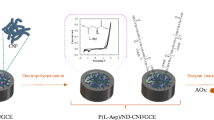
Abstract
Coral-like Ag-Mo2C/C-I and blocky Ag-Mo2C/C-II composites were obtained from one-step in situ calcination of [Ag(HL)3(Mo8O26)]n·nH2O [L: N-(pyridin-3-ylmethyl) pyridine-2-amine] under N2/H2 and N2 atmospheres, respectively. The coral-like morphology of Ag-Mo2C/C-I is composed of interwoven nanorods embedded with small particles, and the nano-aggregate of Ag-Mo2C/C-II is formed by cross-linkage of irregular nanoparticles. The above composites are decorated on glassy carbon electrode (GCE) drop by drop to generate two enzyme-free electrochemical sensors (Ag-Mo2C/C/GCE) for amperometric detection of H2O2. In particular, the coral-like Ag-Mo2C/C-I/GCE sensor possesses rapid response (1.2 s), high sensitivity (466.2 μA·mM−1·cm−2), and low detection limit (25 nM) towards trace H2O2 and has wide linear range (0.08 μM~4.67 mM) and good stability. All these sensing performances are superior to Ag-Mo2C/C-II/GCE, indicating that the calcining atmosphere has an important influence on microstructure and electrochemical properties. The excellent electrochemical H2O2 sensing performance of Ag-Mo2C/C-I/GCE sensor is mainly attributed to the synergism of unique microstructure, platinum-like electron structure of Mo2C, strong interaction between Mo and Ag, as well as the increased active sites and conductivity caused by co-doped Ag and carbon. Furthermore, this sensor has been successfully applied to the detection of H2O2 in human serum sample, contact lens solution, and commercial disinfector, demonstrating the potential in related fields of environment and biology.

Graphical abstract





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gray JT, Kang SW, Yang JI, Kruse N, McEwen JS, Park JC, Ha S (2021) Unravelling the reaction mechanism of gas-phase formic acid decomposition on highly dispersed Mo2C nanoparticles supported on graphene flakes. J Colloid Interface Sci 583:614–625. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2020.09.007
Wu SF, Chen MY, Wang WW, Zhou JB, Tang XR, Zhou DL, Liu C (2021) Molybdenum carbide nanoparticles assembling in diverse heteroatoms doped carbon matrix as efficient hydrogen evolution electrocatalysts in acidic and alkaline medium. Carbon 171:385–394. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2020.09.037
Zhang L, Zhang J (2018) Multiporous molybdenum carbide nanosphere as a new charming electrode material for highly sensitive simultaneous detection of guanine and adenine. Biosens Bioelectron 110:218–224. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2018.03.064
Feng SX, Li YG, Zhang RY, Li YC (2019) A novel electrochemical sensor based on molecularly imprinted polymer modified hollow N, S-Mo2C/C spheres for highly sensitive and selective carbendazim determination. Biosens Bioelectron 142:111491. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2019.111491
Yang S, Zhao JH, Tricard S, Yu LX, Fang J (2020) A sensitive and selective electrochemical sensor based on NP-doped molybdenum carbide@carbon/prussian blue/graphite felt composite electrode for the detection of dopamine. Anal Chim Acta 1094:80–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2019.09.077
Ren HL, Zhang Y, Liu LL, Li YG, Wang DY, Zhang RY, Zhang WJ, Li YC, Ye BC (2019) Synthesis of hollow Mo2C/carbon spheres, and their application to simultaneous electrochemical detection of hydroquinone, catechol, and resorcinol. Microchim Acta 186:306. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3432-7
Patella B, Buscetta M, Vincenzo SD, Ferraro M, Aiello G, Sunseri C, Pace E, Inguanta R, Cipollina C (2021) Electrochemical sensor based on rGO/Au nanoparticles for monitoring H2O2 released by human macrophages. Sensors Actuators B Chem 327:128901. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2020.128901
Mani V, Selvaraj S, Peng TK, Lin HY, Jeromiyas N, Ikeda H, Hayakawa Y, Ponnusamy S, Muthamizhchelvan C, Huang ST (2019) ZnCo2O4 nanoflowers grown on Co3O4 nanowire-decorated Cu foams for in situ profiling of H2O2 in live cells and biological media. ACS Appl Nano Mater 2:5049–5060. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsanm.9b00969
Hira SA, Nallal M, Rajendran K, Song S, Park S, Lee JM, Joo SH, Park KH (2020) Ultrasensitive detection of hydrogen peroxide and dopamine using copolymer-grafted metal-organic framework based electrochemical sensor. Anal Chim Acta 1118:26–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2020.04.043
Yang LZ, Xu CL, Ye WC, Liu WS (2015) An electrochemical sensor for H2O2 based on a new Co-metal-organicframework modified electrode. Sensors Actuators B Chem 215:489–496. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2015.03.104
Sun DP, Yang DC, Wei P, Liu B, Chen ZG, Zhang LY, Lu J (2020) One-step electrodeposition of silver nanostructures on 2D/3D metal-organic framework ZIF-67: comparison and application in electrochemical detection of hydrogen peroxide. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 12:41960–41968. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.0c11269
Liu BB, Wang XY, Zhai YY, Zhang ZL, Liu HQ, Li L, Wei HR (2020) Facile preparation of well conductive 2D MOF for nonenzymatic detection of hydrogen peroxide: relationship between electrocatalysis and metal center. J Electroanal Chem 858:113804. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2019.113804
Chen C, Xiong DK, Gu ML, Lu CX, Yi FY, Ma XH (2020) MOF-derived bimetallic CoFe-PBA composites as highly selective and sensitive electrochemical sensors for hydrogen peroxide and nonenzymatic glucose in human serum. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 12:35365–35374. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.0c09689
Li J, Tang C, Liang TT, Tang CY, Lv XH, Tang KL, Li CM (2020) Porous molybdenum carbide nanostructured catalyst toward highly sensitive biomimetic sensing of H2O2. Electroanalysis 32:1243–1250. https://doi.org/10.1002/elan.202000008
Li B, Liu LH, Song HY, Deng ZP, Huo LH, Gao S (2020) Carbon-doping mesoporous β-Mo2C aggregates for nanomolar electrochemical detection of hydrogen peroxide. ACS Appl Nano Mater 3:7499–7507. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsanm.0c01106
Wu CX, Li R, Wang YL, Lu S, Lin J, Liu YC, Zhang XT (2020) Strong metal-support interactions enable highly transparent Pt-Mo2C counter electrodes of bifacial dye-sensitized solar cells. Chem Commun 56:10046–10049. https://doi.org/10.1039/d0cc03744c
Jiang H, Xing ZP, Zhao TY, Yang ZK, Wang K, Li ZZ, Yang SL, Xie LY, Zhou W (2020) Plasmon Ag nanoparticle/Bi2S3 ultrathin nanobelt/oxygen-doped flower-like MoS2 nanosphere ternary heterojunctions for promoting charge separation and enhancing solar-driven photothermal and photocatalytic performances. Appl Catal, B 27:118947. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2020.118947
Li XM, Ma XL, Du X, Zheng JL, Hao XG, Abudula A, Guan GQ (2016) Silver-doped molybdenum carbide catalyst with high activity for electrochemical water splitting. Phys Chem Chem Phys 18:32780–32785. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6cp06307a
Zhang LN, Li SH, Tan HQ, Khan SU, Ma YY, Zang HY, Wang YH, Li YG (2017) MoP/Mo2C@C: a new combination of electrocatalysts for highly efficient hydrogen evolution over the entire pH range. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9:16270–16279. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.7b03823
Lou XH, Zhu CL, Pan H, Ma J, Zhu SM, Zhang D, Jiang XL (2016) Cost-effective three-dimensional graphene/Ag aerogel composite for high-performance sensing. Electrochim Acta 205:70–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2016.04.102
Yusoff N, Rameshkumar P, Mehmood MS, Pandikumar A, Lee HW, Huang NM (2017) Ternary nanohybrid of reduced graphene oxide-nafion@silver nanoparticles for boosting the sensor performance in non-enzymatic amperometric detection of hydrogen peroxide. Biosens Bioelectron 87:1020–1028. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2016.09.045
Zhang ZY, Deng ZP, Huo LH, Zhao H, Gao S (2013) Well-designed strategy to construct helical silver(I) coordination polymers from flexible unsymmetrical bis(pyridyl) ligands: syntheses, structures, and properties. Inorg Chem 52:5914–5923. https://doi.org/10.1021/ic400055t
Sheng ZM, Gan ZZ, Huang H, Niu RL, Han ZW, Jia RP (2020) M-Nx (M = Fe, Co, Ni, Cu) doped graphitic nanocages with high specific surface area for non-enzymatic electrochemical detection of H2O2. Sensors Actuators B Chem 305:127550. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2019.127550
Vu A, Qian YQ, Stein A (2012) Porous electrode materials for lithium-ion batteries-how to prepare them and what makes them special. Adv Energy Mater 2:1056–1085. https://doi.org/10.1002/aenm.201200320
Asif M, Aziz A, Wang HT, Wang ZY, Wang W, Ajmal M, Xiao F, Chen XD, Liu HF (2019) Superlattice stacking by hybridizing layered double hydroxide nanosheets with layers of reduced graphene oxide for electrochemical simultaneous determination of dopamine, uric acid and ascorbic acid. Microchim Acta 186:61–71. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-3158-y
Song HY, Zhao H, Zhang XF, Xu YM, Cheng XL, Gao S, Huo LH (2019) A hollow urchin-like α-MnO2 as an electrochemical sensor for hydrogen peroxide and dopamine with high selectivity and sensitivity. Microchim Acta 186:210–221. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3316-x
Peng C, Zhou SY, Zhang XM, Zeng TQ, Zhang W, Li HM, Liu XY, Zhao P (2018) One pot synthesis of nitrogen-oped hollow carbon spheres with improved electrocatalytic properties for sensitive H2O2 sensing in human serum. Sensors Actuators B Chem 270:530–537. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2018.05.036
Asif M, Wang HT, Dong S, Aziz A, Zhang GA, Xiao F, Liu HF (2017) Metal oxide intercalated layered double hydroxide nanosphere: with enhanced electrocatalyic activity towards H2O2 for biological applications. Sensors Actuators B Chem 239:243–252. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2016.08.010
Li JH, Jiang JB, Xu ZF, Liu MQ, Tang SP, Yang CM, Qian D (2018) Facile synthesis of Ag@Cu2O heterogeneous nanocrystals decorated N-doped reduced graphene oxide with enhanced electrocatalytic activity for ultrasensitive detection of H2O2. Sensors Actuators B Chem 260:529–540. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2018.01.068
Shu YJ, Zhang WB, Cai HH, Yang Y, Yu X, Gao QS (2019) Expanding the interlayers of molybdenum disulfide toward the highly sensitive sensing of hydrogen peroxide. Nanoscale 11:6644–6653. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9nr00333a
Jahanbakhshi M, Habibi B (2016) A novel and facile synthesis of carbon quantum dots via salep hydrothermal treatment as the silver nanoparticles support: application to electroanalytical determination of H2O2 in fetal bovine serum. Biosens Bioelectron 81:143–150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2016.02.064
Funding
This work is financially supported by the Basic Research Business Fees of Colleges and Universities in Heilongjiang Province (Grant No. 2018-KYYWF-1292, 2019-KYYWF-0456, 2020-KYYWF-0863).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(DOCX 35013 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, B., Wang, XT., Liu, LH. et al. Bimetallic MOFs-derived coral-like Ag-Mo2C/C interwoven nanorods for amperometric detection of hydrogen peroxide. Microchim Acta 188, 234 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-021-04888-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-021-04888-w