Abstract
A facile, economic, and portable test kit based on target-responsive hydrogel with smartphone detection was fabricated for the accurate determination of dichlorvos in tap water and food samples. Carbon dots (CDs) and CdTe quantum dots (QDs) embedded hydrogel were employed as indicator, and fluorescence of CdTe QDs (645 nm) was dynamically quenched by Cu2+ while that of CDs (490 nm) were non-response for Cu2+, em erging a typical ratiometric fluorescence signal. Acetylcholinesterase hydrolyzed acetylthiocholine to generate thiocholine that bound with Cu2+ strongly via S-Cu-S bond. Dichlorvos as competitive inhibitor for acetylcholinesterase prevented the generation of thiocholine, which blocked the formation of Cu-thiocholine complex and changed the ratiometric fluorescence signal. The signal of the test kit, which was recorded by smartphone’s camera, was transduced by ImageJ software into the color parameter that was linearly proportional to the logarithm of dichlorvos concentration. This portable test kit showed wide linear range of 1 to 40 ppb and low detection limit of 0.38 ppb for dichlorvos. This test kit exhibited rapid sample-to-answer detection time (50 min) of dichlorvos in tap water and food samples, and the recoveries were in the range 81.3 to 111% with relative standard deviations of less than 9.1%.
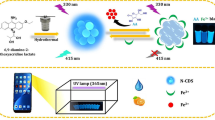
Graphical abstract

A facile and economic portable test kit based on CD-CdTe QD target-responsive hydrogel with smartphone was innovatively fabricated for the accurate determination of organophosphorus pesticides. This portable test kit showed low detection limit of 0.38 ppb for dichlorvos and rapid sample-to-answer detection time (50 min) in tap water and food samples, which offered a new sight for portable monitoring of environmental pollution and food safety.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Devi P, Saini S, Kim KH (2019) The advanced role of carbon quantum dots in nanomedical applications. Biosens Bioelectron 141:111158
Su W, Wu H, Xu HM, Zhang Y, Li YC, Li XH, Fan LZ (2020) Carbon dots: a booming material for biomedical applications. Mater Chem Front 4:821–836
Tong X, Shi SY, Tong CY, Iftikhar A, Long RQ, Zhu YF (2020) Quantum/carbon dots-based fluorescent assays for enzyme activity. TrAC-Trend Anal Chem 131:116008
Shi T, Fu HL, Tan LJ, Wang JT (2019) CdTe quantum dots coated with a molecularly imprinted polymer for fluorometric determination of norfloxacin in seawater. Microchim Acta 186:362
Yang L, Wen JX, Li KJ, Liu L, Wang W (2021) Carbon quantum dots: comprehensively understanding of the internal quenching mechanism and application for catechol detection. Sensors Actuators B Chem 333:129557
Han S, Yang L, Wen ZG, Chu SY, Wang M, Wang ZY, Jiang CL (2020) A dual-response ratiometric fluorescent sensor by europium-doped CdTe quantum dots for visual and colorimetric detection of tetracycline. J Hazard Mater 398:122894
Wang YH, Zhang C, Chen XC, Yang B, Yang L, Jiang CL, Zhang ZP (2016) Ratiometric fluorescent paper sensor utilizing hybrid carbon dots-quantum dots for the visual determination of copper ions. Nanoscale 8:5977–5984
Cao BM, Yuan C, Liu BH, Jiang CL, Guan GJ, Han MY (2013) Ratiometric fluorescence detection of mercuric ion based on the nanohybrid of fluorescence carbon dots and quantum dots. Anal Chim Acta 786:146–152
Castro RC, Soares JX, Ribeiro DSM, Santos JLM (2019) Dual-emission ratiometric probe combining carbon dots and CdTe quantum dots for fluorometric and visual determination of H2O2. Sensors Actuators B Chem 296:126665
Yan YH, Sun J, Zhang K, Zhu HJ, Yu H, Sun MT, Huang DJ, Wang SH (2015) Visualizing gaseous nitrogen dioxide by ratiometric fluorescence of carbon nanodots-quantum dots hybrid. Anal Chem 87:2087–2093
Liu XQ, Wang T, Lu Y, Wang WJ, Zhou ZP, Yan YS (2019) Constructing carbon dots and CdTe quantum dots multi-functional composites for ultrasensitive sensing and rapid degrading ciprofloxacin. Sensors Actuators B Chem 289:242–251
Xu X, He L, Long YW, Pan S, Liu H, Yang JD, Hu XL (2019) S-doped carbon dots capped ZnCdTe quantum dots for ratiometric fluorescence sensing of guanine. Sensors Actuators B Chem 279:44–52
Huang S, Yao JD, Chu X, Liu Y, Xiao Q, Zhang Y (2019) One-step facile synthesis of nitrogen-doped carbon dots: a ratiometric fluorescent probe for evaluation of acetylcholinesterase activity and detection of organophosphorus pesticides in tap water and food. J Agric Food Chem 67:11244–11255
Wu XL, Song Y, Yan X, Zhu CZ, Ma YQ, Du D, Lin YH (2017) Carbon quantum dots as fluorescence resonance energy transfer sensors for organophosphate pesticides determination. Biosens Bioelectron 94:292–297
Jin R, Kong DS, Yan X, Zhao X, Li HX, Liu FM, Sun P, Lin YH, Lu GY (2019) Integrating target-responsive hydrogels with smartphone for on-site ppb-level quantitation of organophosphate pesticides. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 11:27605–27614
Xu J, Hu XT, Khan H, Tian MM, Yang L (2019) Converting solution viscosity to distance-readout on paper substrates based on enzyme-mediated alginate hydrogelation: quantitative determination of organophosphorus pesticides. Anal Chim Acta 1071:1–7
Bala R, Sharma RK, Wangoo N (2016) Development of gold nanoparticles-based aptasensor for the colorimetric detection of organophosphorus pesticide phorate. Anal Bioanal Chem 408:333–338
Harshit D, Charmy K, Nrupesh P (2017) Organophosphorus pesticides determination by novel HPLC and spectrophotometric method. Food Chem 230:448–453
Tan MJ, Hong ZY, Chang MH, Liu CC, Cheng HF, Loh XJ, Chen CH, Liao CD, Kong KV (2017) Metal carbonyl-gold nanoparticle conjugates for highly sensitive SERS detection of organophosphorus pesticides. Biosens Bioelectron 96:167–172
Uniyal S, Sharma RK (2018) Technological advancement in electrochemical biosensor based detection of organophosphate pesticide chlorpyrifos in the environment: a review of status and prospects. Biosens Bioelectron 116:37–50
He L, Jiang ZW, Li W, Li CM, Huang CZ, Li YF (2018) In situ synthesis of gold nanoparticles/metal-organic gels hybrids with excellent peroxidase-like activity for sensitive chemiluminescence detection of organophosphorus pesticides. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 10:28868–28876
Chen HM, Zhang H, Yuan R, Chen SH (2017) Novel double-potential electrochemiluminescence ratiometric strategy in enzyme-based inhibition biosensing for sensitive detection of organophosphorus pesticides. Anal Chem 89:2823–2829
Chang JF, Li HY, Hou T, Li F (2016) Paper-based fluorescent sensor for rapid naked-eye detection of acetylcholinesterase activity and organophosphorus pesticides with high sensitivity and selectivity. Biosens Bioelectron 86:971–977
Yan X, Li HX, Hu TY, Su XG (2017) A novel fluorimetric sensing platform for highly sensitive detection of organophosphorus pesticides by using egg white-encapsulated gold nanoclusters. Biosens Bioelectron 91:232–237
Feng JY, Huang PC, Wu FY (2017) Gold-platinum bimetallic nanoclusters with enhanced peroxidase-like activity and their integrated agarose hydrogel-based sensing platform for the colorimetric analysis of glucose levels in serum. Analyst 142:4106–4115
Gogoi N, Barooah M, Majumdar G, Chowdhury D (2015) Carbon dots rooted agarose hydrogel hybrid platform for optical detection and separation of heavy metal ions. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7:3058–3067
Wang PY, Li HH, Hassan MM, Guo ZM, Zhang ZZ, Chen QS (2019) Fabricating an acetylcholinesterase modulated UCNPs-Cu2+ fluorescence biosensor for ultrasensitive detection of organophosphorus pesticides-diazinon in food. J Agric Food Chem 67:4071–4079
Jiang K, Sun S, Zhang L, Lu Y, Wu AG, Cai CZ, Lin HW (2015) Red, green, and blue luminescence by carbon dots: full-color emission tuning and multicolor cellular imaging. Angew Chem Int Ed 54:5360–5363
Qian J, Wang K, Wang CQ, Ren CC, Liu Q, Hao N, Wang K (2017) Ratiometric fluorescence nanosensor for selective and visual detection of cadmium ions using quencher displacement-induced fluorescence recovery of CdTe quantum dots-based hybrid probe. Sensors Actuators B Chem 241:1153–1160
Liu YH, Duan WX, Song W, Liu JJ, Ren CL, Wu J, Liu D, Chen HL (2017) Red emission B, N, S-co-doped carbon dots for colorimetric and fluorescent dual mode detection of Fe3+ ions in complex biological fluids and living cells. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9:12663–12672
Peng H, Li Y, Jiang CL, Luo CH, Qi RJ, Huang R, Duan CG, Travas-Sejdic J (2016) Tuning the properties of luminescent nitrogen-doped carbon dots by reaction precursors. Carbon 100:386–394
Hao LC, Shen Y, Chen XH, Yang XD, Du QQ, Bian Y, Chen L, Tang K, Zhang R, Zheng YD, Gu SL (2019) Different-sized CdTe QDs on the detection of Cu2+ ions: combining experimental investigation with first-principles verification. Microchem J 148:684–690
Wang AW, Fu L, Rao TK, Cai W, Yuen MF, Zhong JS (2015) Effect of metal ions on the quenching of photoluminescent CdTe QDs and their recovery. Opt Mater 42:548–552
Zhang SX, Xue SF, Deng JJ, Zhang M, Shi GY, Zhou TS (2016) Polyacrylic acid-coated cerium oxide nanoparticles: an oxidase mimic applied for colorimetric assay to organophosphorus pesticides. Biosens Bioelectron 85:457–463
Mehdipour M, Ansari M, Pournamdari M, Zeidabadinejad L, Kazemipour M (2018) Selective extraction of organophosphorous pesticides in plasma by magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers with the aid of computational design. Anal Methods 10:4136–4142
Pimsen R, Khumsri A, Wacharasindhu S, Tumcharern G, Sukwattanasinitt M (2014) Colorimetric detection of dichlorvos using polydiacetylene vesicles with acetylcholinesterase and cationic surfactants. Biosens Bioelectron 62:8–12
Sahub C, Tuntulani T, Nhujak T, Tomapatanaget B (2018) Effective biosensor based on graphene quantum dots via enzymatic reaction for directly photoluminescence detection of organophosphate pesticide. Sensors Actuators B Chem 258:88–97
Cui HF, Wu WW, Li MM, Song XJ, Lv YX, Zhang TT (2018) A highly stable acetylcholinesterase biosensor based on chitosan-TiO2-graphene nanocomposites for detection of organophosphate pesticides. Biosens Bioelectron 99:223–229
Huang N, Qin YF, Li M, Chen TX, Lu MJ, Zhao JJ (2019) A sensitive fluorescence assay of organophosphorus pesticides using acetylcholinesterase and copper-catalyzed click chemistry. Analyst 144:3436–3441
Funding
This work was financially supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (21763005, 21864006), Natural Science Foundation of Guangxi Province (2017GXNSFDA198034, 2017GXNSFFA198005, 2021GXNSFAA075015), Thousands of Young Teachers Training Program of Guangxi Province (guijiaoren[2018]18), and BAGUI Scholar Program of Guangxi Province of China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
ESM 1
(DOC 22858 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, S., Yao, J., Li, B. et al. Integrating target-responsive CD-CdTe QD-based ratiometric fluorescence hydrogel with smartphone for visual and on-site determination of dichlorvos. Microchim Acta 188, 318 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-021-04982-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-021-04982-z