Abstract
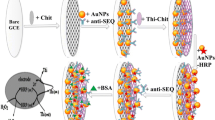
A system for the rapid and ultra-sensitive detection of Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus), a prevalent foodborne pathogen is introduced. Limitations of typical electrochemical sensing, often subjected to interference from non-specific protein adsorption are addressed. A dual-aptamer-based sandwich immunobiosensor is shown for its benefits regarding specificity and anti-fouling capacity, endowed by a sulfonated polyaniline layer combined with signal amplification via highly conductive gold nanoparticles. EIS spectra (Nyquist plots) were recorded at pH 7.4 PBS containing 5 mM Fe(CN)63−/Fe(CN)64−, in order to verify the possibility of the electrochemical sensing for detection of S. aureus. Results demonstrated that the constructed immunobiosensor presents an extended detection range (1 × 101 to 1 × 105 CFU/mL) and detection limit as low as 2 CFU/mL. The resistance values of the immunobiosensor developed maintain at a stable value during 2 weeks. Besides, the specificity of the system is highlighted by testing raw milk, and the results of which demonstrate the excellent prospects of the system for monitoring foodborne pathogens.
Graphical abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Oliveira D, Borges A, Simoes M (2018) Staphylococcus aureus toxins and their molecular activity in infectious diseases. Toxins 10:252
Kamble E, Pardesi K (2021) Antibiotic tolerance in biofilm and stationary-phase. Microb Drug Resist 27:3–12
Dmp DO, Forde BM, Kidd TJ et al (2020) Antimicrobial resistance in ESKAPE pathogens. Clin Microbiol Rev 33:e00181-e219
Cai RF, Zhang ZW, Chen HH et al (2021) A versatile signal-on electrochemical biosensor for Staphylococcus aureus based on triple-helix molecular switch. Sensor Actuat B-Chem 326:128842
Andersson T, Blackberg A, Lood R et al (2020) Development of a molecular imprinting-based surface plasmon resonance biosensor for rapid and sensitive detection of Staphylococcus aureus alpha hemolysin from human serum. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 10:571578
Chen L, Leng YK, Lin B et al (2020) Ultrahigh-sensitivity label-free optical fiber biosensor based on a tapered singlemode-no core-singlemode coupler for Staphylococcus aureus detection. Sensor Actuat B-Chem 320:128283
Yang Y, Zhang ZJ, Wan MH et al (2020) Highly sensitive surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy substrates of Ag@PAN electrospinning nanofibrous membranes for direct detection of Bacteria. ACS Omega 5:19834–19843
Alafeef M, Dighe K, Moitra P et al (2020) Rapid, ultrasensitive, and quantitative detection of SARS-CoV-2 using antisense oligonucleotides directed electrochemical biosensor chip. ACS Nano 14:17028–17045
Zhu PH, Li SS, Zhou S et al (2021) In situ grown COFs on 3D strutted graphene aerogel for electrochemical detection of NO released from living cells. Chem Eng J 420:127559
Masdor NA, Altintas Z, Tothill IE (2016) Sensitive detection of campylobacter jejuni using nanoparticles enhanced QCM sensor. Biosens Bioelectron 78:328–336
Yuan KS, Mei QS, Guo XJ et al (2018) Antimicrobial peptide based magnetic recognition elements and Au@Ag-GO SERS tags with stable internal standards: a three in one biosensor for isolation, discrimination and killing of multiple bacteria in whole blood. Chem Sci 9:8781
Li Y, Han R, Chen M et al (2021) Bovine serum albumin-cross-linked polyaniline nanowires for ultralow fouling and highly sensitive electrochemical protein quantification in human serum samples. Anal Chem 93:4326–4333
Lin PH, Li BR (2020) Antifouling strategies in advanced electrochemical sensors and biosensors. Analyst 145:1110–1120
Jiang C, Wang GX, Hein R et al (2020) Antifouling strategies for selective in vitro and in vivo sensing. Chem Rev 120:3852–3889
Xu TT, Dai HQ, Jin YC (2020) Electrochemical sensing of lead(II) by differential pulse voltammetry using conductive polypyrrole nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 187:23
Gospodinova N, Mokreva P, Terlemezyan L (1994) Influence of hydrolysis on the chemical polymerization of aniline. Polymer 35:3102–3106
Lee CW, Wu JK, Chang CH et al (2020) Sulfonated polyaniline as zwitterionic and conductive interfaces for anti-biofouling on open electrode surfaces in electrodynamic systems. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 12:19102–19109
Coccia F, Tonucci L, Bosco D et al (2012) One-pot synthesis of lignin-stabilised platinum and palladium nanoparticles and their catalytic behaviour in oxidation and reduction reactions. Green Chem. 14:1073
Farzadfard A, Shayeh JS, Rezaei MH et al (2020) Modification of reduced graphene/Au-aptamer to develop an electrochemical based aptasensor for measurement of glycated albumin. Talanta 211:120722
Wu ZQ, Chen XD, Zhu SB et al (2013) Enhanced sensitivity of ammonia sensor using graphene/polyaniline nanocomposite. Sensor Actuat B-Chem 178:485–493
Deshmukh MA, Celiesiute R, Ramanaviciene A (2018) EDTA_PANI/SWCNTs nanocomposite modified electrode for electrochemical determination of copper (II), lead (II) and mercury (II)ions. Electrochim Acta 259:930–938
Kallem P, Ibrahim Y, Hasan SW et al (2021) Fabrication of novel polyethersulfone (PES) hybrid ultrafiltration membranes with superior permeability and antifouling properties using environmentally friendly sulfonated functionalized polydopamine nanofillers. Sep Puri. Technol 261:118311
Tiraferri A, Kang Y, Giannelis EP et al (2012) Superhydrophilic thin-film composite forward osmosis membranes for organic fouling control: fouling behavior and antifouling mechanisms. Environ Sci Technol 20:11135–11144
Puniredd SR, Jayaraman S, Gandhimathi C et al (2015) Deposition of zwitterionic polymer brushes in a dense gas medium. J Colloid Interf Sci 448:156–162
Han E, Li X, Zhang Y et al (2020) Electrochemical immunosensor based on self-assembled gold nanorods for label-free and sensitive determination of Staphylococcus aureus. Anal Biochem 611:113982
Yue H, Zhou YL, Wang PS et al (2016) A facile label-free electrochemiluminescent biosensor for specific detection of Staphylococcus aureus utilizing the binding between immunoglobulin G and protein A. Talanta 153:401–406
Farooq U, Ullah MW, Yang QL et al (2020) High-density phage particles immobilization in surface-modified bacterial cellulose for ultra-sensitive and selective electrochemical detection of Staphylococcus aureus. Biosens Bioelectron. 157:112163
Xu TT, Li JM, Zhang SY et al (2019) Integration of diagnosis and treatment in the detection and kill of S. aureus in the whole blood. Biosens Bioelectron 142:111507
Patel D, Zhou Y, Ramasamyz RP (2021) A bacteriophage-based electrochemical biosensor for detection of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J Electrochem Soc 168:057523
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the University Natural Science Research Project of Jiangsu Province (19KJB430026), the Foundation (GZKF202015) of State Key Laboratory of Biobased Material and Green Papermaking, Qilu University of Technology, Shandong Academy of Sciences, Nanjing Forestry University 2018 Scientific Research Start-up Funds (163105042), and the financial support from China Scholarship Council (CSC).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, H., Xu, T., Zhou, J. et al. Electrochemical sensing of Staphylococcus aureus based on conductive anti-fouling interface. Microchim Acta 189, 97 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-022-05190-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-022-05190-z