Abstract
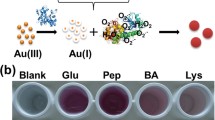
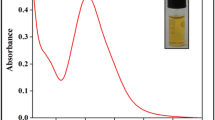
A gold nanoparticle (AuNP)–based sensing strategy based on rapid reduction of Au(I→0) is proposed. As a proof-of-concept study, the proposed sensing principle is designed for simultaneous and colorimetric detection and discrimination of multiple proteins. In the presence of H2O2, the target proteins could reduce Au(I) (i.e. HAuCl2) to AuNPs with different sizes, shapes and dispersion/aggregation states, thus resulting in rapidly colorimetric identification of different proteins. The optical response (i.e. color) of AuNPs is found to be characteristic of a given protein. The color response patterns are characteristic for each protein and can be quantitatively differentiated by statistical techniques. The sensor array is capable of discriminating proteins at concentrations as low as 0.1 μg/mL with high accuracy. A linear relationship was observed between the total Euclidean distances and protein concentration, providing the potential for protein quantification using this sensor array. The limit of detection (LOD) for catalase (Cat) is 0.08 μg/mL. The good linear range (from 0 to 8 μg/mL) has been used for the quantitative assay of Cat. To show a potentially practical application, this method was used to detect and discriminate proteins in human urine and tear samples.

We report a facile gold nanoparticle (AuNP)-based sensing strategy, that is, "a rapid reduction of Au(I) to Au(0) nanoparticles with different sizes and shapes by analytes that having certain reducing capabilities, resulting in different colours." The proposed sensing principle is designed for simultaneous, colorimetric detection and discrimination of multiple proteins.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wei X, Wang Y, Zhao Y, Chen Z (2017) Colorimetric sensor array for protein discrimination based on different DNA chain length-dependent gold nanoparticles aggregation. Biosens Bioelectron 97:332–337
Xi H, He W, Liu Q, Chen Z (2018) Protein discrimination using a colorimetric sensor array based on gold nanoparticle aggregation induced by cationic polymer. ACS Sustainable Chem Eng 6:10751–10757
Špringer T, Hemmerová E, Finocchiaro G, Krištofiková Z, Vyhnálek M, Homola J (2020) Surface plasmon resonance biosensor for the detection of tau-amyloid β complex. Sens Actuators B Chem 316:128146
Zhang C, Li L, Liu Q, Chen Z (2020) Colorimetric differentiation of multiple oxidizing anions based on two core–shell Au@Ag nanoparticles with different morphologies as array recognition elements. Anal Chem 92:7123–7129
Leng Y, Jiang K, Zhang W, Wang Y (2017) Synthesis of gold nanoparticles from Au(I) ions that shuttle to solidify: application on the sensor array design. Langmuir 33:6398–6403
Koç ÖK, Üzer A, Apak R (2020) A colorimetric probe based on 4-mercaptophenol and thioglycolic acid-functionalized gold nanoparticles for determination of phytic acid and Fe(III) ions. Microchim Acta 187:586
Abedalwafa MA, Tang Z, Qiao Y, Mei Q, Yang G, Li Y, Wang L (2020) An aptasensor strip-based colorimetric determination method for kanamycin using cellulose acetate nanofibers decorated DNA–gold nanoparticle bioconjugates. Microchim Acta 187:360
Jia F, Liu Q, Wei W, Chen Z (2019) Colorimetric sensor assay for discrimination of proteins based on exonuclease I-triggered aggregation of DNA-functionalized gold nanoparticles. Analyst 144:4865–4870
Xia F, Zuo X, Yang R, Xiao Y, Kang D, Vallée-Bélisle A, Gong X, Yuen JD, Hsu BBY, Heeger AJ, Plaxco KW (2010) Colorimetric detection of DNA, small molecules, proteins, and ions using unmodified gold nanoparticles and conjugated polyelectrolytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107:10837
Lee JI, Jang SC, Chung J, Choi WK, Hong C, Ahn GR, Kim SH, Lee BY, Chung WJ (2021) Colorimetric allergenic fungal spore detection using peptide-modified gold nanoparticles. Sens Actuators B Chem 327:128894
Mao J, Lu Y, Chang N, Yang J, Zhang S, Liu Y (2016) Multidimensional colorimetric sensor array for discrimination of proteins. Biosens Bioelectron 86:56–61
Mao J, Lu Y, Chang N, Yang J, Yang J, Zhang S, Liu Y (2016) A nanoplasmonic probe as a triple channel colorimetric sensor array for protein discrimination. Analyst 141:4014–4017
Lee PC, Meisel D (1982) Adsorption and surface-enhanced Raman of dyes on silver and gold sols. J Phys Chem 86:3391–3395
Tollefson EJ, Allen CR, Chong G, Zhang X, Rozanov ND, Bautista A, Cerda JJ, Pedersen JA, Murphy CJ, Carlson EE, Hernandez R (2019) Preferential binding of cytochrome c to anionic ligand-coated gold nanoparticles: a complementary computational and experimental approach. ACS Nano 13:6856–6866
Oliveira PFM, AAL M, Buzanich AG, Bienert R, Torresi RM, PHC C, Emmerling F (2020) Tandem X-ray absorption spectroscopy and scattering for in situ time-resolved monitoring of gold nanoparticle mechanosynthesis. Chem Commun 56:10329–10332
Johnson CJ, Dujardin E, Davis SA, Murphy CJ, Mann S (2002) Growth and form of gold nanorods prepared by seed-mediated, surfactant-directed synthesis. J Mater Chem 12:1765–1770
Weaver S, Taylor D, Gate W, Mills G (1996) Photoinitiated reversible formation of small gold crystallites in polymer gels. Langmuir 12:4618–4620
Nasaruddin RR, Chen T, Yao Q, Zang S, Xie J (2021) Toward greener synthesis of gold nanomaterials: from biological to biomimetic synthesis. Coord Chem Rev 426:213540
Johnson RA, Wichern DW (2007) Applied multivariate statistical analysis (ed: Hoag C), 6th edn. Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, pp 1–47. Ch. 1
Jolliffe IT (2002) Principal component analysis, 2nd edn. Springer, New York, pp 150–166. Ch. 7
Haswell SJ (1992) Practical guide to chemometrics (ed: Gemperline P), 2nd edn. New York, pp 453–467. Ch. 4
Kunkely H, Vogler A (1992) Photooxidation of AuCl2- and AuBr2- induced by ds excitation. Inorg Chem 31:4539–4541
Mie G (1908) Contributions to the optics of turbid media, particularly of colloidal metal solutions. Ann Phys 25:377–445
Schreiber A, Huber MC, Cölfen H, Schiller SM (2015) Molecular protein adaptor with genetically encoded interaction sites guiding the hierarchical assembly of plasmonically active nanoparticle architectures. Nat Commun 6:6705
Yoshida H, Kuwauchi Y, Jinschek JR, Sun K, Tanaka S, Kohyama M, Shimada S, Haruta M, Takeda S (2012) Visualizing gas molecules interacting with supported nanoparticulate catalysts at reaction conditions. Science 335:317–319
Yuan Z, Du Y, Tseng Y, Peng M, Cai N, He Y, Chang H, Yeung ES (2015) Fluorescent gold nanodots based sensor array for proteins discrimination. Anal Chem 87:4253–4259
King NP, Bale JB, Sheffler W, McNamara DE, Gonen S, Gonen T, Yeates TO, Baker D (2014) Accurate design of co-assembling multi-component protein nanomaterials. Nature 510:103–108
Rangnekar A, Sarma TK, Singh AK, Deka J, Ramesh A, Chattopadhyay A (2007) Retention of enzymatic activity of α-amylase in the reductive synthesis of gold nanoparticles. Langmuir 23:5700–5706
Yang T, Li Z, Wang L, Guo C, Sun Y (2007) Synthesis, characterization, and self-assembly of protein lysozyme monolayer-stabilized gold nanoparticles. Langmuir 23:10533–10538
Akhavan A, Kalhor HR, Kassaee MZ, Sheikh N, Hassanlou M (2010) Radiation synthesis and characterization of protein stabilized gold nanoparticles. Chem Eng J 159:230–235
Bartram ME, Koel BE (1989) The molecular adsorption of NO2 and the formation of N2O3 on Au (111). Surf Sci 213:137–156
Aroca R, Scraba M (1991) SERS and normal coordinate analysis of maleimide chemisorbed on colloidal silver. Spectrochim Acta A 47:263–269
Schmidbaur H, Dash KC (1973) Organogold chemistry. XIII. 1,8-Naphthyridine complexes of dimethylgold halides and pseudohalides. Simple case of fluxional behavior. J Am Chem Soc 95:4855–4860
Xu S, Lu X, Yao C, Huang F, Jiang H, Hua W, Na N, Liu H, Ouyang J (2014) A visual sensor array for pattern recognition analysis of proteins using novel blue-Emitting fluorescent gold nanoclusters. Anal Chem 86:11634–11639
Xu S, Li W, Zhao X, Wu T, Cui Y, Fan X, Wang W, Luo X (2019) Ultrahighly efficient and stable fluorescent gold nanoclusters coated with screened peptides of unique sequences for effective protein and serum discrimination. Anal Chem 91:13947–13952
Perez RL, Cong M, Vaughan SR, Ayala CE, Galpothdeniya WIS, Mathaga JK, Warner IM (2020) Protein discrimination using a fluorescence-based sensor array of thiacarbocyanine-GUMBOS. ACS Sens 5:2422–2429
Versura P, Nanni P, Bavelloni A, Blalock WL, Piazzi M, Roda A, Campos EC (2010) Tear proteomics in evaporative dry eye disease. Eye 24:1396–1402
Mcgill JI, Liakos GM, Goulding N, Seal DV (1984) Normal tear protein profiles and age-related changes. Brit J Ophthalmol 68:316–320
Funding
This work is supported by the Innovation Scientists and Technicians Troop Construction Projects of Henan Province(C20150029) and the Science Fund of Educational Department of Henan Province of China (21A140020).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(DOC 2371 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Leng, Y., Cheng, J., Liu, C. et al. A rapid reduction of Au(I→0) strategy for the colorimetric detection and discrimination of proteins. Microchim Acta 188, 249 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-021-04906-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-021-04906-x