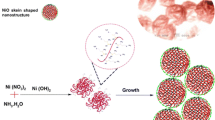
Abstract
Chains of nickel nanoparticles coated with few nitrogen-doped graphitic carbon layers (Ni@NC) are synthesized by hydrogen-assisted pyrolysis of Ni-ZIF. Hydrogen and temperature can play key roles in the formation of oriented Ni@NC nanoparticle chains, and carbon shells can protect Ni nanoparticles from external oxidation and aggregations. Under the optimized potential (0.60 V vs. Ag/AgCl), the Ni@NC7H nanoparticle chains obtained at 700 °C under H2/Ar atmosphere (Ni@NC7H) demonstrate outstanding performances, such as high sensitivity of 1.44 mA mM−1 cm−2 (RSD = 1.0%), low detection limit of 0.34 μM (S/N = 3), broad linear range from 1 μM to 1.81 mM, and excellent application potential in artificial sweat and human serum. Therefore, the findings above indicate that this study will provide a general methodology for the synthesis of chains-like core–shell nanoparticle electrocatalysts for non-enzymatic glucose detection.
Graphical abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adeel M, Rahman MM, Caligiuri I et al (2020) Recent advances of electrochemical and optical enzyme-free glucose sensors operating at physiological conditions. Biosens Bioelectron 165:112331. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2020.112331
Zhang Y, Zhang Y, Zhu H et al (2019) Functionalization of the support material based on N-doped carbon-reduced graphene oxide and its influence on the non-enzymatic detection of glucose. J Alloys Compd 780:98–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.11.368
Brothers MC, DeBrosse M, Grigsby CC et al (2019) Achievements and challenges for real-time sensing of analytes in sweat within wearable platforms. Acc Chem Res 52:297–306. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.accounts.8b00555
Zheng L, Liu Y, Zhang C (2021) A sample-to-answer, wearable cloth-based electrochemical sensor (WCECS) for point-of-care detection of glucose in sweat. Sens Actuators, B 343:130131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2021.130131
Kim J, Campbell AS, de Ávila BEF, Wang J (2019) Wearable biosensors for healthcare monitoring. Nat Biotechnol 37:389–406. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41587-019-0045-y
Cheng S, DelaCruz S, Chen C et al (2019) Hierarchical Co3O4/CuO nanorod array supported on carbon cloth for highly sensitive non-enzymatic glucose biosensing. Sens Actuators, B 298:126860. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2019.126860
Liao QL, Jiang H, Zhang XW et al (2019) A single nanowire sensor for intracellular glucose detection. Nanoscale 11:10702–10708. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9nr01997a
Lu M, Deng Y, Li Y et al (2020) Core-shell MOF@MOF composites for sensitive nonenzymatic glucose sensing in human serum. Anal Chim Acta 1110:35–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2020.02.023
Mao X, Zhang C (2022) A microfluidic cloth-based photoelectrochemical analytical device for the detection of glucose in saliva. Talanta 238:123052. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2021.123052
Chen X, Liu D, Cao G et al (2019) In situ synthesis of a sandwich-like graphene@ZIF-67 heterostructure for highly sensitive nonenzymatic glucose sensing in human serums. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 11:9374–9384. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.8b22478
Hwang D-W, Lee S, Seo M, Chung TD (2018) Recent advances in electrochemical non-enzymatic glucose sensors—a review. Anal Chim Acta 1033:1–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2018.05.051
Kumar R (2020) NiCo2O4 nano-/microstructures as high-performance biosensors: a review. Nano-Micro Lett 12:122. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40820-020-00462-w
Zhang Y, He Z, Dong Q et al (2022) 3D CoxP@NiCo-LDH heteronanosheet array: as a high sensitivity sensor for glucose. Microchem J 172:106923. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2021.106923
Zhao S, Wang Y, Dong J et al (2016) Ultrathin metal-organic framework nanosheets for electrocatalytic oxygen evolution. Nat Energy 1:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1038/nenergy.2016.184
Wang Y, Liu B, Shen X et al (2021) Engineering the activity and stability of MOF-nanocomposites for efficient water oxidation. Adv Energy Mater 11:2003759. https://doi.org/10.1002/aenm.202003759
Kempahanumakkagari S, Vellingiri K, Deep A et al (2018) Metal–organic framework composites as electrocatalysts for electrochemical sensing applications. Coord Chem Rev 357:105–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2017.11.028
Li S, Lin J, Xiong W et al (2021) Design principles and direct applications of cobalt-based metal-organic frameworks for electrochemical energy storage. Coord Chem Rev 438:213872. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2021.213872
Zhao L, Wei Q, Zhang L et al (2021) NiCo alloy decorated on porous N-doped carbon derived from ZnCo-ZIF as highly efficient and magnetically recyclable catalyst for hydrogen evolution from ammonia borane. Renew Energy 173:273–282. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2021.03.100
Zhang Y, Liu Y-Q, Bai Y et al (2020) Confinement preparation of hierarchical NiO-N-doped carbon@reduced graphene oxide microspheres for high-performance non-enzymatic detection of glucose. Sens Actuators, B 309:127779. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2020.127779
Oh S, Lee S, Oh M (2020) Zeolitic imidazolate framework-based composite incorporated with well-dispersed CoNi nanoparticles for efficient catalytic reduction reaction. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 12:18625–18633. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.0c03756
Li R, Ren X, Feng X et al (2014) A highly stable metal- and nitrogen-doped nanocomposite derived from Zn/Ni-ZIF-8 capable of CO2 capture and separation. Chem Commun 50:6894. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4cc01087f
Choi CH, Choi WS, Kasian O et al (2017) Unraveling the nature of sites active toward hydrogen peroxide reduction in Fe-N-C catalysts. Angew Chemie Int Ed 56:8809–8812. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201704356
Liu P, Zhang Y, Yan J et al (2019) Synthesis of lightweight N-doped graphene foams with open reticular structure for high-efficiency electromagnetic wave absorption. Chem Eng J 368:285–298. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.02.193
Xia BY, Yan Y, Li N et al (2016) A metal–organic framework-derived bifunctional oxygen electrocatalyst. Nat Energy 1:15006. https://doi.org/10.1038/nenergy.2015.6
Ma Y, Dichiara AB, He D et al (2016) Control of product nature and morphology by adjusting the hydrogen content in a continuous chemical vapor deposition process for carbon nanotube synthesis. Carbon 107:171–179. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2016.05.060
Lu W, Jian M, Wang Q et al (2019) Hollow core-sheath nanocarbon spheres grown on carbonized silk fabrics for self-supported and nonenzymatic glucose sensing. Nanoscale 11:11856–11863. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9nr01791g
Chen D, Yu J, Cui Z et al (2020) Hierarchical architecture derived from two-dimensional zeolitic imidazolate frameworks as an efficient metal-based bifunctional oxygen electrocatalyst for rechargeable Zn–air batteries. Electrochim Acta 331:135394. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2019.135394
Tsai C-W, Kroon RE, Swart HC et al (2019) Photoluminescence of metal-imidazolate complexes with Cd(II), Zn(II), Co(II) and Ni(II) cation nodes and 2-methylimidazole organic linker. J Lumin 207:454–459. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jlumin.2018.11.026
Zhang J, Zhang M, Qiu L et al (2019) Three-dimensional interconnected core–shell networks with Ni(Fe)OOH and M-N–C active species together as high-efficiency oxygen catalysts for rechargeable Zn–air batteries. J Mater Chem A 7:19045–19059. https://doi.org/10.1039/C9TA06852J
Chen D, Li G, Chen X et al (2021) Developing nitrogen and Co/Fe/Ni multi-doped carbon nanotubes as high-performance bifunctional catalyst for rechargeable zinc-air battery. J Colloid Interface Sci 593:204–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2021.02.115
Fu Z, Hu J, Hu W et al (2018) Quantitative analysis of Ni2+/Ni3+ in Li[NixMnyCoz]O2 cathode materials: non-linear least-squares fitting of XPS spectra. Appl Surf Sci 441:1048–1056. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.02.114
Perazzolo V, Durante C, Pilot R et al (2015) Nitrogen and sulfur doped mesoporous carbon as metal-free electrocatalysts for the in situ production of hydrogen peroxide. Carbon 95:949–963. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2015.09.002
Cao F, Zhao M, Yu Y et al (2016) Synthesis of two-dimensional CoS1.097/nitrogen-doped carbon nanocomposites using metal-organic framework nanosheets as precursors for supercapacitor application. J Am Chem Soc 138:6924–6927. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.6b02540
Sheng ZH, Shao L, Chen JJ et al (2011) Catalyst-free synthesis of nitrogen-doped graphene via thermal annealing graphite oxide with melamine and its excellent electrocatalysis. ACS Nano 5:4350–4358. https://doi.org/10.1021/nn103584t
Shu Y, Yan Y, Chen J et al (2017) Ni and NiO nanoparticles decorated metal-organic framework nanosheets: facile synthesis and high-performance nonenzymatic glucose detection in human serum. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9:22342–22349. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.7b07501
Zhang L, Ye C, Li X et al (2018) A CuNi/C nanosheet array based on a metal–organic framework derivate as a supersensitive non-enzymatic glucose sensor. Nano-Micro Lett 10:28. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40820-017-0178-9
Lavanya N, Leonardi SG, Marini S et al (2020) MgNi2O3 nanoparticles as novel and versatile sensing material for non-enzymatic electrochemical sensing of glucose and conductometric determination of acetone. J Alloys Compd 817:152787. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.152787
Unmüssig T, Weltin A, Urban S et al (2018) Non-enzymatic glucose sensing based on hierarchical platinum micro-/nanostructures. J Electroanal Chem 816:215–222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2018.03.061
Ezzati M, Shahrokhian S, Hosseini H (2020) In situ two-step preparation of 3D NiCo-BTC MOFs on a glassy carbon electrode and a graphitic screen printed electrode as nonenzymatic glucose-sensing platforms. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 8:14340–14352. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.0c03806
Pu X, Zhao D, Fu C et al (2021) Understanding and calibration of charge storage mechanism in cyclic voltammetry curves. Angew Chemie Int Ed 60:21310–21318. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.202104167
Sun S, Shi N, Liao X et al (2020) Facile synthesis of CuO/Ni(OH)2 on carbon cloth for non-enzymatic glucose sensing. Appl Surf Sci 529:147067. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2020.147067
Wang Q, Huang X, Zhao ZL et al (2020) Ultrahigh-loading of Ir single atoms on NiO matrix to dramatically enhance oxygen evolution reaction. J Am Chem Soc 142:7425–7433. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.9b12642
Chen X, He X, Gao J et al (2019) Three-dimensional porous Ni, N-codoped C networks for highly sensitive and selective non-enzymatic glucose sensing. Sens Actuators, B 299:126945. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2019.126945
Ding J, Li X, Zhou L et al (2020) Electrodeposition of nickel nanostructures using silica nanochannels as confinement for low-fouling enzyme-free glucose detection. J Mater Chem B 8:3616–3622. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9tb02472g
Zhan T, Yin H, Zhu J et al (2019) Ni3(PO4)2 nanoparticles decorated carbon sphere composites for enhanced non-enzymatic glucose sensing. J Alloys Compd 786:18–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.01.304
Meng A, Yuan X, Li Z et al (2019) Direct growth of 3D porous (Ni-Co)3S4 nanosheets arrays on rGO-PEDOT hybrid film for high performance non-enzymatic glucose sensing. Sens Actuators, B 291:9–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2019.04.042
Wang F, Feng Y, He S et al (2020) Nickel nanoparticles-loaded three-dimensional porous magnetic graphene-like material for non-enzymatic glucose sensing. Microchem J 155:104748. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2020.104748
Rahsepar M, Foroughi F, Kim H (2019) A new enzyme-free biosensor based on nitrogen-doped graphene with high sensing performance for electrochemical detection of glucose at biological pH value. Sens Actuators, B 282:322–330. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2018.11.078
Liu W, Zhao X, Guo Q et al (2022) Preparation of electrochemical sensor based on the novel NiO quantum dots modified Cu/Cu2O 3D hybrid electrode and its application for non-enzymatic detection of glucose in serums and beverages. J Alloys Compd 895:162573. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2021.162573
Li Y, Deng D, Wang H et al (2022) Controlled synthesis of Cu-Sn alloy nanosheet arrays on carbon fiber paper for self-supported nonenzymatic glucose sensing. Anal Chim Acta 1190:339249. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2021.339249
Gupta P, Gupta VK, Huseinov A et al (2021) Highly sensitive non-enzymatic glucose sensor based on carbon nanotube microelectrode set. Sens Actuators, B 348:130688. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2021.130688
Chakraborty P, Dhar S, Deka N et al (2020) Non-enzymatic salivary glucose detection using porous CuO nanostructures. Sens Actuators, B 302:127134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2019.127134
Su Y, Luo B, Zhang JZ (2016) Controllable cobalt oxide/Au hierarchically nanostructured electrode for nonenzymatic glucose sensing. Anal Chem 88:1617–1624. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.5b03396
Acknowledgements
This work was partially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21776147, 21606140, 61604086, 21905153, and 51472174), the International Science & Technology Cooperation Program of China (2014DFA60150), the Department of Science and Technology of Shandong Province (ZR2018BB066 and 2016GGX104010), the Qingdao Municipal Science and Technology Bureau (19-6-1-91-nsh), and the Department of Education of Shandong Province (J16LA14 and J17KA013). Also, L. F. Dong thanks financial support from the Malmstrom Endowed Fund at Hamline University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, G., Xie, G., Gong, C. et al. Hydrogen-assisted synthesis of Ni-ZIF-derived nickel nanoparticle chains coated with nitrogen-doped graphitic carbon layers as efficient electrocatalysts for non-enzymatic glucose detection. Microchim Acta 189, 80 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-022-05172-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-022-05172-1