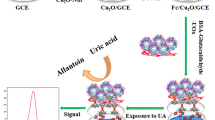
Abstract
In a new approach, we considered the special affinity between Ni and poly-histidine tags of recombinant urate oxidase to utilize Ni-MOF for immobilizing the enzyme. In this study, a carbon paste electrode (CPE) was modified by histidine-tailed urate oxidase (H-UOX) and nickel-metal–organic framework (Ni-MOF) to construct H-UOX/Ni-MOF/CPE, which is a rapid, sensitive, and simple electrochemical biosensor for UA detection. The use of carboxy-terminal histidine-tailed urate oxidase in the construction of the electrode allows the urate oxidase enzyme to be positioned correctly in the electrode. This, in turn, enhances the efficiency of the biosensor. Characterization was carried out by X-ray diffraction (XRD), energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET), and field emission scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM). At optimum conditions, the biosensor provided a short response time, linear response within 0.3–10 µM and 10–140 µM for UA with a detection limit of 0.084 µM, repeatability of 3.06%, and reproducibility of 4.9%. Furthermore, the biosensor revealed acceptable stability and selectivity of UA detection in the presence of the commonly coexisted ascorbic acid, dopamine, L-cysteine, urea, and glucose. The detection potential was at 0.4 V vs. Ag/AgCl.
Graphical abstract




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Plausinaitis D, Sinkevicius L, Samukaite-Bubniene U, Ratautaite V, Ramanavicius A (2020) Evaluation of electrochemical quartz crystal microbalance based sensor modified by uric acid-imprinted polypyrrole. Talanta 220:121414
Zhang W, Liu L, Lia Y, Wang D, Ma H, Ren H, Shi Y, Han Y, Ye BC (2018) Electrochemical sensing platform based on the biomass-derived microporous carbons for simultaneous determination of ascorbic acid, dopamine, and uric acid. Biosens Bioelectron 121:96–43
Ivekovic D, Japec M, Solar M, Zivkovic N (2012) Amperometric uric acid biosensor with improved analytical performances based on alkaline-stable H2O2 transducer. Int J Electrochem Sci 7:3252–3264
Liu L, Liu L, Wang Y, Ye BC (2019) A novel electrochemical sensor based on bimetallic metal–organic framework-derived porous carbon for detection of uric acid. Talanta 199:478–484
Saqib M, Qi L, Hui P, Nsabimana A, Halawa M, Zhang W, Xu G (2018) Development of luminol-N-hydroxyphthalimide chemiluminescence system for highly selective and sensitive detection of superoxide dismutase, uric acid and Co 2+. Biosens Bioelectron 99:519–524
Vakh C, Koronkiewicz S, Kalinowski S, Moskvin L, Bulatov A (2017) An automatic chemiluminescence method based on the multi-pumping flow system coupled with the fluidized reactor and direct-injection detector: determination of uric acid in saliva samples. Talanta 167:725–732
Dai X, Fang X, Zhang C, Xu R, Xu B (2007) Determination of serum uric acid using high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC)/isotope dilution mass spectrometry (ID-MS) as a candidate reference method. J Chromatogr B 857:287–295
Xu P, Li R, Tu Y, Yan J (2015) A gold nanocluster-based sensor for sensitive uric acid detection. Talanta 144:704–709
Bi H, Li Y, Lio S, Guo P, Wei Z, Lv C, Zhang J, Zhao XS (2012) Carbon-nanotube-modified glassy carbon electrode for simultaneous determination of dopamine, ascorbic acid and uric acid: the effect of functional groups. Sens Actuators B: Chem 171–172:1132–1140
Erden PE, Kilic E (2013) A review of enzymatic uric acid biosensors based on amperometric detection. Talanta 107:312–323
Liu Y, Yuan M, Liu L, Guo R (2013) A facile electrochemical uricase biosensor designed from gold/amino acid nanocomposites. Sens Actuators B: Chem 176:592–597
Ghanbari-Ardestani S, Khojasteh-Band S, Zaboli M, Hassani Z, Mortezavi M, Mahani M, Torkzadeh-Mahani M (2019) The effect of different percentages of triethanolammonium butyrate ionic liquid on the structure and activity of urate oxidase: molecular docking, molecular dynamics simulation, and experimental study. J Mol Liq 292:111318
Li W, Xu S, Zhang B, Zhu Y, Hua Y, Kong X, Sun L, Hong J (2017) Directed evolution to improve the catalytic efficiency of urate oxidase from Bacillus subtilis. PLOS ONE 1–18
Alakel N, Middeke JM, Schetelig J, Bornhauser M (2017) Prevention and treatment of tumor lysis syndrome, and the efficacy and role of rasburicase. OncoTargets and Ther 10:597–605
Pui CH, Mahmoud HH, Wiley JM, Woods GM, Leverger G, Camitta B, Hastings C, Blaney SM, Relling MV, Reaman GH (2001) Recombinant urate oxidase for the prophylaxis or treatment of hyperuricemia in patients with leukemia or lymphoma. Am J Clin Oncol 19:697–704
Chen D, Wang Q, Jin J, Wu P, Wang H, Yu S, Zhang H, Cai C (2010) Low-potential detection of endogenous and physiological uric acid at uricase-thioninesingle-walled carbon nanotube modified electrodes. Anal Chem 82:2448–2455
Lian X, Fang Y, Joseph E, Wang Q, Li J, Banerjee S, Lollar C, Wang X, Zhou HC (2017) Enzyme–MOF (metal–organic framework) composites. Chem Soc Rev 46:3386–3401
Liu X, Qi W, Wang Y, Su R, He Z (2017) A facile enzyme immobilization strategy with high stable hierarchically porous metal-organic frameworks. Nanoscale 9:17561–17570
Liu X, Qi W, Wang Y, Lin D, Yang X, Su R, He Z (2018) Rational design of mimic multi-enzyme systems in hierarchically porous biomimetic metal-organic frameworks. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 10(39):33407–33415
Zhou Y, Mao Z, Wang W, Yang Z, Liu X (2016) In-situ fabrication of graphene oxide hybrid Ni-based metal–organic framework (Ni-MOFs@GO) with ultrahigh capacitance as electrochemical pseudocapacitor materials. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8(42):28904–28916
Stock N, Biswas Sh (2012) Synthesis of metal-organic frameworks (MOFs): routes to various MOF topologies, morphologies, and composites. Chem Rev 112(2):933–969
Long JR, Yaghi OM (2009) The pervasive chemistry of metal–organic frameworks. Chem Soc Rev 38:1213–1214
Wu CD, Zhao M (2017) Incorporation of molecular catalysts in metal–organic frameworks for highly efficient heterogeneous catalysis. Adv Mater 29:1605446
Horcajada P, Serre C, Maurin G, Ramsahye NA, Balas F, Vallet-Regi M, Sebban M, Taulelle F, Ferey G (2008) Flexible porous metal-organic frameworks for a controlled drug delivery. J Am Chem Soc 130(21):6774–6780
Horcajada P, Chalati T, Serre C, Gillet B, Sebrie C, Baati T, Eubank JF, Heurtaux D, Clayette P, Kreuz C, Chang JS, Hwang YK, Marsaud V, Bories PN, Cynober L, Gil S, Férey G, Couvreur P, Gref R (2010) Porous metal–organic-framework nanoscale carriers as a potential platform for drug delivery and imaging. Nat Mater 9:172–178
Xiao Y, Cui Y, Zheng Q, Xiang S, Qian G, Chen B (2010) A microporous luminescent metal–organic framework for highly selective and sensitive sensing of Cu2+ in aqueous solution. Chem Commun 46:5503–5505
Liao FS, Lo WS, Hsu YS, Wu CC, Wang SC, Shieh FK, Morabito JV, Chou LY, Wu KCW, Tsung CK (2017) Shielding against unfolding by embedding enzymes in metal− organic frameworks via a de novo approach. J Am Chem Soc 139(19):6530–6533
Motamedi A, Barani M, Lohrasbi-Nejad A, Mortazavi M, Riahi-Medvar A, Varma RS, Torkzade-Mahani M (2021) Enhancement of thermostability of Aspergillus flavus urate oxidase by immobilization on the Ni-based magnetic metal–organic framework. Nanomaterials 11(7):1759
Ravikumar R, Chen LC, Jayaraman P, Poh CL, Chan CC (2017) Chitosan-nickel film based interferometric optical fiber sensor for label free detection of histidine tagged proteins. Biosens Bioelectron 99:578–585
Chang AY, Chau V, Landas JA, Pang Y (2017) Preparation of calcium competent Escherichia coli and heat-shock transformation. JEMI methods 1:22–25
Taherimehr Zahra, Zaboli Maryam, Torkzadeh-Mahani Masoud (2020) New insight into the molecular mechanism of the trehalose effect on urate oxidase stability. J Biomol Struct Dyn 4:1461–1471
Zaboli M, Saeidnia F, Zaboli M, Torkzadeh-Mahani M (2021) Stabilization of recombinant d-Lactate dehydrogenase enzyme with trehalose: response surface methodology and molecular dynamics simulation study. Process Biochemi 101:26–35
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantification of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72(1–2):248–254
Manivel P, Suryanarayanan V, Nesakumar N, Velayutham D, Madasamy K, Kathiresan M, Kulandaisamy AJ, Rayappan JBB (2018) A novel electrochemical sensor based on a nickel-metal organic framework for efficient electrocatalytic oxidation and rapid detection of lactate. New J Chem 42:11839–11846
Phan NTS, Nguyen TT, Ta AH (2012) The arylation of aldehydes with arylboronic acids using metal-organic framework Ni(HBTC)BPY as an efficient heterogeneous catalyst. J Mol Catal A Chem 365:95–102
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to dedicate the present dissertation to the late Mr. Alireza Afzalipour and Mrs. Fakhereh Saba, the founders of the University of Kerman, because of their foresight and generosity in establishing this institution to train future generations of scientists. In addition, the authors acknowledge their appreciation to the late Dr. Parviz Dabiri for his generous support in establishing our research laboratory.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Mashkoori, A., Mostafavi, A., Shamspur, T. et al. Electrochemical enzyme-based blood uric acid biosensor: new insight into the enzyme immobilization on the surface of electrode via poly-histidine tag. Microchim Acta 189, 326 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-022-05408-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-022-05408-0