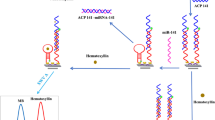
Abstract
A highly sensitive electrochemical biosensors has been developed for the detection of multiplex micro ribonucleic acids (miRNAs) by modifying an electrode with reduced graphene oxide/poly(2-aminobenzylamine)/gold nanoparticles and adopting porous, hollow silver-gold nanoparticles as tagged labeling with metal ions. In addition, an anti-deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA)-RNA hybrid [S9.6] antibody was used to detect different hybridized capture DNAs and miRNAs that can detect multiple miRNAs simultaneously. The developed electrochemical platform exhibits high selectivity, stability, and sensitivity with a wide linear range from 1 fM to 10 nM and a low detection limit of 0.98 fM, 3.58 fM, and 0.25 fM for miRNA-155, miRNA-21, and miRNA-16, respectively. In addition, the proposed electrochemical biosensor capable for the simultaneous detection of miRNA-155, miRNA-16, and miRNA-21, which are breast cancer biomarkers, in normal human serum, can be adopted and potentially used for breast cancer screening.
Graphical abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
References
C. Global Burden of Disease Cancer (2017) Global, regional, and national cancer incidence, mortality, years of life lost, years lived with disability, and disability-adjusted life-years for 32 cancer groups, 1990 to 2015: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study Global Burden of Cancer 2015 Global Burden of Cancer 2015. JAMA Oncology 3(4):524–548. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaoncol.2016.5688
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A (2018) Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 68(6):394–424. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21492
A. C. Society, "Breast cancer facts & figures 2019–2020.," American Cancer Society Inc., Atlanta, USA., pp. 3–38, 2019
Bhat SA, Majid S, Hassan T (2019) MicroRNAs and its emerging role as breast cancer diagnostic marker- a review. Advances in Biomarker Sciences and Technology 1:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.abst.2019.05.001
Wang W, Luo Y-p (2015) MicroRNAs in breast cancer: oncogene and tumor suppressors with clinical potential. Journal of Zhejiang University-SCIENCE B 16(1):18–31. https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B1400184
Wang F, Zheng Z, Guo J, Ding X (2010) Correlation and quantitation of microRNA aberrant expression in tissues and sera from patients with breast tumor. Gynecologic Oncology 119(3):586–593. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygyno.2010.07.021
Han J-G, Jiang Y-D, Zhang C-H, Yang Y-M, Pang D, Song Y-N, Zhang G-Q (2017) A novel panel of serum miR-21/miR-155/miR-365 as a potential diagnostic biomarker for breast cancer, (in eng). Ann Surg Treat Res 92(2):55–66. https://doi.org/10.4174/astr.2017.92.2.55
Liu B, Su F, Chen M, Li Y, Qi X, Xiao J, Li X, Liu X, Liang W, Zhang Y, Zhang J (2017) Serum miR-21 and miR-125b as markers predicting neoadjuvant chemotherapy response and prognosis in stage II/III breast cancer. Human Pathology 64:44–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.humpath.2017.03.016
Kumarswamy R, Volkmann I, Thum T (2011) Regulation and function of miRNA-21 in health and disease, (in eng). RNA Biol 8(5):706–713. https://doi.org/10.4161/rna.8.5.16154
Nassar FJ, Nasr R, Talhouk R (2017) MicroRNAs as biomarkers for early breast cancer diagnosis, prognosis and therapy prediction. Pharmacology & Therapeutics 172:34–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharmthera.2016.11.012
Mattiske S, Suetani RJ, Neilsen PM, Callen DF (2012) The oncogenic role of miR-155 in breast cancer. Cancer Epidemiology Biomarkers & Prevention 21(8):1236–1243. https://doi.org/10.1158/1055-9965.Epi-12-0173
Macfarlane L-A, Murphy PR (2010) MicroRNA: biogenesis, function and role in cancer, (in eng). Curr Genomics 11(7):537–561. https://doi.org/10.2174/138920210793175895
Schwarzenbach H, da Silva AM, Calin G, Pantel K (2015) Data normalization strategies for MicroRNA quantification. Clin Chem 61(11):1333–1342. https://doi.org/10.1373/clinchem.2015.239459
Hamam R, Hamam D, Alsaleh KA, Kassem M, Zaher W, Alfayez M, Aldahmash A, Alajez NM (2017) Circulating microRNAs in breast cancer: novel diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers. Cell Death & Disease 8(9):e3045. https://doi.org/10.1038/cddis.2017.440
Fiammengo R (2017) Can nanotechnology improve cancer diagnosis through miRNA detection? Biomark Med 11(1):69–86. https://doi.org/10.2217/bmm-2016-0195
Mohammadniaei M, Nguyen HV, Tieu MV, Lee M-H (2019) 2D materials in development of electrochemical point-of-care cancer screening devices. Micromachines 10(10):662 [Online]. Available: https://www.mdpi.com/2072-666X/10/10/662
Topkaya SN, Azimzadeh M, Ozsoz M (2016) Electrochemical biosensors for cancer biomarkers detection: recent advances and challenges. Electroanalysis 28(7):1402–1419. https://doi.org/10.1002/elan.201501174
Cardoso AR, Moreira FTC, Fernandes R, Sales MGF (2016) Novel and simple electrochemical biosensor monitoring attomolar levels of miRNA-155 in breast cancer. Biosensors and Bioelectronics 80:621–630. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2016.02.035
Guo J, Yuan C, Yan Q, Duan Q, Li X, Yi G (2018) An electrochemical biosensor for microRNA-196a detection based on cyclic enzymatic signal amplification and template-free DNA extension reaction with the adsorption of methylene blue. Biosensors and Bioelectronics 105:103–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2018.01.036
Azimzadeh M, Rahaie M, Nasirizadeh N, Ashtari K, Naderi-Manesh H (2016) An electrochemical nanobiosensor for plasma miRNA-155, based on graphene oxide and gold nanorod, for early detection of breast cancer. Biosensors and Bioelectronics 77:99–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2015.09.020
Azab SM, Elhakim HKA, Fekry AM (2019) The strategy of nanoparticles and the flavone chrysin to quantify miRNA-let 7a in zepto-molar level: Its application as tumor marker. Journal of Molecular Structure 1196:647–652. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2019.06.111
Peng H, Zhang L, Soeller C, Travas-Sejdic J (2009) Conducting polymers for electrochemical DNA sensing. Biomaterials 30(11):2132–2148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2008.12.065
Y. Fang and E. Wang, "Electrochemical biosensors on platforms of graphene," Chemical Communications, vol. 49, no. 83, pp. 9526–9539, 2013, doi: https://doi.org/10.1039/C3CC44735A
Shao Y, Wang J, Wu H, Liu J, Aksay IA, Lin Y (2010) Graphene based electrochemical sensors and biosensors: a review. Electroanalysis 22(10):1027–1036. https://doi.org/10.1002/elan.200900571
Ruecha N, Rodthongkum N, Cate DM, Volckens J, Chailapakul O, Henry CS (2015) Sensitive electrochemical sensor using a graphene–polyaniline nanocomposite for simultaneous detection of Zn(II), Cd(II), and Pb(II). Analytica Chimica Acta 874:40–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2015.02.064
Liu S, Xing X, Yu J, Lian W, Li J, Cui M, Huang J (2012) A novel label-free electrochemical aptasensor based on graphene–polyaniline composite film for dopamine determination. Biosensors and Bioelectronics 36(1):186–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2012.04.011
Zhuang Z, Li J, Xu R, Xiao D (2011) Electrochemical detection of dopamine in the presence of ascorbic acid using overoxidized polypyrrole/graphene modified electrodes. Int J Electrochem Sci 6(6):2149–2161
Ye D, Luo L, Ding Y, Chen Q, Liu X (2011) A novel nitrite sensor based on graphene/polypyrrole/chitosan nanocomposite modified glassy carbon electrode. Analyst 136(21):4563–4569. https://doi.org/10.1039/C1AN15486A
Sriprachuabwong C, Karuwan C, Wisitsorrat A, Phokharatkul D, Lomas T, Sritongkham P, Tuantranont A (2012) Inkjet-printed graphene-PEDOT:PSS modified screen printed carbon electrode for biochemical sensing. Journal of Materials Chemistry 22(12):5478–5485. https://doi.org/10.1039/C2JM14005E
Chuekachang S, Janmanee R, Baba A, Phanichphant S, Sriwichai S, Shinbo K, Kato K, Kaneko F, Fukuda N, Ushijima H (2013) Electrochemically controlled detection of adrenaline on poly(2-aminobenzylamine) thin films by surface plasmon resonance spectroscopy and quartz crystal microbalance. Surf Interface Anal 45(11–12):1661–1666. https://doi.org/10.1002/sia.5301
Putnin T, Jumpathong W, Laocharoensuk R, Jakmunee J, Ounnunkad K (2018) A sensitive electrochemical immunosensor based on poly(2-aminobenzylamine) film modified screen-printed carbon electrode for label-free detection of human immunoglobulin G. Artificial Cells, Nanomedicine, and Biotechnology 46(5):1042–1051. https://doi.org/10.1080/21691401.2017.1360322
Tao Y, Yin D, Jin M, Fang J, Dai T, Li Y, Li Y, Pu Q, Xie G (2017) Double-loop hairpin probe and doxorubicin-loaded gold nanoparticles for the ultrasensitive electrochemical sensing of microRNA. Biosensors and Bioelectronics 96:99–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2017.04.040
Shuai H-L, Huang K-J, Zhang W-J, Cao X, Jia M-P (2017) Sandwich-type microRNA biosensor based on magnesium oxide nanoflower and graphene oxide–gold nanoparticles hybrids coupling with enzyme signal amplification. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical 243:403–411. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2016.12.001
Tian L, Qian K, Qi J, Liu Q, Yao C, Song W, Wang Y (2018) Gold nanoparticles superlattices assembly for electrochemical biosensor detection of microRNA-21. Biosensors and Bioelectronics 99:564–570. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2017.08.035
Liang J, Chen Z, Guo L, Li L (2011) Electrochemical sensing of l-histidine based on structure-switching DNAzymes and gold nanoparticle–graphene nanosheet composites. Chemical Communications 47(19):5476–5478. https://doi.org/10.1039/C1CC10965K
Hong W, Bai H, Xu Y, Yao Z, Gu Z, Shi G (2010) Preparation of gold nanoparticle/graphene composites with controlled weight contents and their application in biosensors. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C 114(4):1822–1826. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp9101724
Guo S, Wen D, Zhai Y, Dong S, Wang E (2010) latinum nanoparticle ensemble-on-graphene hybrid nanosheet: one-pot, rapid synthesis, and used as new electrode material for electrochemical Sensing. ACS Nano 4(7):3959–3968. https://doi.org/10.1021/nn100852h
Huang J, Tian J, Zhao Y, Zhao S (2015) Ag/Au nanoparticles coated graphene electrochemical sensor for ultrasensitive analysis of carcinoembryonic antigen in clinical immunoassay. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical 206:570–576. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2014.09.119
Shuai H-L, Huang K-J, Xing L-L, Chen Y-X (2016) Ultrasensitive electrochemical sensing platform for microRNA based on tungsten oxide-graphene composites coupling with catalyzed hairpin assembly target recycling and enzyme signal amplification. Biosensors and Bioelectronics 86:337–345. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2016.06.057
Rasheed PA, Sandhyarani N (2017) Electrochemical DNA sensors based on the use of gold nanoparticles: a review on recent developments. Microchimica Acta 184(4):981–1000. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2143-1
Rafiee-Pour H-A, Behpour M, Keshavarz M (2016) A novel label-free electrochemical miRNA biosensor using methylene blue as redox indicator: application to breast cancer biomarker miRNA-21. Biosensors and Bioelectronics 77:202–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2015.09.025
Hu T, Zhang L, Wen W, Zhang X, Wang S (2016) Enzyme catalytic amplification of miRNA-155 detection with graphene quantum dot-based electrochemical biosensor. Biosensors and Bioelectronics 77:451–456. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2015.09.068
Kilic T, Topkaya SN, Ozkan Ariksoysal D, Ozsoz M, Ballar P, Erac Y, Gozen O (2012) Electrochemical based detection of microRNA, mir21 in breast cancer cells. Biosensors and Bioelectronics 38(1):195–201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2012.05.031
Xu S, Chang Y, Wu Z, Li Y, Yuan R, Chai Y (2020) One DNA circle capture probe with multiple target recognition domains for simultaneous electrochemical detection of miRNA-21 and miRNA-155. Biosensors and Bioelectronics 149:111848. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2019.111848
Tang H, Zhu J, Wang D, Li Y (2019) Dual-signal amplification strategy for miRNA sensing with high sensitivity and selectivity by use of single Au nanowire electrodes. Biosensors and Bioelectronics 131:88–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2019.02.023
Wang J, Lu Z, Tang H, Wu L, Wang Z, Wu M, Yi X, Wang J (2017) Multiplexed electrochemical detection of MiRNAs from sera of glioma patients at different stages via the novel conjugates of conducting magnetic microbeads and diblock oligonucleotide-modified gold nanoparticles. Analytical Chemistry 89(20):10834–10840. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.7b02342
Putnin T, Ngamaroonchote A, Wiriyakun N, Ounnunkad K, Laocharoensuk R (2019) Dually functional polyethylenimine-coated gold nanoparticles: a versatile material for electrode modification and highly sensitive simultaneous determination of four tumor markers. Microchimica Acta 186(5):305. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3370-4
Li T, Yang M Electrochemical sensor utilizing ferrocene loaded porous polyelectrolyte nanoparticles as label for the detection of protein biomarker IL-6. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical 158(1):361–365, 2011. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2011.06.035
Wang Z, Liu N, Ma Z (2014) Platinum porous nanoparticles hybrid with metal ions as probes for simultaneous detection of multiplex cancer biomarkers. Biosensors and Bioelectronics 53:324–329. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2013.10.009
Phillips DD, Garboczi DN, Singh K, Hu Z, Leppla SH, Leysath CE (2013) The sub-nanomolar binding of DNA-RNA hybrids by the single-chain Fv fragment of antibody S9.6, (in eng). J Mol Recognit 26(8):376–381. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmr.2284
Zouari M, Campuzano S, Pingarrón JM, Raouafi N (2018) Amperometric biosensing of miRNA-21 in serum and cancer cells at nanostructured platforms using anti-DNA-RNA hybrid antibodies, (in eng). ACS Omega 3(8):8923–8931. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.8b00986
Wang M, Yin H, Zhou Y, Sui C, Wang Y, Meng X, Waterhouse GIN, Ai S (2019) Photoelectrochemical biosensor for microRNA detection based on a MoS2/g-C3N4/black TiO2 heterojunction with Histostar@AuNPs for signal amplification. Biosensors and Bioelectronics 128:137–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2018.12.048
Wang M, Li B, Zhou Q, Yin H, Zhou Y, Ai S (2015) Label-free, ultrasensitive and electrochemical immunosensing platform for microRNA detection using anti-DNA:RNA hybrid antibody and enzymatic signal amplification. Electrochim Acta 165:05135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2015.03.011
Tran HV, Piro B, Reisberg S, Huy Nguyen L, Dung Nguyen T, Duc HT, Pham MC (2014) An electrochemical ELISA-like immunosensor for miRNAs detection based on screen-printed gold electrodes modified with reduced graphene oxide and carbon nanotubes. Biosensors and Bioelectronics 62:25–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2014.06.014
Vargas E, Torrente-Rodríguez RM, Ruiz-Valdepeñas Montiel V, Povedano E, Pedrero M, Montoya JJ, Campuzano S, Pingarrón JM (2017) Magnetic beads-based sensor with tailored sensitivity for rapid and single-step amperometric determination of miRNAs. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 18(11):2151
Torrente-Rodríguez RM, Montiel VCR-V, Campuzano S, Farchado-Dinia M, Barderas R, Segundo-Acosta PS, Montoya JJ, Pingarron JM (2016) Fast electrochemical miRNAs determination in cancer cells and tumor tissues with antibody-functionalized magnetic microcarriers. ACS Sensors 1(7):896–903
Tran HV, Piro B, Reisberg S, Duc HT, Pham MC (2013) Antibodies directed to RNA/DNA hybrids: an electrochemical immunosensor for MicroRNAs detection using graphene-composite electrodes. Analytical Chemistry 85(17):8469–8474. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac402154z
Wu H, Wang P, He H, Jin Y (2012) Controlled synthesis of porous Ag/Au bimetallic hollow nanoshells with tunable plasmonic and catalytic properties. Nano Research 5(2):135–144. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-012-0194-5
Eigler S, Enzelberger-Heim M, Grimm S, Hofmann P, Kroener W, Geworski A, Dotzer C, Röckert M, Xiao J, Papp C, Lytken O, Steinrück H-P, Müller P, Hirsch A (2013) Wet chemical synthesis of graphene. Adv Mater 25(26):3583–3587. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201300155
Panwar V, Chattree A, Pal K (2015) A new facile route for synthesizing of graphene oxide using mixture of sulfuric–nitric–phosphoric acids as intercalating agent. Physica E: Low-dimensional Systems and Nanostructures 73:235–241. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physe.2015.06.006
S. Arumugam and S. A. John, "Gold nanoparticles modified electrodes for biosensors," Nova Science Publishers, Inc., chapter 4, edition 1, pp. 1–32, 2009
Kalimuthu P, John SA (2008) Size dependent electrocatalytic activity of gold nanoparticles immobilized onto three dimensional sol–gel network. Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry 617(2):164–170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2008.02.012
Toh SY, Loh KS, Kamarudin SK, Daud WRW (2014) Graphene production via electrochemical reduction of graphene oxide: synthesis and characterisation. Chemical Engineering Journal 251:422–434. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2014.04.004
Li F, Han J, Jiang L, Wang Y, Li Y, Dong Y, Wei Q (2015) An ultrasensitive sandwich-type electrochemical immunosensor based on signal amplification strategy of gold nanoparticles functionalized magnetic multi-walled carbon nanotubes loaded with lead ions. Biosensors and Bioelectronics 68:626–632. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2015.01.049
Campuzano S, Torrente-Rodríguez RM, López-Hernández E, Conzuelo F, Granados R, Sánchez-Puelles JM, Pingarrón JM (2014) Magnetobiosensors based on viral protein p19 for microRNA determination in cancer cells and tissues. Angew Chem Int Ed 53(24):6168–6171
Salahandish R, Ghaffarinejad A, Omidinia E, Zargartalebi H, Majidzadeh-A K, Naghib SM, Sanati-Nezhad A (2018) Label-free ultrasensitive detection of breast cancer miRNA-21 biomarker employing electrochemical nano-genosensor based on sandwiched AgNPs in PANI and N-doped graphene. Biosensors and Bioelectronics 120:129–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2018.08.025
Zhu D, Liu W, Zhao D, Hao Q, Li J, Huang J, Shi J, Chao J, Su S, Wang L (2017) Label-free electrochemical sensing platform for MicroRNA-21 detection using thionine and gold nanoparticles co-functionalized MoS2 nanosheet. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces 9(41):35597–35603. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.7b11385
Chand R, Ramalingam S, Neethirajan S (2018) 2D transition-metal dichalcogenide MoS2 based novel nanocomposite and nanocarrier for multiplex miRNAs detection. Nanoscale 10:–8225. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8NR00697K
Tian R, Li Y, Bai J (2019) Hierarchical assembled nanomaterial paper based analytical devices for simultaneously electrochemical detection of microRNAs. Analytica Chimica Acta 1058:89–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2019.01.036
Wan Z, Umer M, Lobino M, Thiel D, Nguyen N-T, Trinchi A, Shiddiky MJA, Gao Y, Li Q (2020) Laser induced self-N-doped porous graphene as an electrochemical biosensor for femtomolar miRNA detection. Carbon 163:385–394. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2020.03.043
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Nanotechnology Center (NANOTEC), National Science and Technology Development Agency (NSTDA), Grant No. P1851652. TP would like to express her gratitude to the National Nanotechnology Center (NANOTEC) and the National Science and Technology Development Agency (NSTDA) for postdoctoral fellowship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
This paper is dedicated to the memory of the late Noppadol Aroonyadet.
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
ESM 1
(DOCX 3244 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pimalai, D., Putnin, T., Waiwinya, W. et al. Development of electrochemical biosensors for simultaneous multiplex detection of microRNA for breast cancer screening. Microchim Acta 188, 329 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-021-04995-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-021-04995-8