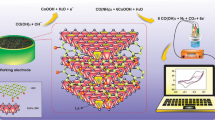
Abstract
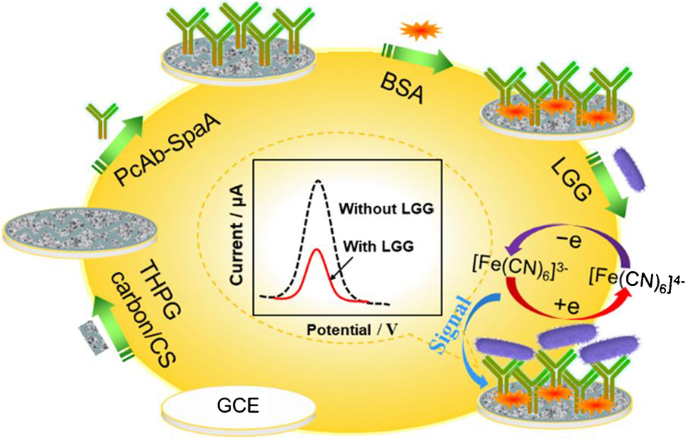
An ultrasensitive label-free electrochemical immunosensor was fabricated for quantitative detection of Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG (LGG). The N/O co-doped three-dimensional hierarchical porous graphitic (THPG) carbon was synthesized by a one-step synthesis of polyaniline hydrogel, and followed by simple carbonization and chemical activation procedures. Because of the unique structure design, the obtained THPG carbon networks possess an ultra-large specific surface area of 4859 m2 g−1 along with a class of highly graphitic carbons. The results offer an enormous surface area and excellent electrical conductivity for label-free electrochemical immunosensing of probiotic L. rhamnosus strain. Under optimal conditions, the immunosensor showed a good linear relationship between peak current and concentration of LGG (R2 = 0.9976), with a detection limit of 2 CFU mL−1. Furthermore, this label-free immunosensor also shows good specificity, long-term stability, and reliability, and could be applied to detect probiotic LGG in dairy products and drinks with satisfactory results. The present protocol was shown to be quite promising for practical screening and functional evaluation of probiotic products containing LGG.
Graphical abstract
A ultrasensitive label-free electrochemical immunosensor based on THPG carbon was fabricated for detection of Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shah B, Li B, Al Sabbah H, Xu W, Mraz J (2020) Effects of prebiotic dietary fibers and probiotics on human health: with special focus on recent advancement in their encapsulated formulations. Trends Food Sci Tech 102:178–192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2020.06.010
Preidis G, Weizman A, Kashyap P, Morgan R (2020) AGA technical review on the role of probiotics in the management of gastrointestinal disorders. Gastroenterology 159(2):708–738. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2020.05.060
Freedman S, Williamson-Urquhart S, Farion K, Gouin S, Willan A, Poonai N, Hurley K, Sherman P, Finkelstein Y, Lee B (2018) Multicenter trial of a combination probiotic for children with gastroenteritis. New Engl J Med 379(21):2015–2026. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1802597
Sireswar S, Biswas S, Dey G (2020) Adhesion and anti-inflammatory potential of lactobacillus rhamnosus GG in a sea buckthorn based beverage matrix. Food Funct 11(3):2555–2572. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9fo02249j
Capurso L (2019) Thirty years of lactobacillus rhamnosus GG: a review. J Clin Gastroenterol 53:S1–S41. https://doi.org/10.1097/MCG.0000000000001170
Yang Z, Wei Y, Rao S, Gao L, Yin Y, Xue F, Fang W, Gu R, Jiao X (2016) Immunomagnetic separation combined with colony immunoblotting for selective enrichment and detection of piliated lactobacillus rhamnosus strains. J Appl Microbiol 121(5):1406–1415. https://doi.org/10.1111/jam.13275
Douillard FP, Ribbera A, Jarvinen HM, Kant R, Pietila TE, Randazzo C, Paulin L, Laine PK, Caggia C, Ossowski V, Reunanen J (2013) Comparative genomic and functional analysis of lactobacillus casei and lactobacillus rhamnosus strains marketed as probiotics. Appl. Environ. Microb. 79(6):1923–1933. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.03467-12
Von Ossowski I, Reunanen J, Satokari R, Vesterlun S, Kankainen M, Huhtinen H, Tynkkynen S, Salminen S, Vos W, Palva A (2010) Mucosal adhesion properties of the probiotic lactobacillus rhamnosus GG SpaCBA and SpaFED pilin subunits. Appl. Environ. Microb. 76(7):2049–2057. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.01958-09
Reunanen J, Von Ossowski I, Hendrickx A, Palva A, Vos W (2012) Characterization of the SpaCBA pilus fibers in the probiotic lactobacillus rhamnosus GG. Appl Environ Microb 78(7):2337–2344. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.07047-11
Lebeer S, Claes I, Tytgat HL, Verhoeven TL, Marien E, von Ossowski I, Reunanen J, Palva A, de Vos WM, De Keersmaecker SC (2012) Functional analysis of lactobacillus rhamnosus GG pili in relation to adhesion and immunomodulatory interactions with intestinal epithelial cells. Appl. Environ. Microb. 78(1):185–193. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.06192-11
Xue Y, Jiang D, Hu Q, Rao S, Gao L, Yang Z (2019) Electrochemical magnetic bead-based immunosensor for rapid and quantitative detection of probiotic lactobacillus rhamnosus in dairy products. Food Anal Method 12(5):1197–1207. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-019-01457-z
Akanny E, Bonhommé A, Commun C, Doleans-Jordheim A, Bessueille F, Bourgeois S, Bordes C (2019) Development of uncoated near-spherical gold nanoparticles for the label-free quantification of lactobacillus rhamnosus GG by surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Anal Bioanal Chem 411(21):5563–5576. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-019-01938-4
Marcos-Fernández R, Ruiz L, Blanco-Míguez A, Margolles A, Sánchez B (2020) Cell wall hydrolase as a surface-associated protein target for the specific detection of lactobacillus rhamnosus using flow cytometry. Innov Food Sci Emerg 59:102240. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ifset.2019.102240
Gracias K, McKillip J (2004) A review of conventional detection and enumeration methods for pathogenic bacteria in food. Can J Microbiol 50(11):883–890. https://doi.org/10.1139/W04-080
Pang B, Zhao C, Li L, Song X, Xu K, Wang J, Liu Y, Fu K, Bao H, Song D (2018) Development of a low-cost paper-based ELISA method for rapid Escherichia coli O157: H7 detection. Anal Biochem 542:58–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ab.2017.11.010
Shih C, Chang C, Hsu M, Lin J, Kuan C, Wang H, Huang C, Chung M, Huang K, Hsu C (2015) Paper-based ELISA to rapidly detect Escherichia coli. Talanta 145:2–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2015.07.051
Ahlroos T, Tynkkynen S (2009) Quantitative strain-specific detection of lactobacillus rhamnosus GG in human faecal samples by real-time PCR. J Appl Microbiol 106(2):506–514. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2672.2008.04018.x
Okai C, Itani Y, Furuta A, Mizunoe Y, Iwase T (2019) Rapid identification and quantification of lactobacillus rhamnosus–targeting real-time PCR using a TaqMan probe. Jpn J Infect Dis 72:323–325. https://doi.org/10.7883/yoken.JJID.2019.102
Jiang Y, Zou S, Cao X (2017) A simple dendrimer-aptamer based microfluidic platform for E. coli O157: H7 detection and signal intensification by rolling circle amplification. Sens. Actuators B Chem 251:976–984. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2017.05.146
Wang H, Zhao Y, Bie S, Suo T, Jia G, Liu B, Ye R, Li Z (2019) Development of an electrochemical biosensor for rapid and effective detection of pathogenic Escherichia coli in licorice extract. Appl Sci-Basel 9(2):295. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9020295
Zhu F, Zhao G, Dou W (2018) A non-enzymatic electrochemical immunoassay for quantitative detection of Escherichia coli O157: H7 using au@Pt and graphene. Anal Biochem 559:34–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ab.2018.08.016
Zhu F, Zhao G, Dou W (2018) Electrochemical sandwich immunoassay for Escherichia coli O157: H7 based on the use of magnetic nanoparticles and graphene functionalized with electrocatalytically active au@Pt core/shell nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 185(10):455. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-2984-2
Jijie R, Kahlouche K, Barras A, Yamakawa N, Bouckaert J, Gharbi T, Szunerits S, Boukherroub R (2018) Reduced graphene oxide/polyethylenimine based immunosensor for the selective and sensitive electrochemical detection of uropathogenic Escherichia coli. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 260:255–263. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2017.12.169
Wang H, Xiu Y, Chen Y, Sun L, Yang L, Chen H, Niu X (2019) Electrochemical immunosensor based on an antibody-hierarchical mesoporous SiO2 for the detection of Staphylococcus aureus. RSC Adv 9(28):16278–16287. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9ra00907h
Bekir K, Barhoumi H, Braiek M, Chrouda A, Zine N, Abid N, Maaref A, Bakhrouf A, Ouada H, Jaffrezic-Renault N (2015) Electrochemical impedance immunosensor for rapid detection of stressed pathogenic Staphylococcus aureus bacteria. Environ Sci Pollut R 22(20):15796–15803. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4761-7
Chiriacò M, Parlangeli I, Sirsi F, Poltronieri P, Primiceri E (2018) Impedance sensing platform for detection of the food pathogen listeria monocytogenes. Electronics-Switz 7(12):347. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics7120347
Mantzila A, Maipa V, Prodromidis M (2008) Development of a faradic impedimetric immunosensor for the detection of salmonella typhimurium in milk. Anal Chem 80(4):1169–1175. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac071570l
Dutta S, Bhaumik A, Wu K (2014) Hierarchically porous carbon derived from polymers and biomass: effect of interconnected pores on energy applications. Energy Environ Sci 7(11):3574–3592. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4ee01075b
Pan L, Yu G, Zhai D, Lee H, Zhao W, Liu N, Wang H, Tee B, Shi Y, Cui Y, Bao Z (2012) Hierarchical nanostructured conducting polymer hydrogel with high electrochemical activity. P. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 109:(24):9287-9292. 10.1073/pnas.1202636109
To J, Chen Z, Yao H, He J, Kim K, Chou H, Pan L, Wilcox J, Cui Y, Bao Z (2015) Ultrahigh surface area three-dimensional porous graphitic carbon from conjugated polymeric molecular framework. Acs Central Sci 1(2):68–76. https://doi.org/10.1021/acscentsci.5b00149
Huang Y, Zhu F, Guan J, Wei W, Zou L (2021) Label-free amperometric immunosensor based on versatile carbon nanofibers network coupled with au nanoparticles for aflatoxin B1 detection. Biosensors-Basel 11(1):5. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11010005
Chen Y, Jiao L, Yan H, Xu W, Wu Y, Wang H, Gu W, Zhu C (2020) Hierarchically porous S/N codoped carbon nanozymes with enhanced peroxidase-like activity for total antioxidant capacity biosensing. Anal Chem 92(19):13518–13524. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.0c02982
Riaz M, Yuan Z, Mahmood A, Liu F, Sui X, Chen J, Huang Q, Liao X, Wei L, Chen Y (2020) Hierarchically porous carbon nanofibers embedded with cobalt nanoparticles for efficient H2O2 detection on multiple sensor platforms. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 319:128243. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2020.128243
Wang Y, Qiao M, Mamat X (2021) Nitrogen-doped macro-meso-micro hierarchical ordered porous carbon derived from ZIF-8 for boosting supercapacitor performance. Appl Surf Sci 540:148352. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2020.148352
Zhang W, Wu Z, Jiang H, Yu S (2014) Nanowire-directed templating synthesis of metal–organic framework nanofibers and their derived porous doped carbon nanofibers for enhanced electrocatalysis. J Am Chem Soc 136(41):14385–14388. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja5084128
Qie L, Chen W, Xu H, Xiong X, Jiang Y, Zou F, Hu X, Xin Y, Zhang Z, Huang Y (2013) Synthesis of functionalized 3D hierarchical porous carbon for high-performance supercapacitors. Energy Environ Sci 6(8):2497–2504. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3ee41638k
Wang Q, Yan J, Fan Z (2016) Carbon materials for high volumetric performance supercapacitors: design, progress, challenges and opportunities. Energy Environ Sci 9(3):729–762. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5ee03109e
Nishihara H, Kyotani T (2012) Templated nanocarbons for energy storage. Adv Mater 24(33):4473–4498. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201201715
Ma Z, Shi W, Yan K, Pan L, Yu G (2019) Doping engineering of conductive polymer hydrogels and their application in advanced sensor technologies. Chem Sci 10(25):6232–6244. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9sc02033k
Li P, Jin Z, Peng L, Zhao F, Xiao D, Jin Y, Yu G (2018) Stretchable all-gel-state fiber-shaped supercapacitors enabled by macromolecularly interconnected 3D graphene/nanostructured conductive polymer hydrogels. Adv Mater 30(18):1800124. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201800124
To J, He J, Mei J, Haghpanah R, Chen Z, Kurosawa T, Chen S, Bae W, Pan L, Tok J (2016) Hierarchical N-doped carbon as CO2 adsorbent with high CO2 selectivity from rationally designed polypyrrole precursor. J Am Chem Soc 138(3):1001–1009. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.5b11955
Silva R, Voiry D, Chhowalla M, Asefa T (2013) Efficient metal-free electrocatalysts for oxygen reduction: polyaniline-derived N-and O-doped mesoporous carbons. J Am Chem Soc 135(21):7823–7826. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja402450a
Niu J, Liang J, Shao R, Liu M, Dou M, Li Z, Huang Y, Wang F (2017) Tremella-like N. O-codoped hierarchically porous carbon nanosheets as high-performance anode materials for high energy and ultrafast Na-ion capacitors Nano Energy 41:285–292. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nanoen.2017.09.041
Yu W, Wang H, Liu S, Mao N, Liu X, Shi J, Liu W, Chen S, Wang X (2016) N, O-codoped hierarchical porous carbons derived from algae for high-capacity supercapacitors and battery anodes. J Mater Chem A 4(16):5973–5983. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6ta01821a
Khodadadi A, Faghih-Mirzaei E, Karimi-Maleh H, Abbaspourrad A, Agarwal S, Gupta V (2019) A new epirubicin biosensor based on amplifying DNA interactions with polypyrrole and nitrogen-doped reduced graphene: experimental and docking theoretical investigations. Sens Actuators B Chem 284:568–574. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2018.12.164
Atchudan R, Muthuchamy N, Edison T, Perumal S, Vinodh R, Park K, Lee Y (2019) An ultrasensitive photoelectrochemical biosensor for glucose based on bio-derived nitrogen-doped carbon sheets wrapped titanium dioxide nanoparticles. Biosens Bioelectron 126:160–169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2018.10.049
Yang Z, Xue Y, Rao S, Zhang M, Gao L, Yin Y, Chen D, Zhou X, Jiao X (2017) Isolation of probiotic piliated lactobacillus rhamnosus strains from human fecal microbiota using SpaA antiserum-based colony immunoblotting. J Microbiol Biotechnol 27(11):1971–1982. https://doi.org/10.4014/jmb.1705.05055
Guo Z, Wang F, Xia Y, Li J, Tamirat A, Liu Y, Wang L, Wang Y, Xia Y (2018) In situ encapsulation of core–shell-structured co@Co3O4 into nitrogen-doped carbon polyhedra as a bifunctional catalyst for rechargeable Zn–air batteries. J Mater Chem A 6(4):1443–1453. https://doi.org/10.1039/d0ta90204g
Balasubramanian P, Balamurugan T, Chen S, Chen T, Sathesh T (2018) Rational design of cu@Cu2O nanospheres anchored B, N co-doped mesoporous carbon: a sustainable electrocatalyst to assay eminent neurotransmitters acetylcholine and dopamine. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 7(6):5669–5680. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.8b04473
Zhu Y, Murali S, Stoller M, Ganesh K, Cai W, Ferreira P, Pirkle A, Wallace R, Cychosz K, Thommes M (2011) Carbon-based supercapacitors produced by activation of graphene. Science 332(6037):1537–1541. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1200770
Lan Q, Shen H, Li J, Ren C, Hu X, Yang Z (2020) Facile synthesis of novel reduced graphene oxide@polystyrene nanospheres for sensitive label-free electrochemical immunoassary. 56:699-702 https://doi.org/10.1039/c9cc07934c
Yang Z, Lan Q, Li J, Wu J, Tang Y, Hu X (2017) Efficient streptavidin-functionalized nitrogen-doped graphene for the development of highly sensitive electrochemical immunosensor. Biosens Bioelectron 89:312–318. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2016.09.026
Zou Y, Jing L, Zhe S, Kraatzb H (2018) Gold nanoparticles-based multifunctional nanoconjugates for highly sensitive and enzyme-free detection of E.coli K12. Talanta 193:15–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2018.09.068
Bhardwaj J, Devarakonda S, Kumar S, Jang J (2017) Development of a paper-based electrochemical immunosensor using an antibody-single walled carbon nanotubes bio-conjugate modified electrode for label-free detection of foodborne pathogens. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 253:115–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2017.06.108
Villalonga M, Borisova B, Arenas C, Villalonga A, Arevalo-Villena M, Sanchez A, Pingarron J, Briones-Perez A, Villalonga R (2019) Disposable electrochemical biosensors for Brettanomyces bruxellensis and total yeast content in wine based on core-shell magnetic nanoparticles. Sensor Actuat B-Chem 279:15–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2018.09.092
Freitas M, Viswanathan S, Nouws H, Oliveira M, Delerue-Matos C (2014) Iron oxide/gold core/shell nanomagnetic probes and CdS biolabels for amplified electrochemical immunosensing of salmonella typhimurium. Biosens Bioelectron 51(1):195–200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2013.07.048
Francesca M, Roberto P, Donatella A (2018) Sensitive detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7 in food products by impedimetric immunosensors. Sensors 18(7):2168. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18072168
Acknowledgements
Much thanks to The Testing Center of Yangzhou University due to all the characterization.
Funding
The funding of this work was provided by Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (No. BK20180922 and BK20190890), Natural science fund for colleges and universities in Jiangsu Province (No. 19KJB550002), State Key Laboratory of Analytical Chemistry for Life Science (No. SKLACLS2001), Nanjing University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing of interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(DOCX 626 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, Y., Wang, J., Du, Y. et al. N, O-codoped hierarchical porous graphitic carbon for electrochemical immunosensing of Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG. Microchim Acta 189, 5 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-021-05049-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-021-05049-9