Abstract
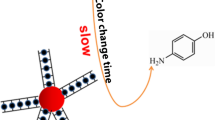
It was found that dimension change of aptamer DNA significantly weakened the mimicking activity of gold nanozyme, which was contrary to previous research. Based on this, a rapid colorimetric method for the detection of low concentrations of mercury in environmental media was fabricated. It was observed that 40 nM Hg2+ causes color changes in solution. The detection limit of absorbance measurements was estimated to be 9.3 × 10–11 M. The assay was fast and could complete a single test in half an hour. The detection results for real environment samples confirmed the reliability of the colorimetric analysis in practical application. The proposed assay provides an alternative method for real-time monitoring of mercury in the environment. In particular, the charge effect on the affinity of nanozyme consummated the DNA regulation mechanism for the simulated enzyme activity.
Graphical abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yang LX, Zhang YY, Wang FF, Luo ZD, Guo SJ, Strähle U (2020) Toxicity of mercury: molecular evidence. Chemosphere 245:125586
Song YH, Ma QF, Cheng HY, Liu JH, Wang YC (2021) Simultaneous enrichment of inorganic and organic species of lead and mercury in pg L-1 levels by solid phase extraction online combined with high performance liquid chromatography and inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. Anal Chim Acta 1157:338388
Shih TT, Chen JY, Luo YT, Lin CH, Liu YH, Su YA, Chao PC, Sun YC (2019) Development of a titanium dioxide-assisted preconcentration/on-site vapor-generation chip hyphenated with inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry for online determination of mercuric ions in urine samples. Anal Chim Acta 1063(31):82–90
Sogame Y, Tsukagoshi A (2020) Development of a liquid chromatography-inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry method for the simultaneous determination of methylmercury and inorganic mercury in human blood. J Chromatogr B 1136:121855
Volkov DS, Proskurnin MA, Korobov MV (2014) Survey study of mercury determination in detonation nanodiamonds by pyrolysis flameless atomic absorption spectroscopy. Diam Relat Mater 50:60–65
Liu YC, Zou J, Luo B, Yu HR, Zhao ZG, Xia H (2021) Ivy extract-assisted photochemical vapor generation for sensitive determination of mercury by atomic fluorescence spectrometry. Microchem J 169:106547
Zheng H, Hong JJ, Luo XL, Li S, Wang MX, Yang BY, Wang M (2019) Combination of sequential cloud point extraction and hydride generation atomic fluorescence spectrometry for preconcentration and determination of inorganic and methyl mercury in water samples. Microchem J 145:806–812
Huang DL, Liu XG, Lai C, Qin L, Zhang C, Yi H, Zeng GM, Li B, Deng R, Liu SY, Zhang YJ (2018) Colorimetric determination of mercury(II) using gold nanoparticles and double ligand exchange. Microchim Acta 186:31
Li L, Li BX, Qi YY, Jin Y (2009) Label-free aptamer-based colorimetric detection of mercury ions in aqueous media using unmodified gold nanoparticles as colorimetric probe. Anal Bioanal Chem 393(8):2051–2057
Lian Q, Liu H, Zheng XF, Li X, Zhang FJ, Gao J (2019) Enhanced peroxidase-like activity of CuO/Pt nanoflowers for colorimetric and ultrasensitive Hg2+ detection in water sample. Appl Surf Sci 483(31):551–561
Liu R, Zuo L, Huang XR, Liu SM, Yang GY, Li SY, Lv CY (2019) Colorimetric determination of lead(II) or mercury(II) based on target induced switching of the enzyme-like activity of metallothionein-stabilized copper nanoclusters. Microchim Acta 186:250
Qi YY, Ma JX, Chen XD, Xiu FR, Chen YT, Lu YW (2020) Practical aptamer-based assay of heavy metal mercury ion in contaminated environmental samples: convenience and sensitivity. Anal Bioanal Chem 412:439–448
Qi YY, Song DD, Chen YT (2021) Colorimetric oligonucleotide-based sensor for ultra-low Hg2+ in contaminated environmental medium: convenience, sensitivity and mechanism. Sci Total Environ 766:142579
Wang YW, Liu Q, Wang L, Tang S, Yang HH, Song H (2018) A colorimetric mercury(II) assay based on the Hg(II)-stimulated peroxidase mimicking activity of a nanocomposite prepared from graphitic carbon nitride and gold nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 186:7
Wang JJ, Zhou PL, Tao H, Wang XL, Wu YG (2020) Oligonucleotide-induced regulation of the oxidase-mimicking activity of octahedral Mn3O4 nanoparticles for colorimetric detection of heavy metals. Microchim Acta 187:99
Zhang Y, Ju P, Sun LP, Wang Z, Zhai XF, Jiang F, Sun CJ (2020) Colorimetric determination of Hg2+ based on the mercury-stimulated oxidase mimetic activity of Ag3PO4 microcubes. Microchim Acta 187:422
Guo XR, Huang JZ, Wei TB, Zeng Q, Wang LS (2020) Fast and selective detection of mercury ions in environmental water by paper-based fluorescent sensor using boronic acid functionalized MoS2 quantum dots. J Hazard Mater 381:120969
Li ZH, Sun HJ, Ma XY, Su RF, Sun R, Yang CY, Sun CY (2020) Label-free fluorescence “turn-on” strategy for mercury (II) detection based on the T-Hg2+-T configuration and the DNA-sensitized luminescence of terbium (III). Anal Chim Acta 1099(22):136–144
Maimaitiyiming X, Shi C (2021) Poly(1,4-diethynylphenylene-4,6-pyrimidine)s for fluorescence detection of mercury(II) ion. Mater Chem Phys 257:123783
Qi YY, Xiu FR, Yu GD, Huang LL, Li BX (2017) Simple and rapid chemiluminescence aptasensor for Hg2+ in contaminated samples: a new signal amplification mechanism. Biosens Bioelectron 87(15):439–446
Chen ZY, Gupta A, Chattopadhyay S (2021) Detection of mercury in spiked cosmetics by surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy using silver shelled iron oxide nanoparticles. Sensor Actuat B: Chem 337:129788
Zhao YB, Yamaguchi Y, Ni Y, Li MD, Dou XM (2020) A SERS-based capillary sensor for the detection of mercury ions in environmental water. Spectrochim Acta A 233:118193
Teodoro KB, Migliorini FL, Facure MH, Correa DS (2019) Conductive electrospun nanofibers containing cellulose nanowhiskers and reduced graphene oxide for the electrochemical detection of mercury(II). Carbohy Polym 207(1):747–754
Salandari N, Ensafi AA, Rezaei B (2021) Ultra-sensitive electrochemical aptasensor based on zeolitic imidazolate framework-8 derived Ag/Au core-shell nanoparticles for mercury detection in water samples. Sensor Actuat B: Chem 331:129426
Zou YS, Zhang YL, Xie ZZ, Luo SY, Zeng YM, Chen QZ, Liu GK, Tian ZQ (2019) Improved sensitivity and reproducibility in electrochemical detection of trace mercury (II) by bromide ion & electrochemical oxidation. Talanta 203(1):186–193
Qi YY, Li BX (2011) A sensitive, label-free, aptamer-based biosensor using a gold nanoparticle-initiated chemiluminescence system. Chem Eur J 17:1642–1648
Li HX, Rothberg L (2004) Colorimetric detection of DNA sequences based on electrostatic interactions with unmodifed gold nanoparticles. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 101(39):14036–14039
Hizir MS, Top M, Balcioglu M, Rana M, Robertson NM, Shen F, Sheng J, Yigit MV (2016) Multiplexed activity of perAuxidase: DNA-capped AuNPs act as adjustable peroxidase. Anal Chem 88(1):600–605
Yang Y, Yin YG, Li XL, Wang S, Dong YY (2020) Development of a chimeric aptamer and an AuNPs aptasensor for highly sensitive and specific identification of Aflatoxin B1. Sensor Actuat B: Chem 319:128250
Ono A, Togashi H (2004) Highly selective oligonucleotide-based sensor for mercury(II) in aqueous solutions. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 43(33):4300–4302
Song ZQ, Xiu F-R, Qi YY (2022) Degradation and partial oxidation of waste plastic express packaging bags in supercritical water: Resources transformation and pollutants removal. J Hazard Mater 423:127018
Zhang ZF, Cui H, Lai CZ, Liu LJ (2005) Gold nanoparticle-catalyzed luminol chemiluminescence and its analytical applications. Anal Chem 77:3324–3329
Huang K, Yang H, Zhou ZG, Yu MX, Li FY, Gao X, Yi T, Huang CH (2008) Multisignal chemosensor for Cr3+ and its application in bioimaging. Org Lett 10(12):2557–2560
Wu Y, Zheng JW, Li Z, Zhao YR, Zhang Y (2009) A novel reagentless amperometric immunosensor based on gold nanoparticles/TMB/Nafion-modified electrode. Biosens Bioelectron 24(3):1389–1393
Gao LZ, Zhuang J, Nie L, Zhang JB, Zhang Y, Gu N, Wang TH, Feng J, Yang DG, Perrett S, Yan XY (2007) Intrinsic peroxidase-like activity of ferromagnetic nanoparticles. Nat Nanotechnol 2:577–583
Funding
This work was supported financially by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21605018) and the Natural Science Basic Research Project of Shaanxi Province of China (No. 2020JM-528 and No. 2021JZ-52).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qi, Y., Wang, Y., Chen, Y. et al. Rapid color-fading colorimetric sensing of Hg in environmental samples: regulation mechanism from DNA dimension. Microchim Acta 189, 76 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-022-05177-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-022-05177-w