Abstract
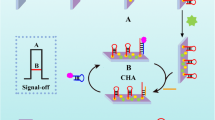
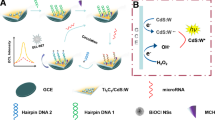
An ultrasensitive photochemical biosensor based on the target miRNA-triggered catalytic hairpin assembly (CHA) reaction between Au nanoparticles (AuNPs)/C3N4 nanosheets and CdS quantum dots (QDs) was developed for the determination of miRNAs. Firstly, AuNPs/C3N4 nanosheets were immobilized onto a working glassy carbon electrode. Then, the hairpin probe 1 (H1) was loaded through Au–S bonding. Afterward, the unbound sites were blocked with 6-mercaptohexanol to avoid nonspecific adsorption. In the presence of the target miRNA, the CHA reaction between the H1 and hairpin probe 2-CdS QDs (H2-CdS QDs) could be triggered. As a result, the AuNPs/C3N4 nanosheet and CdS QDs were linked by the double helix structure H1-H2. Unlike the other CHA reactions, H2 used in this work is longer than H1 so that the AuNPs/C3N4 nanosheets could touch the CdS QDs. Given the matched energy band positions between the C3N4 nanosheet and CdS QDs, a strong photocurrent could be obtained after the CHA reaction was triggered by the target miRNA. In addition, p-type C3N4 nanosheets and n-type CdS QDs presented reduction photocurrents and oxidation photocurrents, respectively. Therefore, the photocurrents were vectors in this design that can eliminate the interference of nonspecific adsorption and avoid the generation of false-positive signals. Under the optimal conditions, the limit of detection was 92 aM. The constructed photoelectrochemical biosensor showed good reproducibility and selectivity in the analysis of serum samples, which indicates its great prospects in disease diagnostics and bioanalysis.
Graphical abstract











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lee RC, Feinbaum RL, Ambros V (1993) The C. elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense complementarity to lin-14. Cell 75:843–54
Peng Y, Croce CM (2016) The role of MicroRNAs in human cancer. Signal Transduct Target Ther 1:15004
Iorio MV, Croce CM (2012) MicroRNA dysregulation in cancer: diagnostics, monitoring and therapeutics. A comprehensive review. EMBO Mol Med 4:143–159
Lautner G, Gyurcsányi RE (2014) Electrochemical detection of miRNAs. Electroanalysis 26:1224–1235
Kimura Y, Ikeuchi M, Inoue Y, Ikuta K (2018) 3D microdevices that perform sample purification and multiplex qRT-PCR for early cancer detection with confirmation of specific RNAs. Sci Rep 8:17480
Premaratne G, Mubarak ZHA, Senavirathna L, Liu L, Krishnan S (2017) Measuring ultra-low levels of nucleotide biomarkers using quartz crystal microbalance and SPR microarray imaging methods: a comparative analysis. Sens Actuators, B Chem 253:368–375
Pall GS, Hamilton AJ (2008) Improved northern blot method for enhanced detection of small RNA. Nat Protoc 3:1077–1084
Yu Z-B, Han S-P, Bai Y-F, Zhu C, Pan Y, Guo X-R (2012) microRNA expression profiling in fetal single ventricle malformation identified by deep sequencing. Int J Mol Med 29:53–60
Luby BM, Zheng G (2017) Specific and direct amplified detection of microRNA with MicroRNA:Argonaute-2 Cleavage (miRACle) beacons. Angew Chem Int Ed 56:13704–13708
Cui L, Zhou J, Yang X-Y, Dong J, Wang X, Zhang C-Y (2020) Catalytic hairpin assembly-based electrochemical biosensor with tandem signal amplification for sensitive microRNA assay. Chem Commun 56:10191–10194
Kerr E, Farr R, Doeven EH, Nai YH, Alexander R, Guijt RM et al (2021) Amplification-free electrochemiluminescence molecular beacon-based microRNA sensing using a mobile phone for detection. Sensors Actuators B Chem 330:129261
Xia L-Y, Li M-J, Wang H-J, Yuan R, Chai Y-Q (2019) A novel “signal on” photoelectrochemical strategy based on dual functional hemin for microRNA assay. Chem Commun 55:9721–9724
Du X-Y, Wu S-H, Huang X-B, Sun J-J (2021) Ag nanocubes coupled with heating-enhanced DSN-assisted cycling amplification for surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy detection of MicroRNA-21. ACS Appl Nano Mater 4:2565–2574
Juthani N, Doyle PS (2020) A platform for multiplexed colorimetric microRNA detection using shape-encoded hydrogel particles. Analyst 145:5134–5140
Mo F, Wu J, Chen M, Meng H, Han Q, Fu Y (2019) Enzyme-free “on-off-on” photoelectrochemical biosensor based on cascaded quadratic amplification strategy for miRNA 141 detection. Sens Actuators, B Chem 289:269–276
Wang Y, Su YR, Qiao L, Liu LX, Su Q, Zhu CQ et al (2011) Synthesis of one-dimensional TiO2/V2O5branched heterostructures and their visible light photocatalytic activity towards Rhodamine B. Nanotechnology 22:225702
Boruah PK, Szunerits S, Boukherroub R, Das MR (2018) Magnetic Fe3O4@V2O5/rGO nanocomposite as a recyclable photocatalyst for dye molecules degradation under direct sunlight irradiation. Chemosphere 191:503–513
Dong Y-X, Cao J-T, Wang B, Ma S-H, Liu Y-M (2017) Exciton–plasmon interactions between CdS@g-C3N4 heterojunction and Au@Ag nanoparticles coupled with DNAase-triggered signal amplification: toward highly sensitive photoelectrochemical bioanalysis of microRNA. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 5:10840–10848
Chen Y, Deng W, Tan Y, Xie Q (2020) CdS quantum-dots-decorated V2O5 nanosheets as chemically etchable active materials for sensitive photoelectrochemical immunoassay of carcinoembryonic antigen. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 12:29066–29073
Wang Q, Yin H, Zhou Y, Wang J, Ai S (2021) Investigation of the inhibited biotoxicity of heavy metals towards 5- formylcytosine in rice by hydrochar based on photoelectrochemical biosensor. J Hazard Mater 414:125293
Liu L, Ma K, Xu X, Shangguan C, Lv J, Zhu S et al (2020) MoS2-ReS2 Heterojunctions from a bimetallic co-chamber feeding atomic layer deposition for ultrasensitive MiRNA-21 detection. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 12:29074–29084
Yuan C, He Z, Chen Q, Wang X, Zhai C, Zhu M (2021) Selective and efficacious photoelectrochemical detection of ciprofloxacin based on the self-assembly of 2D/2D g-C3N4/Ti3C2 composites. Appl Surf Sci 539:148241
Zhang J, Shang M, Gao Y, Yan J, Song W (2020) High-performance VS2 QDs-based type II heterostructured photoanode for ultrasensitive aptasensing of lysozyme. Sensors Actuators B Chem 304:127411
Victorious A, Saha S, Pandey R, Soleymani L (2021) Enhancing the sensitivity of photoelectrochemical DNA biosensing using plasmonic DNA barcodes and differential signal readout. Angew Chem Int Ed 60:7316–7322
Yang K, Li J, Lamy de la Chapelle M, Huang G, Wang Y, Zhang J et al (2021) A terahertz metamaterial biosensor for sensitive detection of microRNAs based on gold-nanoparticles and strand displacement amplification. Biosens Bioelectron 175:112874
Fan Y, Liu Y, Zhou Q, Du H, Zhao X, Ye F et al (2021) Catalytic hairpin assembly indirectly covalent on Fe3O4@C nanoparticles with signal amplification for intracellular detection of miRNA. Talanta 223:121675
Ju T, Zhai X, Liu X, Han K (2021) A toehold-mediated strand displacement cascade-based DNA assay method via flow cytometry and magnetic separation. Anal Methods 13:1013–1018
Liu C, Zhang S, Li X, Xue Q, Jiang W (2019) Multi-code magnetic beads based on DNAzyme-mediated double-cycling amplification for a point-of-care assay of telomerase activity. Analyst 144:4241–4249
Hu Z, Xu F, Sun G, Zhang S, Zhang X (2020) Homogeneous multiplexed digital detection of microRNA with ligation-rolling circle amplification. Chem Commun 56:5409–5412
Yang L, Fang J, Li J, Ou X, Zhang L, Wang Y et al (2021) An integrated fluorescence biosensor for microRNA detection based on exponential amplification reaction-triggered three-dimensional bipedal DNA walkers. Anal Chim Acta 1143:157–165
Meng T, Jia H, An S, Wang H, Yang X, Zhang Y (2020) Pd nanoparticles-DNA layered nanoreticulation biosensor based on target-catalytic hairpin assembly for ultrasensitive and selective biosensing of microRNA-21. Sensors Actuators B Chem 323:128621
Li J, Koo KM, Wang Y, Trau M (2019) Native MicroRNA targets trigger self-assembly of nanozyme-patterned hollowed nanocuboids with optimal interparticle gaps for plasmonic-activated cancer detection. Small 15:1904689
Madrakian T, Maleki S, Afkhami A (2017) Surface decoration of cadmium-sulfide quantum dots with 3-mercaptopropionic acid as a fluorescence probe for determination of ciprofloxacin in real samples. Sens Actuators, B Chem 243:14–21
Ma X, Xu H, Qian K, Kandawa-Schulz M, Miao W, Wang Y (2020) Electrochemical detection of microRNAs based on AuNPs/CNNS nanocomposite with Duplex-specific nuclease assisted target recycling to improve the sensitivity. Talanta 208:120441
Butwong N, Noipa T, Burakham R, Srijaranai S, Ngeontae W (2011) Determination of arsenic based on quenching of CdS quantum dots fluorescence using the gas-diffusion flow injection method. Talanta 85:1063–1069
Masteri-Farahani M, Mosleh N (2019) Modified CdS quantum dots as selective turn-on fluorescent nanosensor for detection and determination of methamphetamine. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 30:21170–21176
Gonullu MP, Ates H (2020) Investigation of the impact of annealing on the structural, optical and morphological evolution of mixture-phase ALD-TiO2 films containing brookite. Superlattice Microst 147:106699
Ahamad T, Majeed Khan MA, Kumar S, Ahamed M, Shahabuddin M, Alhazaa AN (2016) CdS quantum dots: growth, microstructural, optical and electrical characteristics. Appl Phys B 122:179
Singh AP, Arora P, Basu S, Mehta BR (2016) Graphitic carbon nitride based hydrogen treated disordered titanium dioxide core-shell nanocatalyst for enhanced photocatalytic and photoelectrochemical performance. Int J Hydrogen Energy 41:5617–5628
Xiong E, Zhang X, Liu Y, Zhou J, Yu P, Li X et al (2015) Ultrasensitive electrochemical detection of nucleic acids based on the dual-signaling electrochemical ratiometric method and exonuclease III-assisted target recycling amplification strategy. Anal Chem 87:7291–7296
Zhang L, Xiao X, Xu Y, Chen D, Chen J, Ma Y et al (2018) Electrochemical assay for continuous monitoring of dynamic DNA methylation process. Biosens Bioelectron 100:184–191
Ma X, Qian K, Ejeromedoghene O, Kandawa-Schulz M, Wang Y (2020) Electrochemical detection of microRNA based on SA-PPy/AuNPs nanocomposite with the signal amplification through catalytic hairpin assembly reaction and the spontaneous catalytic reaction of Fe3+/Cu2+. Electrochimica Acta 362:137168
Funding
This investigation was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundations of China (No. 81571812) and A Project Funded by the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (1107047002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, X., Ma, Y., Ejeromedoghene, O. et al. Photoelectrochemical detection of microRNAs based on target-triggered self-assembly of energy band position–matched CdS QDs and C3N4 nanosheets. Microchim Acta 189, 65 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-022-05168-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-022-05168-x