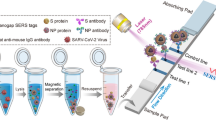
Abstract
A portable surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS)–lateral flow immunoassay (LFIA) detector has been developed for the automatic and highly sensitive detection of West Nile virus (WNV) non-structural protein 1 (NS1) and actual WNV samples. Au@Ag nanoparticles (Au@Ag NPs) labeled with double-layer Raman molecules were used as SERS tags to prepare WNV-specific SERS–LFIA strips. On this platform, the WNV-specific antigen NS1 protein was quantitatively and sensitively detected. The detection limit for the WNV NS1 protein was 0.1 ng/mL, which was 100-fold more sensitive than visual signals. The detection limit for inactivated WNV virions was 0.2 × 102 copies/μL. The sensitivity of the SERS–LFIA detector was comparable to that of the fluorescence quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction assay. The prepared SERS–LFIA strips exhibited high sensitivity and good specificity for WNV. Thus, the strips developed herein have clinical application value. Moreover, the portable SERS–LFIA detector enabled automatic and rapid detection of the SERS–LFIA strips. The platform established herein is expected to make a substantial contribution to the diagnosis and control of outbreaks of emerging infectious diseases, including WNV.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cui F, Zhou HS (2020) Diagnostic methods and potential portable biosensors for coronavirus disease 2019. Biosens Bioelectron 165:112349. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2020.112349
Priyadarsini SL, Suresh M, Huisingh D (2020) What can we learn from previous pandemics to reduce the frequency of emerging infectious diseases like COVID-19? Glob Transit 2:202–220. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.glt.2020.09.003
Kraemer MUG, Golding N, Bisanzio D, Bhatt S, Pigott DM, Ray SE, Brady OJ, Brownstein JS, Faria NR, Cummings DAT (2019) Utilizing general human movement models to predict the spread of emerging infectious diseases in resource poor settings. Sci Rep 9(1):5151. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-41192-3
Boga JA, Alvarez-Arguelles ME, Rojo-Alba S, Rodriguez M, de Ona M, Melon S (2019) Simultaneous detection of dengue virus, Chikungunya virus, Zika virus, yellow fever virus and West Nile virus. J Virol Methods 268:53–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jviromet.2019.03.014
Duan D, Fan K, Zhang D, Tan S, Liang M, Liu Y, Zhang J, Zhang P, Liu W, Qiu X, Kobinger GP, Fu Gao G, Yan X (2015) Nanozyme-strip for rapid local diagnosis of Ebola. Biosens Bioelectron 74:134–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2015.05.025
Lee S, Mehta S, Erickson D (2016) Two-color lateral flow assay for multiplex detection of causative agents behind acute febrile illnesses. Anal Chem 88(17):8359–8363. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.6b01828
Rong Z, Wang Q, Sun N, Jia X, Wang K, Xiao R, Wang S (2019) Smartphone-based fluorescent lateral flow immunoassay platform for highly sensitive point-of-care detection of Zika virus nonstructural protein 1. Anal Chim Acta 1055:140–147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2018.12.043
Aberle SW, Kolodziejek J, Jungbauer C, Stiasny K, Aberle JH, Zoufaly A, Hourfar MK, Weidner L, Nowotny N (2018) Increase in human West Nile and Usutu virus infections, Austria, 2018. Eurosurveillance 23(43). https://doi.org/10.2807/1560-7917
Kaiser JA, Barrett ADT (2019) Twenty years of progress toward West Nile virus vaccine development. Viruses 11(9). https://doi.org/10.3390/v11090823
Napp S, Petric D, Busquets N (2018) West Nile virus and other mosquito-borne viruses present in Eastern Europe. Pathog Glob Health 112(5):233–248. https://doi.org/10.1080/20477724.2018.1483567
Ziegler U, Luhken R, Keller M, Cadar D, van der Grinten E, Michel F, Albrecht K, Eiden M, Rinder M, Lachmann L, Hoper D, Vina-Rodriguez A, Gaede W, Pohl A, Schmidt-Chanasit J, Groschup MH (2019) West Nile virus epizootic in Germany, 2018. Antivir Res 162:39–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.antiviral.2018.12.005
Bolfa P, Jeon I, Loftis A, Leslie T, Marchi S, Sithole F, Beck C, Lecollinet S, Zientara S, Hans A, Issel CJ (2017) Detection of West Nile virus and other common equine viruses in three locations from the Leeward Islands, West Indies. Acta Trop 174:24–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actatropica.2017.06.023
David S, Abraham AM (2016) Epidemiological and clinical aspects on West Nile virus, a globally emerging pathogen. Infect Dis (Lond) 48(8):571–586. https://doi.org/10.3109/23744235.2016.1164890
Gorchakov R, Gulas-Wroblewski BE, Ronca SE, Ruff JC, Nolan MS, Berry R, Alvarado RE, Gunter SM, Murray KO (2019) Optimizing PCR detection of West Nile virus from body fluid specimens to delineate natural history in an infected human cohort. Int J Mol Sci 20(8). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20081934
Cao L, Fu S, Lu Z, Tang C, Gao X, Li X, Lei W, He Y, Li M, Cao Y, Wang H, Liang G (2019) Detection of West Nile virus infection in viral encephalitis cases, China. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis 19(1):45–50. https://doi.org/10.1089/vbz.2018.2275
Busquets N, Laranjo-Gonzalez M, Soler M, Nicolas O, Rivas R, Talavera S, Villalba R, San Miguel E, Torner N, Aranda C, Napp S (2019) Detection of West Nile virus lineage 2 in north-eastern Spain (Catalonia). Transbound Emerg Dis 66(2):617–621. https://doi.org/10.1111/tbed.13086
He Y, Su S, Xu T, Zhong Y, Zapien JA, Li J, Fan C, Lee S-T (2011) Silicon nanowires-based highly-efficient SERS-active platform for ultrasensitive DNA detection. Nano Today 6(2):122–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nantod.2011.02.004
Gao R, Cheng Z, deMello AJ, Choo J (2016). Lab Chip 16(6):1022–1029. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5lc01249j
Gracie K, Correa E, Mabbott S, Dougan JA, Graham D, Goodacre R, Faulds K (2014) Simultaneous detection and quantification of three bacterial meningitis pathogens by SERS. Chem Sci 5(3):1030–1040. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3sc52875h
Kang JW, So PTC, Dasari RR, Lim DK (2015) High resolution live cell Raman imaging using subcellular organelle-targeting SERS-sensitive gold nanoparticles with highly narrow intra-Nanogap. Nano Lett 15(3):1766–1772. https://doi.org/10.1021/nl504444w
Ko J, Lee C, Choo J (2015) Highly sensitive SERS-based immunoassay of aflatoxin B1 using silica-encapsulated hollow gold nanoparticles. J Hazard Mater 285:11–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2014.11.018
Liu K, Bai Y, Zhang L, Yang Z, Fan Q, Zheng H, Yin Y, Gao C (2016) Porous au-Ag Nanospheres with high-density and highly accessible hotspots for SERS analysis. Nano Lett 16(6):3675–3681. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.nanolett.6b00868
Zhou W, Gao X, Liu D, Chen X (2015) Gold nanoparticles for in vitro diagnostics. Chem Rev 115(19):10575–10636. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrev.5b00100
Zhang X, Du X (2016) Carbon Nanodot-decorated Ag@SiO2 nanoparticles for fluorescence and surface-enhanced Raman scattering immunoassays. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8(1):1033–1040. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.5b11446
Pang Y, Wang C, Wang J, Sun Z, Xiao R, Wang S (2016) Fe3O4@Ag magnetic nanoparticles for microRNA capture and duplex-specific nuclease signal amplification based SERS detection in cancer cells. Biosens Bioelectron 79:574–580. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2015.12.052
Ye H, Liu Y, Zhan L, Liu Y, Qin Z (2020) Signal amplification and quantification on lateral flow assays by laser excitation of plasmonic nanomaterials. Theranostics 10(10):4359–4373. https://doi.org/10.7150/thno.44298
Ngo HT, Gandra N, Fales AM, Taylor SM, Vo-Dinh T (2016) Sensitive DNA detection and SNP discrimination using ultrabright SERS nanorattles and magnetic beads for malaria diagnostics. Biosens Bioelectron 81:8–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2016.01.073
Wang J, Zhang L, Huang Y, Dandapat A, Dai L, Zhang G, Lu X, Zhang J, Lai W, Chen T (2017) Hollow Au-Ag nanoparticles labeled Immunochromatography strip for highly sensitive detection of clenbuterol. Sci Rep 7:41419. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep41419
Eryilmaz M, Acar Soykut E, Cetin D, Boyaci IH, Suludere Z, Tamer U (2019) SERS-based rapid assay for sensitive detection of group A Streptococcus by evaluation of the swab sampling technique. Analyst 144(11):3573–3580. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9an00173e
Gao X, Zheng P, Kasani S, Wu S, Yang F, Lewis S, Nayeem S, Engler-Chiurazzi EB, Wigginton JG, Simpkins JW, Wu N (2017) Paper-based surface-enhanced Raman scattering lateral flow strip for detection of neuron-specific enolase in blood plasma. Anal Chem 89(18):10104–10110. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.7b03015
Stambach NR, Carr SA, Cox CR, Voorhees KJ (2015) Rapid detection of Listeria by bacteriophage amplification and SERS-lateral flow immunochromatography. Viruses 7(12):6631–6641. https://doi.org/10.3390/v7122962
Tran V, Walkenfort B, Konig M, Salehi M, Schlucker S (2019) Rapid, quantitative, and ultrasensitive point-of-care testing: a portable SERS reader for lateral flow assays in clinical chemistry. Angew Chem Int Ed 58(2):442–446. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201810917
Zhang D, Huang L, Liu B, Ge Q, Dong J, Zhao X (2019) Rapid and ultrasensitive quantification of multiplex respiratory tract infection pathogen via lateral flow microarray based on SERS Nanotags. Theranostics 9(17):4849–4859. https://doi.org/10.7150/thno.35824
Wang R, Kim K, Choi N, Wang X, Lee J, Jeon JH, G-e R, Choo J (2018) Highly sensitive detection of high-risk bacterial pathogens using SERS-based lateral flow assay strips. Sensors Actuators B 270:72–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2018.04.162
Sánchez-Purrà M, Roig-Solvas B, Versiani A, Rodriguez-Quijada C, de Puig H, Bosch I, Gehrke L, Hamad-Schifferli K (2017) Design of SERS nanotags for multiplexed lateral flow immunoassays. Mol Syst Des Eng 2(4):401–409. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7me00052a
Fu X, Cheng Z, Yu J, Choo P, Chen L, Choo J (2016) A SERS-based lateral flow assay biosensor for highly sensitive detection of HIV-1 DNA. Biosens Bioelectron 78:530–537. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2015.11.099
Xiao R, Lu L, Rong Z, Wang C, Peng Y, Wang F, Wang J, Sun M, Dong J, Wang D, Wang L, Sun N, Wang S (2020) Portable and multiplexed lateral flow immunoassay reader based on SERS for highly sensitive point-of-care testing. Biosens Bioelectron 168:112524. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2020.112524
Jia X, Wang C, Rong Z, Li J, Wang K, Qie Z, Xiao R, Wang S (2018) Dual dye-loaded Au@Ag coupled to a lateral flow immunoassay for the accurate and sensitive detection of mycoplasma pneumoniae infection. RSC Adv 8(38):21243–21251. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8ra03323d
Ding XX, Li XF, Deng YQ, Guo YH, Hao W, Che XY, Qin CF, Fu N (2014) Development of a double antibody sandwich ELISA for West Nile virus detection using monoclonal antibodies against non-structural protein 1. PLoS One 9(10):e108623. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0108623
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
ESM 1
(DOCX 6315 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jia, X., Liu, Z., Peng, Y. et al. Automatic and sensitive detection of West Nile virus non-structural protein 1 with a portable SERS–LFIA detector. Microchim Acta 188, 206 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-021-04857-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-021-04857-3