Abstract
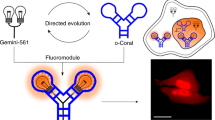
A novel nanoparticle-based fluorescence probe was developed for NF-κB transcription factor detection and in situ imaging via steric hindrance. The probe contains gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) to quench fluorescence, and nucleic acids immobilized on the surface of AuNPs to output fluorescence. In the basal state, Cy5 labeled DNA1 folds its long chain into a hairpin structure and quenches fluorescence by forcing the Cy5 fluorophore close to the surface of AuNPs. After the probe enters the cell, the NF-κB transcription factor can bind to the κB site in the DNA duplex of the nucleic acids. The steric hindrance caused by NF-κB leads to the extension of the long chain of DNA1 and the removal of the Cy5 fluorophore from the surface of AuNPs, thereby restoring the fluorescence of the probe. By measuring NF-κB in cell lysis in vitro, the probe obtains a detection limit of 0.38 nM and the linear range from 0.5 to 16 nM. Repeated measurements showed the recovery in the cell nuclear extract was between 93.38 and 109.32%, with relative standard deviation less than 5%. By monitoring the sub-localization of the Cy5 fluorophore in single cell, the probe system can effectively distinguish active NF-κB (nucleus) and inactive NF-κB (cytoplasm) through in situ imaging. The well-designed probe will make up for the shortcomings of the existing technology, and reveal the regulatory role of transcription factors in many disease processes.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adcock IM, Caramori G (2009) Transcription factors. In: Barnes PJ, Drazen JM, Rennard SI and Thomson NC (eds) Asthma and COPD (second edition), Chapter 31
Yusuf D, Butland SL, Swanson MI, Bolotin E, Ticoll A, Cheung WA, Zhang XYC (2012) The transcription factor encyclopedia. Genome Biol 13:R24
Fan Z, Wang J, Hao N, Li Y, Yin Y, Wang Z, Ding Y, Zhao J, Zhang K, Huang W (2019) Ultrasensitive detection of transcription factors with a highly-efficient diaminoterephthalate fluorophore via an electrogenerated chemiluminescence strategy. Chem Commun 55:11892–11895. https://doi.org/10.1039/C9CC05692K
Li B, Xia A, Zhang S, Suo T, Ma Y, Huang H, Zhang X, Chen Y, Zhou X (2021) A CRISPR-derived biosensor for the sensitive detection of transcription factors based on the target-induced inhibition of Cas12a activation. Biosens Bioelectron 173:112619. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2020.112619
Tong L, Yuan Y, Wu S (2015) Therapeutic microRNAs targeting the NF-kappa B signaling circuits of cancers. Adv Drug Del Rev 81:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addr.2014.09.004
Guerrini L, Blasi F, Denis-Donini S (1995) Synaptic activation of NF-kappa B by glutamate in cerebellar granule neurons in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 92:9077–9081. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.92.20.9077
Lin YC, Brown K, Siebenlist U (1995) Activation of NF-kappa B requires proteolysis of the inhibitor I kappa B-alpha: signal-induced phosphorylation of I kappa B-alpha alone does not release active NF-kappa B. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 92:552–556. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.92.2.552
Li J-W, Zhang X-Y, Wu H, Ba Y-P (2020) Transcription factor engineering for high-throughput strain evolution and organic acid bioproduction: a review. Front Bioeng Biotech 8:98. https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2020.00098
Zhang K, Fan Z, Huang Y, Xie M, Zhao J, Wang J (2020) A well-designed gold nanoparticle based fluorescence probe for assay Argonaute2 and Let-7a interaction in living cells. Sensor Actuat B: Chem 312:128000. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2020.128000
Mieszawska AJ, Mulder WJM, Fayad ZA, Cormode DP (2013) Multifunctional gold nanoparticles for diagnosis and therapy of disease. Mol Pharm 10:831–847. https://doi.org/10.1021/mp3005885
Singh P, Pandit S, Mokkapati VRSS, Garg A, Ravikumar V, Mijakovic I (2018) Gold nanoparticles in diagnostics and therapeutics for human cancer. Int J Mol Sci 19:1979. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19071979
Smith JE, Chávez JL, Hagen JA, Kelley-Loughnane N (2016) Design and development of aptamer–gold nanoparticle based colorimetric assays for in-the-field applications. J Vis Exp 112:54063. https://doi.org/10.3791/54063
Chen GH, Chen WY, Yen YC, Wang CW, Chang HT, Chen CF (2014) Detection of mercury(II) ions using colorimetric gold nanoparticles on paper-based analytical devices. Anal Chem 86:6843–6849. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac5008688
Chang CC, Chen CP, Wu TH, Yang CH, Lin CW, Chen CY (2019) Gold nanoparticle-based colorimetric strategies for chemical and biological sensing applications. Nanomaterials (Basel) 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9060861
Elghanian R, Storhoff JJ, Mucic RC, Letsinger RL, Mirkin CA (1997) Selective colorimetric detection of polynucleotides based on the distance-dependent optical properties of gold nanoparticles. Science 277:1078–1081. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.277.5329.1078
Iglesias MS, Grzelczak M (2020) Using gold nanoparticles to detect single-nucleotide polymorphisms: toward liquid biopsy. Beilstein J Nanotech 11:263–284. https://doi.org/10.3762/bjnano.11.20
Kohout C, Santi C, Polito L (2018) Anisotropic gold nanoparticles in biomedical applications. Int J Mol Sci 19:3385. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19113385
Saha A, Basiruddin SK, Sarkar R, Pradhan N, Jana NR (2009) Functionalized plasmonic−fluorescent nanoparticles for imaging and detection. J Phys Chem C 113:18492–18498. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp904791h
Bai X, Wang Y, Song Z, Feng Y, Chen Y, Zhang D, Feng L (2020) The basic properties of gold nanoparticles and their applications in tumor diagnosis and treatment. Int J Mol Sci 21:2480. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21072480
Hu X, Zhang Y, Ding T, Liu J, Zhao H (2020) Multifunctional gold nanoparticles: a novel nanomaterial for various medical applications and biological activities. Front Bioeng Biotech 8:990–990. https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2020.00990
Dykman LA, Khlebtsov NG (2019) Gold nanoparticles in chemo-, immuno-, and combined therapy: review [invited]. Biomedical Optics Express 10:3152–3182. https://doi.org/10.1364/BOE.10.003152
Lévy R, Shaheen U, Cesbron Y, Sée V (2010) Gold nanoparticles delivery in mammalian live cells: a critical review. Nano Rev 1. https://doi.org/10.3402/nano.v1i0.4889
Frens G (1973) Controlled nucleation for the regulation of the particle size in monodisperse gold suspensions. Nat Phys Sci 241:20–22. https://doi.org/10.1038/physci241020a0
Hinman SS, McKeating KS, Cheng Q (2017) DNA linkers and diluents for ultrastable gold nanoparticle bioconjugates in multiplexed assay development. Anal Chem 89:4272–4279. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.7b00341
Storhoff J, Elghanian R, Mucic R, Mirkin C, Letsinger R (1998) One-pot colorimetric differentiation of polynucleotides with single base imperfections using gold nanoparticle probes. J Am Chem Soc 120:1959–1964. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja972332i
Dam DHM, Lee RC, Odom TW (2014) Improved in vitro efficacy of gold nanoconstructs by increased loading of G-quadruplex aptamer. Nano Lett 14:2843–2848. https://doi.org/10.1021/nl500844m
Wu G-R, Mu T-C, Gao Z-X, Wang J, Sy M-S, Li C-Y (2017) Prion protein is required for tumor necrosis factor α (TNFα)-triggered nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) signaling and cytokine production. J Biol Chem 292:18747–18759. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M117.787283
Hayden MS, Ghosh S (2014) Regulation of NF-κB by TNF family cytokines. Semin Immunol 26:253–266. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.smim.2014.05.004
Li X, Yang J, Yuan R, Xiang Y (2019) Programming cascaded recycling amplifications for highly sensitive and label-free electrochemical sensing of transcription factors in tumor cells. Biosens Bioelectron 142:111574. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2019.111574
Rasheed PA, Lee J-S (2018) Ultrasensitive colorimetric detection of NF-κB protein at picomolar levels using target-induced passivation of nanoparticles. Anal Bioanal Chem 410:1397–1403. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-017-0783-y
Zou M, Li X, Li D, Yuan R, Xiang Y (2019) Target-induced steric hindrance protection of DNAzyme junctions for completely enzyme-free and amplified sensing of transcription factors. Sensor Actuat B: Chem 298:126865. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2019.126865
Li B, Chen Y, Wang J, Lu Q, Zhu W, Luo J, Hong J, Zhou X (2019) Detecting transcription factors with allosteric DNA-silver nanocluster switches. Anal Chim Acta 1048:168–177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2018.10.023
Li B, Xu L, Chen Y, Zhu W, Shen X, Zhu C, Luo J, Li X, Hong J, Zhou X (2017) Sensitive and label-free fluorescent detection of transcription factors based on DNA-Ag nanoclusters molecular beacons and exonuclease III-assisted signal amplification. Anal Chem 89:7316–7323. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.7b00055
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 81702993 and 21705061), Jiangsu Provincial Key Medical Discipline (Laboratory) (ZDXKA2016017), and Innovation Capacity Development Plan of Jiangsu Province (BM2018023).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Nanomaterials for biomedical imaging and targeting
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(DOCX 2738 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ding, Y., Fan, Z., Yao, B. et al. Nanoparticle-based fluorescence probe for detection of NF-κB transcription factor in single cell via steric hindrance. Microchim Acta 188, 226 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-021-04878-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-021-04878-y