Abstract
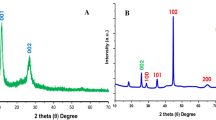
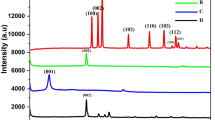
A sensitive voltammetric sensor has been developed for hazardous methyl parathion detection (MP) using graphene oxide@Ce-doped TiO2 nanoparticle (GO@Ce-doped TiO2 NP) electrocatalyst. The GO@Ce-doped TiO2 NPs were prepared through the sol-gel method and characterized by various physicochemical and electrochemical techniques. The GO@Ce-doped TiO2 NP–modified glassy carbon electrode (GCE) addresses excellent electrocatalytic activity towards MP detection for environmental safety and protection. The developed strategy of GO@Ce-doped TiO2 NPs at GCE surfaces for MP detection achieved excellent sensitivity (2.359 μA μM−1 cm−2) and a low detection limit (LOD) 0.0016 μM with a wide linear range (0.002 to 48.327 μM). Moreover, the fabricated sensor shows high selectivity and long-term stability towards MP detection; this significant electrode further paves the way for real-time monitoring of environmental quantitative samples with satisfying recoveries.
Graphical abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fahimi-Kashani N, Hormozi-Nezhad MR (2016) Gold-nanoparticle-based colorimetric sensor array for discrimination of organophosphate pesticides. Anal Chem 88(16):8099–8106
Huang G, Ouyang J, Baeyens WR, Yang Y, Tao C (2002) High-performance liquid chromatographic assay of dichlorvos, isocarbophos and methyl parathion from plant leaves using chemiluminescence detection. Anal Chim Acta 474(1–2):21–29
Wang J, Chatrathi MP, Mulchandani A, Chen W (2001) Capillary electrophoresis microchips for separation and detection of organophosphate nerve agents. Anal Chem 73(8):1804–1808
Juhler RK (1997) Optimized method for the determination of organophosphorus pesticides in meat and fatty matrices. J Chromatogr A 786(1):145-153
Ramachandran T, Dhayabaran VV (2019) Utilization of a MnO2/ polythiophene/rGO nanocomposite modified glassy carbon electrode as an electrochemical sensor for methyl parathion. J Mater Sci Mater Electron 30(13):12315–12327
Rassaei L, Marken F, Sillanpää M, Amiri M, Cirtiu CM, Sillanpää M (2011) Nanoparticles in electrochemical sensors for environmental monitoring. TrAC Trends Anal Chem 30(11):1704–1715
Xiaoping T, Yan L, Tingying Z, Shasha L, Xi L, Hexiang T, Yang Y, Chunlian C (2019) Ultrasensitive electrochemical detection of methyl parathion pesticide based on cationic water-soluble pillar [5] arene and reduced graphene nanocomposite. RSC Adv 9:345–353
Cuiling X, Kangbing W, Shengshui H, Dafu C (2002) Electrochemical detection of parathion at a glassy-carbon electrode modified with hexadecane. Anal Bioanal Chem 373:284–288
Yuhui L, Xin C, Zhiqi L, Lili S, Guozhen F, Jifeng L, Shuo W (2020) Electrochemical detection of organophosphorus pesticides based on amino acids-conjugated P3TAA-modified electrodes. Analyst 9:345
Amal HA, Hassana B, Silio LM, Fatma HMA, Walaa AM, Maria del Pilar TS, Maria IP (2018) Electrochemical sensing of methyl parathion on magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer. Biosens Bioelectron 118:181–187
Mohamed K, Haytham AA, Craig EB (2018) Non-enzymatic electrochemical platform for parathion pesticide sensing based on nanometer-sized nickel oxide modified screen-printed electrodes. Food Chem 255:104–111
Shaktivel M, Pitchaimani V, Chen SM, Lin KC (2020) Three-dimensional zinc oxide nanostars anchored on graphene oxide for voltammetric determination of methyl parathion. Microchim Acta 187:1–13
Xike T, Lin L, Yong L, Chao Y, Zhaoxin Z, Yulun N (2018) Yanxin Wang Nonenzymatic electrochemical sensor based on CuO-TiO2 for sensitive and selective detection of methyl parathion pesticide in ground water. Sensors Actuators B Chem 256:135–142
Liu B, Chen HM, Liu C, Andrews SC, Hahn C, Yang P (2013) Large-scale synthesis of transition-metal-doped TiO2 nanowires with controllable overpotential. J Am Chem Soc 135(27):9995–9998
Basavarajappa PS, Patil SB, Ganganagappa N, Reddy KR, Raghu AV, Reddy CV (2020) Recent progress in metal-doped TiO2, non-metal doped/codoped TiO2 and TiO2 nanostructured hybrids for enhanced photocatalysis. Int J Hydrog Energy 45(13):7764–7778
Štengl V, Bakardjieva S, Murafa N (2009) Preparation and photocatalytic activity of rare earth doped TiO2 nanoparticles. Mater Chem Phys 114(1):217–226
Shetti NP, Nayak DS, Malode SJ, Kulkarni RM (2017) Electrochemical sensor based upon ruthenium doped TiO2 nanoparticles for the determination of flufenamic acid. J Electrochem Soc 164(5):B3036–B3042
Xu AW, Gao Y, Liu HQ (2002) The preparation, characterization, and their photocatalytic activities of rare-earth-doped TiO2 nanoparticles. J Catal 207(2):151–157
Dhanalakshmi J, Iyyapushpam S, Nishanthi S, Malligavathy M, Padiyan DP (2017) Nanotechnology. Investigation of oxygen vacancies in Ce coupled TiO2 nanocomposites by Raman and PL spectra. Adv Nat Sci Nanosci Nanotechnol 8(1):015015
Tayel A, Ramadan AR, El Seoud OA (2018) Titanium dioxide/graphene and titanium dioxide/graphene oxide nanocomposites: synthesis, characterization and photocatalytic applications for water decontamination. Catalysis 8(11):491
Ali AA, Madkour M, Sagheer FA, Zaki MI, Abdel Nazeer A (2020) Low-temperature catalytic CO oxidation over non-Noble, efficient chromia in reduced graphene oxide and graphene oxide nanocomposites. Catalysis 10(1):105
Sun D, Luo Y, Debliquy M, Zhang C (2018) Graphene-enhanced metal oxide gas sensors at room temperature: a review. Beilstein J Nanotechnol 9(1):2832–2844
Xue X, Qin W, Dan W, He L, Yong Z, Feng R, Bin D (2014) Determination of methyl parathion by a molecularly imprinted sensor based on nitrogen doped graphene sheets. Electrochim Acta 116:366–371
Durairaj S, Ruby J, Kaliyamoorthy JB, George Peter GK, Kunjithapatham S (2017) Titanium dioxide anchored graphene oxide nanosheets for highly selective voltammetric sensing of dopamine. Microchim Acta 184:781–790
Yan N, Zhu Z, Zhang J, Zhao Z, Liu Q (2012) Preparation and properties of Ce-doped TiO2 photocatalyst. Mater Res Bull 47(8):1869–1873
Jafari A, Khademi S, Farahmandjou M (2018) Nano-crystalline Ce-doped TiO2 powders: sol-gel synthesis and optoelectronic properties. Mater Res Express 5(9):095008
Kaur N, Shahi SK, Singh V (2015) Anomalous behavior of visible light active TiO2 for the photocatalytic degradation of different reactive dyes. Photochem Photobiol Sci 14(11):2024–2034
Basheer C (2012) Application of titanium dioxide-graphene composite material for photocatalytic degradation of alkylphenols. J Chem 2013:456586. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/456586
Rani BJ, Praveenkumar M, Ravichandran S, Ganesh V, Guduru RK, Ravi G, Yuvakkumar (2019) R Ultrafine M-doped TiO2 (M= Fe, Ce, La) nanosphere photoanodes for photoelectrochemical water-splitting applications. Mater Charact 152:188–203
Wang P, Liu ZG, Chen X, Meng FL, Liu JH, Huang XJ (2013) UV irradiation synthesis of an Au–graphene nanocomposite with enhanced electrochemical sensing properties. J Mater Chem A 1(32):9189–9195
Kissinger PT, Heineman WR (1983) Cyclic voltammetry. J Chem Educ 60(9):702
Karikalan N, Velmurugan M, Chen SM, Karuppiah C, Al-Anazi K, Ali MA, Lou BS (2016) Flame synthesis of nitrogen doped carbon for the oxygen reduction reaction and non-enzymatic methyl parathion sensor. RSC Adv 6(75):71507–71516
Erk N (2004) Voltammetric behaviour and determination of moxifloxacin in pharmaceutical products and human plasma. Anal Bioanal Chem 378(5):1351–1356
Li Y, Zou L, Song G, Li K, Ye B (2013) Electrochemical behavior of sophoridine at a new amperometric sensor based on l-Theanine modified electrode and its sensitive determination. J Electroanal Chem 709:1–9
Ansari S, Ansari MS, Satsangee S, Jain R (2019) WO3 decorated graphene nanocomposite based electrochemical sensor: a prospect for the detection of anti-anginal drug. Anal Chim Acta 1046:99–109
Reddy YVM, Bathinapatla S, Łuczak T, Osińska M, Maseed H, Ragavendra P, Sarma LS, Srikanth V, Madhavi G (2018) An ultra-sensitive electrochemical sensor for the detection of acetaminophen in the presence of etilefrine using bimetallic Pd–Ag/reduced graphene oxide nanocomposites. New J Chem 42(4):3137–3146
Acknowledgements
The research was funded by the Deanship of Scientific Research at Princess Nourah bint Abdulrahman University through the Fast-track Research Funding Program.
Funding
This study received financial assistance from the National Kaohsiung University of Science and Technology.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(DOCX 2070 kb).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nehru, R., Hsu, YF., Wang, SF. et al. Graphene oxide@Ce-doped TiO2 nanoparticles as electrocatalyst materials for voltammetric detection of hazardous methyl parathion. Microchim Acta 188, 216 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-021-04847-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-021-04847-5