Abstract
Nucleic acid amplification tests (NAATs) are powerful tools for the Japanese encephalitis virus (JEV). We demonstrated highly sensitive, specific, and rapid detection of JEV by colorimetric reverse-transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification (cRT-LAMP). Under optimized conditions, the RT-LAMP assay results showed that the limit of detection was approximately equivalent to 1 RNA genome copy/μL with an assay time of 30 min. The assay was highly specific to JEV when tested with other mosquito-borne virus panels (Zika virus and dengue virus types 2–4). The ability to detect JEV directly from crude human sample matrices (serum and urine) demonstrated the suitability of our JEV RT-LAMP for widespread clinical application. The JEV RT-LAMP provides combination of rapid colorimetric determination of true-positive JEV RT-LAMP amplicons with our recently developed JEV-nanobarcodes, measured at absorbance wavelenght of 530 (A530) and 650 (A650), which have a limit of detection of 23.3 ng/μL. The AuNP:polyA10-JEV RT-LAMP nanobarcodes exhibited superior capability for stabilizing the true-positive JEV RT-LAMP amplicons against salt-induced AuNP aggregation, which improved the evaluation of true/false positive signals in the assay. These advances enable to expand the use of RT-LAMP for point-of-care tests, which will greatly bolster JEV clinical programs.
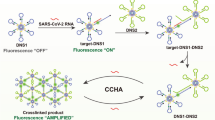
Graphical abstract

The JEV RT-LAMP nanobarcode assay targeting the envelope (E) gene and MgSO4 induced AuNP aggregation, indicated by an instant pink-to-violet colorimetric read-out.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ricklin ME, Garcia-Nicolas O, Brechbuhl D, Python S, Zumkehr B, Posthaus H, Oevermann A, Summerfield A (2016) Japanese encephalitis virus tropism in experimentally infected pigs. Vet Res 47:34. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13567-016-0319-z
Oliveira ARS, Cohnstaedt LW, Noronha LE, Mitzel D, McVey DS, Cernicchiaro N (2020) Perspectives regarding the risk of introduction of the Japanese encephalitis virus (JEV) in the United States. Front Vet Sci 7:48. https://doi.org/10.3389/fvets.2020.00048
Tajima S, Shibasaki KI, Taniguchi S, Nakayama E, Maeki T, Lim CK, Saijo M (2019) E and prM proteins of genotype V Japanese encephalitis virus are required for its increased virulence in mice. Heliyon 5:e02882. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e02882
Gao X, Liu H, Li X, Fu S, Cao L, Shao N, Zhang W, Wang Q, Lu Z, Lei W, He Y, Cao Y, Wang H, Liang G (2019) Changing geographic distribution of Japanese encephalitis virus genotypes, 1935-2017. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis 19:35–44. https://doi.org/10.1089/vbz.2018.2291
Hills SL, Walter EB, Atmar RL, Fischer M, Group AJEVW (2019) Japanese encephalitis vaccine: recommendations of the advisory committee on immunization practices. MMWR Recomm Rep 68:1–33. https://doi.org/10.15585/mmwr.rr6802a1
Misra UK, Kalita J (2010) Overview: Japanese encephalitis. Prog Neurobiol 91:108–120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pneurobio.2010.01.008
Ricklin ME, Garcia-Nicolas O, Brechbuhl D, Python S, Zumkehr B, Nougairede A, Charrel RN, Posthaus H, Oevermann A, Summerfield A (2016) Vector-free transmission and persistence of Japanese encephalitis virus in pigs. Nat Commun 7:10832. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms10832
Young CL, Lyons AC, Hsu WW, Vanlandingham DL, Park SL, Bilyeu AN, Ayers VB, Hettenbach SM, Zelenka AM, Cool KR, Peterson GJ, Higgs S, Huang YS (2020) Protection of swine by potent neutralizing anti-Japanese encephalitis virus monoclonal antibodies derived from vaccination. Antivir Res 174:104675. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.antiviral.2019.104675
Kumari R, Joshi PL (2012) A review of Japanese encephalitis in Uttar Pradesh, India. WHO South-East Asia J Public Health 1:374–395
Le Flohic G, Porphyre V, Barbazan P, Gonzalez JP (2013) Review of climate, landscape, and viral genetics as drivers of the Japanese encephalitis virus ecology. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 7:e2208. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pntd.0002208
Shao N, Li F, Nie K, Fu SH, Zhang WJ, He Y, Lei WW, Wang QY, Liang GD, Cao YX, Wang HY (2018) TaqMan real-time RT-PCR assay for detecting and differentiating Japanese encephalitis virus. Biomed Environ Sci 31:208–214. https://doi.org/10.3967/bes2018.026
Chanama S, Sukprasert W, Sa-ngasang A, An A, Sangkitporn S, Kurane I, Anantapreecha S (2005) Detection of Japanese encephalitis (JE) virus-specific IgM in cerebrospinal fluid and serum samples from JE patients. Jpn J Infect Dis 58:294–296
Cha GW, Cho JE, Ju YR, Hong YJ, Han MG, Lee WJ, Choi EY, Jeong YE (2014) Comparison of four serological tests for detecting antibodies to Japanese encephalitis virus after vaccination in children. Osong Public Health Res Perspect 5:286–291. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrp.2014.08.003
Zanoli LM, Spoto G (2013) Isothermal amplification methods for the detection of nucleic acids in microfluidic devices. Biosensors (Basel) 3:18–43. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios3010018
Yue S, Li Y, Qiao Z, Song W, Bi S (2021) Rolling circle replication for biosensing, bioimaging, and biomedicine. Trends Biotechnol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibtech.2021.02.007
Bi S, Yue S, Zhang S (2017) Hybridization chain reaction: a versatile molecular tool for biosensing, bioimaging, and biomedicine. Chem Soc Rev 46:4281–4298. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7cs00055c
Lee SH, Ahn G, Kim MS, Jeong OC, Lee JH, Kwon HG, Kim YH, Ahn JY (2018) Poly-adenine-coupled LAMP barcoding to detect apple scar skin viroid. ACS Comb Sci 20:472–481. https://doi.org/10.1021/acscombsci.8b00022
Gao J, Huang X, Liu H, Zan F, Ren J (2012) Colloidal stability of gold nanoparticles modified with thiol compounds: bioconjugation and application in cancer cell imaging. Langmuir 28:4464–4471. https://doi.org/10.1021/la204289k
Lu W, Wang L, Li J, Zhao Y, Zhou Z, Shi J, Zuo X, Pan D (2015) Quantitative investigation of the poly-adenine DNA dissociation from the surface of gold nanoparticles. Sci Rep 5:10158. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep10158
Pei H, Li F, Wan Y, Wei M, Liu H, Su Y, Chen N, Huang Q, Fan C (2012) Designed diblock oligonucleotide for the synthesis of spatially isolated and highly hybridizable functionalization of DNA-gold nanoparticle nanoconjugates. J Am Chem Soc 134:11876–11879. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja304118z
Liu J (2012) Adsorption of DNA onto gold nanoparticles and graphene oxide: surface science and applications. Phys Chem Chem Phys 14:10485–10496. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2cp41186e
Ahn SJ, Baek YH, Lloren KKS, Choi WS, Jeong JH, Antigua KJC, Kwon HI, Park SJ, Kim EH, Kim YI, Si YJ, Hong SB, Shin KS, Chun S, Choi YK, Song MS (2019) Rapid and simple colorimetric detection of multiple influenza viruses infecting humans using a reverse transcriptional loop-mediated isothermal amplification (RT-LAMP) diagnostic platform. BMC Infect Dis 19:676. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12879-019-4277-8
Lopez-Jimena B, Wehner S, Harold G, Bakheit M, Frischmann S, Bekaert M, Faye O, Sall AA, Weidmann M (2018) Development of a single-tube one-step RT-LAMP assay to detect the Chikungunya virus genome. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 12:e0006448. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pntd.0006448
Kaneko H, Kawana T, Fukushima E, Suzutani T (2007) Tolerance of loop-mediated isothermal amplification to a culture medium and biological substances. J Biochem Biophys Methods 70:499–501. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbbm.2006.08.008
Wan L, Chen T, Gao J, Dong C, Wong AH, Jia Y, Mak PI, Deng CX, Martins RP (2017) A digital microfluidic system for loop-mediated isothermal amplification and sequence specific pathogen detection. Sci Rep 7:14586. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-14698-x
Rasti R, Nanjebe D, Karlstrom J, Muchunguzi C, Mwanga-Amumpaire J, Gantelius J, Martensson A, Rivas L, Galban F, Reutersward P, Andersson Svahn H, Alvesson HM, Boum Y 2nd, Alfven T (2017) Health care workers' perceptions of point-of-care testing in a low-income country-a qualitative study in Southwestern Uganda. PLoS One 12:e0182005. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0182005
Niemz A, Ferguson TM, Boyle DS (2011) Point-of-care nucleic acid testing for infectious diseases. Trends Biotechnol 29:240–250. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibtech.2011.01.007
Notomi T, Okayama H, Masubuchi H, Yonekawa T, Watanabe K, Amino N, Hase T (2000) Loop-mediated isothermal amplification of DNA. Nucleic Acids Res 28:E63. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/28.12.e63
Huang W, Zhang H, Xu J, Wang S, Kong X, Ding W, Xu J, Feng J (2017) Loop-mediated isothermal amplification method for the rapid detection of Ralstonia solanacearum phylotype I mulberry strains in China. Front Plant Sci 8:76. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2017.00076
Li J, Hu X, Wang X, Yang J, Zhang L, Deng Q, Zhang X, Wang Z, Hou T, Li S (2021) A novel one-pot rapid diagnostic technology for COVID-19. Anal Chim Acta 1154:338310. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2021.338310
Wang Y, Li H, Wang Y, Zhang L, Xu J, Ye C (2017) Loop-mediated isothermal amplification label-based gold nanoparticles lateral flow biosensor for detection of Enterococcus faecalis and Staphylococcus aureus. Front Microbiol 8:192. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2017.00192
Teixeira A, Paris JL, Roumani F, Dieguez L, Prado M, Espina B, Abalde-Cela S, Garrido-Maestu A, Rodriguez-Lorenzo L (2020) Multifuntional gold nanoparticles for the SERS detection of pathogens combined with a LAMP-in-microdroplets approach. Materials (Basel):13. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13081934
Kong X, Qin W, Huang X, Kong F, Schoen CD, Feng J, Wang Z, Zhang H (2016) Development and application of loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) for detection of Plasmopara viticola. Sci Rep 6:28935. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep28935
Lee S, Kim JH, Han BK, Kim WI, Cho BK, Woo SM, Kim YH, Ahn JY (2020) Wax-printed well pads and colorimetric LAMP detection of ApxIA toxin gene. Mol Cell Toxicol 16:263–270
Teoh BT, Sam SS, Tan KK, Johari J, Danlami MB, Hooi PS, Md-Esa R, AbuBakar S (2013) Detection of dengue viruses using reverse transcription-loop-mediated isothermal amplification. BMC Infect Dis 13:387. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2334-13-387
Parida MM, Santhosh SR, Dash PK, Tripathi NK, Lakshmi V, Mamidi N, Shrivastva A, Gupta N, Saxena P, Babu JP, Rao PV, Morita K (2007) Rapid and real-time detection of Chikungunya virus by reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay. J Clin Microbiol 45:351–357. https://doi.org/10.1128/JCM.01734-06
Nunes MR, Vianez JL Jr, Nunes KN, da Silva SP, Lima CP, Guzman H, Martins LC, Carvalho VL, Tesh RB, Vasconcelos PF (2015) Analysis of a reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification (RT-LAMP) for yellow fever diagnostic. J Virol Methods 226:40–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jviromet.2015.10.003
Lamb LE, Bartolone SN, Tree MO, Conway MJ, Rossignol J, Smith CP, Chancellor MB (2018) Rapid detection of Zika virus in urine samples and infected mosquitos by reverse transcription-loop-mediated isothermal amplification. Sci Rep 8:3803. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-22102-5
Ganguli A, Mostafa A, Berger J, Aydin MY, Sun F, Ramirez SAS, Valera E, Cunningham BT, King WP, Bashir R (2020) Rapid isothermal amplification and portable detection system for SARS-CoV-2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 117:22727–22735. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2014739117
Ma YD, Li KH, Chen YH, Lee YM, Chou ST, Lai YY, Huang PC, Ma HP, Lee GB (2019) A sample-to-answer, portable platform for rapid detection of pathogens with a smartphone interface. Lab Chip 19:3804–3814. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9lc00797k
Huang SH, Yang TC, Tsai MH, Tsai IS, Lu HC, Chuang PH, Wan L, Lin YJ, Lai CH, Lin CW (2008) Gold nanoparticle-based RT-PCR and real-time quantitative RT-PCR assays for detection of Japanese encephalitis virus. Nanotechnology 19:405101. https://doi.org/10.1088/0957-4484/19/40/405101
Pantawane PB, Dhanze H, Ravi Kumar G, M RG, Dudhe NC, Bhilegaonkar KN (2019) TaqMan real-time RT-PCR assay for detecting Japanese encephalitis virus in swine blood samples and mosquitoes. Anim Biotechnol 30:267–272. https://doi.org/10.1080/10495398.2018.1481417
Wu X, Lin H, Chen S, Xiao L, Yang M, An W, Wang Y, Yao X, Yang Z (2017) Development and application of a reverse transcriptase droplet digital PCR (RT-ddPCR) for sensitive and rapid detection of Japanese encephalitis virus. J Virol Methods 248:166–171. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jviromet.2017.06.015
Liu H, Liu ZJ, Jing J, Ren JQ, Liu YY, Guo HH, Fan M, Lu HJ, Jin NY (2012) Reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification for rapid detection of Japanese encephalitis virus in swine and mosquitoes. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis 12:1042–1052. https://doi.org/10.1089/vbz.2012.0991
Acknowledgments
We thank Professor Yun Hee Baek for providing the DENV types 2–4 and Zika nucleic acid. We thank all the participants who worked in BSL-3 for their support in cultivating all the viruses. This work was supported by a National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korean government (MEST) (NRF-2019R1A2C1010860) and a Korea Institute of Planning and Evaluation for Technology in Food, Agriculture and Forestry (IPET) through Crop Viruses and Pests Response Industry Technology Development Program, funded by Ministry of Agriculture, Food and Rural Affairs (MAFRA) (321108-04).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Gna Ahn and Se Hee Lee performed the experiments and analyzed the data; Min-Suk Song and Beom-Ku Han contributed clinical materials/analysis tools; Yang-Hoon Kim and Ji-Young Ahn wrote the paper.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supporting information
ESM 1
(DOCX 1631 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ahn, G., Lee, S.H., Song, MS. et al. JEV-nanobarcode and colorimetric reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification (cRT-LAMP). Microchim Acta 188, 333 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-021-04986-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-021-04986-9