Abstract
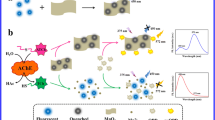
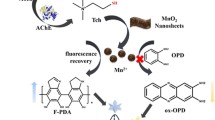
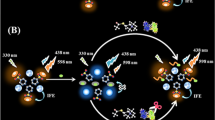
Butyrylcholinesterase (BChE) can modulate the expression level of cholinesterase, which emerges as an important clinical diagnose index. However, the currently reported assays for BChE are suffering from the problem of interferences. A ratiometric fluorescence assay was developed based on the MnO2 nanosheet (NS)–modulated fluorescence of sulfur quantum dots (S-dots) and o-phenylenediamine (OPD). MnO2 NS can not only quench the fluorescence of blue emissive S-dots, but also enhance the yellow emissive OPD by catalyzing its oxidation reactions. Upon introducing BChE and substrate into the system, their hydrolysate can reduce MnO2 into Mn2+, leading to the fluorescence recovery of S-dots and failure of OPD oxidation. BChE activity can be quantitatively detected by recording the change of fluorescence signals in the blue and yellow regions. A linear relationship is observed between the ratio of F435/F560 and the concentration of BChE in the range 30 to 500 U/L, and a limit of detection of 17.8 U/L has been calculated. The ratiometric fluorescence assay shows an excellent selectivity to acetylcholinesterase and tolerance to various other species. The method developed provides good detection performances in human serum medium and for screening of inhibitors.
Graphical abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen Y-C, Chou W-H, Fang C-P, Liu T-H, Tsou H-H, Wang Y et al (2019) Serum level and activity of butylcholinesterase: a biomarker for post-stroke dementia. J Clin Med 8:1778
Yang Y, Liu H, Chen Z, Wu T, Jiang Z, Tong L, Tang B (2019) A simple 3D-printed enzyme reactor paper spray mass spectrometry platform for detecting BuChE activity in human serum. Anal Chem 91:12874–12881
Williams A, Zhou S, Zhan C-G (2019) Discovery of potent and selective butyrylcholinesterase inhibitors through the use of pharmacophore-based screening. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 29:126754
Therkorn J, Drewry DG III, Tiburzi O, Astatke M, Young C, Rainwater-Lovett K (2020) Review of biomarkers and analytical methods for organophosphate pesticides and applicability to nerve agents. Mil Med 185:e414–ee21
Ellman GL, Courtney KD, Andres V, Featherstone RM (1961) A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochem Pharmacol 7:88–95
Liu D-M, Xu B, Dong C (2021) Recent advances in colorimetric strategies for acetylcholinesterase assay and their applications, TrAC. Trends Anal Chem 142:116320
Li Q, Wu J, Yang Q, Li H, Li F (2021) pH and redox dual-response disulfide bond-functionalized red-emitting gold nanoclusters for monitoring the contamination of organophosphorus pesticides in foods. Anal Chem 93:7362–7368
Nechaeva N, Prokopkina T, Makhaeva G, Rudakova E, Boltneva N, Dishovsky C, Eremenko A, Kurochkin I (2018) Quantitative butyrylcholinesterase activity detection by surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Sensors Actuators B Chem 259:75–82
Ding J, Qin W (2009) Potentiometric sensing of butyrylcholinesterase based on in situ generation and detection of substrates. Chem Commun:971–973
Chen G, Feng H, Jiang X, Xu J, Pan S, Qian Z (2018) Redox-controlled fluorescent nanoswitch based on reversible disulfide and its application in butyrylcholinesterase activity assay. Anal Chem 90:1643–1651
Zhang Q, Fu C, Guo X, Gao J, Zhang P, Ding C (2021) Fluorescent determination of butyrylcholinesterase activity and its application in biological imaging and pesticide residue detection. ACS Sens 6:1138–1146
Yoo S, Han MS (2019) A fluorescent probe for butyrylcholinesterase activity in human serum based on a fluorophore with specific binding affinity for human serum albumin. Chem Commun 55:14574–14577
Deng W, Chen P, Hu P, He Z, Zhang M, Yuan X, Huang K (2019) Enzymatic reaction modulated synthesis of quantum dots for visual detection of cholinesterase activity and inhibitor. Sensors Actuators B Chem 292:180–186
Zhang N, Si Y, Sun Z, Chen L, Li R, Qiao Y, Wang H (2014) Rapid, selective, and ultrasensitive fluorimetric analysis of mercury and copper levels in blood using bimetallic gold–silver nanoclusters with “silver effect”-enhanced red fluorescence. Anal Chem 86:11714–11721
Su D, Li H, Yan X, Lin Y, Lu G (2021) Biosensors based on fluorescence carbon nanomaterials for detection of pesticides. TrAC Trends Anal Chem 134:116126
Zhang Z, Shikha S, Liu J, Zhang J, Mei Q, Zhang Y (2019) Upconversion nanoprobes: recent advances in sensing applications. Anal Chem 91:548–568
Shen L, Wang H, Liu S, Bai Z, Zhang S, Zhang X, Zhang C (2018) Assembling of sulfur quantum dots in fission of sublimed sulfur. J Am Chem Soc 140:7878–7884
Wang Z, Zhang C, Wang H, Xiong Y, Yang X, Shi Y-e et al (2020) Two-step oxidation synthesis of sulfur with a red aggregation-induced emission. Angew Chem Int Ed 59:9997–10002
Song Y, Tan J, Wang G, Gao P, Lei J, Zhou L (2020) Oxygen accelerated scalable synthesis of highly fluorescent sulfur quantum dots. Chem Sci 11:772–777
Zhang Z-Y, Xu W-W, Xu W-S, Niu J, Sun X-H, Liu Y (2020) A synergistic enhancement strategy for realizing ultralong and efficient room-temperature phosphorescence. Angew Chem Int Ed 59:18748–18754
Pal A, Arshad F, Sk MP (2020) Emergence of sulfur quantum dots: unfolding their synthesis, properties, and applications. Adv Colloid Interf Sci 285:102274
Gao P, Wang G, Zhou L (2020) Luminescent sulfur quantum dots: synthesis, properties and potential applications. ChemPhotoChem 4:5235–5244
Chen J, Meng H, Tian Y, Yang R, Du D, Li Z et al (2019) Recent advances in functionalized MnO2 nanosheets for biosensing and biomedicine applications. Nanoscale Horiz 4:321–338
Wen J, Yang K, Sun S (2020) MnO2-based nanosystems for cancer therapy. Chem Commun 56:7065–7079
Yan X, Song Y, Zhu C, Li H, Du D, Su X et al (2018) MnO2 nanosheet-carbon dots sensing platform for sensitive detection of organophosphorus pesticides. Anal Chem 90:2618–2624
Ma Y, Zhang Y, Li X, Yang P, Yue J-Y, Jiang Y, Tang B (2020) Linker-eliminated nano metal–organic framework fluorescent probe for highly selective and sensitive phosphate ratiometric detection in water and body fluids. Anal Chem 92:3722–3727
Tan H, Wu X, Weng Y, Lu Y, Huang Z-Z (2020) Self-assembled FRET nanoprobe with metal–organic framework as a scaffold for ratiometric detection of hypochlorous acid. Anal Chem 92:3447–3454
Fan D, Shang C, Gu W, Wang E, Dong S (2017) Introducing ratiometric fluorescence to MnO2 nanosheet-based biosensing: a simple, label-free ratiometric fluorescent sensor programmed by cascade logic circuit for ultrasensitive GSH detection. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9:25870–25877
Wang S, Sun J, Zhao J, Lu S, Yang X (2018) Photo-induced electron transfer-based versatile platform with G-quadruplex/hemin complex as quencher for construction of DNA logic circuits. Anal Chem 90:3437–3442
Wang H, Wang Z, Xiong Y, Kershaw SV, Li T, Wang Y, Zhai Y, Rogach AL (2019) Hydrogen peroxide assisted synthesis of highly luminescent sulfur quantum dots. Angew Chem Int Ed 58:7040–7044
Kai K, Yoshida Y, Kageyama H, Saito G, Ishigaki T, Furukawa Y, Kawamata J (2008) Room-temperature synthesis of manganese oxide monosheets. J Am Chem Soc 130:15938–15943
Lei J, Huang Z, Gao P, Sun J, Zhou L (2021) Polyvinyl alcohol enhanced fluorescent sulfur quantum dots for highly sensitive detection of Fe3+ and temperature in cells. Part Part Syst Charact 38:2000332
Shen L, Wei J, Liu Z, Bai Z, Li Y, Zhang D, Zhang C (2020) Stable layered sulfur nanosheets prepared by one-step liquid-phase exfoliation of natural sublimed sulfur with bovine serum albumin for photocatalysis. Chem Mater 32:10476–10481
Anbarasu M, Anandan M, Chinnasamy E, Gopinath V, Balamurugan K (2015) Synthesis and characterization of polyethylene glycol (PEG) coated Fe3O4 nanoparticles by chemical co-precipitation method for biomedical applications. Spectrochim Acta, Part A 135:536–539
2006 Mechanisms and dynamics of fluorescence quenching, in: J.R. Lakowicz (Ed.) Principles of fluorescence spectroscopy, Springer US, Boston, pp. 331–51
Rajendiran N, Thulasidhasan J (2016) Spectroscopic, electrochemical and molecular docking studies of dothiepin and doxepin with bovine serum albumin and DNA base. Luminescence 31:1438–1447
Li W, Rong Y, Wang J, Li T, Wang Z (2020) MnO2 switch-bridged DNA walker for ultrasensitive sensing of cholinesterase activity and organophosphorus pesticides. Biosens Bioelectron 169:112605
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21804030), the Natural Science Foundation of Hebei Province (B2020201082, B2019201067), the Outstanding Youth Project of N\atural Science Foundation of Hebei Province (B2020201060), One Hundred Talent Project of Hebei Province (E2019050011), the Science and Technology Project of Hebei Education Department (BJ2020033), and the Natural Science Interdisciplinary Research Program of Hebei University (DXK201906).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
ESM 1
(DOCX 808 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, Z., Li, P., Jiao, M. et al. Ratiometric sensing of butyrylcholinesterase activity based on the MnO2 nanosheet–modulated fluorescence of sulfur quantum dots and o-phenylenediamine. Microchim Acta 188, 294 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-021-04949-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-021-04949-0