Chemosphere 286:131593–131601. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.131593
GaoY WY, Yan Y, Tang K, Ding C (2020) Self-assembly of poly (ionic liquid) functionalized mesoporous magnetic microspheres for the solid-phase extraction of preservatives from milk samples. J Sep Sci 43:766–773. https://doi.org/10.1002/jssc.201900851
Pajewska-Szmyt M, Biniewska E, Buszewski B, Gadzała-Kopciuch R (2020) Synthesis of magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer sorbents for isolation of parabens from breast milk. Materials 13:4328–4345. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13194328
Huang Y, Peng J, Huang X (2018) One-pot preparation of magnetic carbon adsorbent derived from pomelo peel for magnetic solid-phase extraction of pollutants in environmental waters. J Chromatogr A 1546:28–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2018.03.001
Ariffn MM, Sohaimi NM, Yih BS, Saleh NM (2019) Magnetite nanoparticles coated with surfactant Slygard 309 and its application as an adsorbent for paraben extraction from pharmaceutical and water samples. Anal Methods 11:4126–4136. https://doi.org/10.1039/C9AY01147A
Ariffn MM, Azmi AHM, Saleh NM, Mohamad S, Rozi SKM (2019) Surfactant functionalisation of magnetic nanoparticles: A greener method for parabens determination in water samples by using magnetic solid phase extraction. Microchem J 147:930–940. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2019.04.017
Zhang Q, Zhi Y, Bao L, Zheng Y, Wang X, Jiang L, Wu Y (2021) Determination of six parabens in biological samples by magnetic solid-phase extraction with magnetic mesoporous carbon adsorbent and UHPLC-MS/MS. J Chromatogr B 1179:122817–122822. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchromb.2021.122817
Wang YX, Cui YY, Zhang Y, Yang CX (2022) Synthesis of reusable and renewable microporous organic networks for the removal of halogenated contaminants. J Hazard Mater 424:127485. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.127485
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21904053, 82003502 and 32072141).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interest.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, XS., Zhao, J., Wang, LL. et al. Core–shell-structured magnetic covalent organic frameworks for effective extraction of parabens prior to their determination by HPLC. Microchim Acta 189, 340 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-022-05444-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-022-05444-w