Abstract
A new kind of NiFe2O4-based magnetic covalent organic framework nanocomposites (NiFe2O4@COFs) was fabricated through facile synthesis approach under room temperature. The NiFe2O4@COFs exhibited higher adsorption capacity for brominated flame retardants than carbon nanotube material based on hydrophobic interactions, π-π stacking interaction, and van der Waals forces. In addition, the adsorption isotherm and the kinetic model were more suitable for Langmuir and pseudo-second-order model, respectively. NiFe2O4-based magnetic covalent organic framework nanocomposites combined with HPLC-UV (absorption wavelength: 214 nm) technology has excellent adsorption performance, which exhibited low detection limits (0.03–1.9 μg L−1), wide linear range (0.11–1000 μg L−1), good recoveries (91.5–102%) with a relative standard deviation of less than 2.9%. Finally, the prepared magnetic material was successfully used asadsorbents of magnetic solid-phase extraction and applied to the determination of five BFRs from the real water samples.
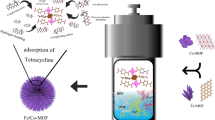
Graphical abstract

The adsorption and removal of BFRs by NiFe2O4@COFs from water samples.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Li Y, Yang CX, Qian HL, Zhao X, Yan XP (2019) Carboxyl-functionalized covalent organic frameworks for the adsorption and removal of triphenylmethane dyes. ACS Appl Nano Mater 2:7290–7298
Kalachova K, Hradkova P, Lankova D, Hajslova J, Pulkrabova J (2012) Occurrence of brominated flame retardants in household and car dust from the Czech Republic. Sci Total Environ 441:182–193
Besis A, Christia C, Poma G, Covaci A, Samara C (2017) Legacy and novel brominated flame retardants in interior car dust-implications for human exposure. Environ Pollut 230:871–881
Abdallah AE, Pawar G, Harrad S (2015) Evaluation of in vitro vs. in vivo methods for assessment of dermal absorption of organic flame retardants: a review. Environ Int 74:13–22
Han Q, Huang X, Xing Q, Shi P (2012) A review of environment problems in the coastal sea of South China. Aquat Ecosyst Health Manage 15:108–117
Munoz CC, Vermeiren P (2020) Maternal transfer of persistent organic pollutants to sea turtle eggs: a meta-analysis addressing knowledge and data gaps toward an improved synthesis of research outputs. Environ Toxicol Chem 39:9–29
Liu AF, Qu GB, Yu M, Liu YW, Shi JB, Jiang GB (2016) Tetrabromobisphenol-A/S and nine novel analogs in biological samples from the Chinese Bohai Sea: implications for trophic transfer. Environ Sci Technol 50:4203–4211
Qiu Y, Liu K, Zhou S, Chen D, Qu H, Wang X, Hu Y, Wang Y (2019) Polyhalogenated carbazoles in surface sediment from Sanmen Bay, East China Sea: spatial distribution and congener profile. Bul Environ Contam Toxicol 103:41–47
Vijwani H, Nadagouda MN, Namboodiri V, Mukhopadhyay SM (2015) Hierarchical hybrid carbon nano-structures as robust and reusable adsorbents: kinetic studies with model dye compound. Chem Eng J 268:197–207
Chen J, Guan M, Li K, Tang S (2020) Novel quaternary ammonium-functionalized covalent organic frameworks/poly(2,6-dimethyl-1,4-phenylene oxide) hybrid anion exchange membranes with enhanced ion conductivity and stability. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 12:15138–15144
Li Y, Zhang H, Chen Y, Huang L, Lin Z, Cai Z (2019) Core-shell structured magnetic covalent organic framework nanocomposites for triclosan and triclocarban adsorption. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 11:22492–22500
Luo Y-H, He X-T, Hong D-L, Chen C, Chen F-H, Jiao J, Zhai L-H, Guo L-H, Sun B-W (2018) A dynamic 3D hydrogen bonded organic frameworks with highly water affinity. Adv Funct Mater 28:1804821–1804827
Zhou Q, Wang Y, Xiao J, Zhan Y (2019) Preparation of magnetic core-shell Fe3O4@polyaniline composite material and its application in adsorption and removal of tetrabromobisphenol A and decabromodiphenyl ether. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 183:109471–109477
Yang J, Li JY, Qiao JQ, Cui SH, Lian HZ, Chen HY (2014) Magnetic solid phase extraction of brominated flame retardants and pentachlorophenol from environmental waters with carbon doped Fe3O4 nanoparticles. Appl Surf Sci 321:126–135
Wang X, Lu M, Pei Y, Lu X, Du X (2015) Two mesoporous cellular foams materials and their adsorption properties to brominated flame retardants. J Porous Mater 22:83–90
Côté AP, Benin AI, Ockwig NW, O'Keeffe M, Matzger AJ (2005) Porous, crystalline, covalent organic frameworks. Science 310:1166–1170
Yan Y, Lu Y, Wang B, Gao Y, Zhao L, Liang H, Wu D (2018) Self-assembling hydrophilic magnetic covalent organic framework nanospheres as a novel matrix for phthalate ester recognition. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 10:26539–26545
Wang W, Deng S, Ren L, Li D, Wang W, Vakili M, Wang B, Huang J, Wang Y, Yu G (2018) Stable covalent organic frameworks as efficient adsorbents for high and selective removal of an aryl-organophosphorus flame retardant from water. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 10:30265–30272
Lu M, Li Q, Liu J, Zhang F-M, Zhang L, Wang J-L, Kang Z-H, Lan Y-Q (2019) Installing earth-abundant metal active centers to covalent organic frameworks for efficient heterogeneous photocatalytic CO2 reduction. Appl Catal B 254:624–633
Wang M, Hu M, Liu J, Guo C, Peng D, Jia Q, He L, Zhang Z, Du M (2019) Covalent organic framework-based electrochemical aptasensors for the ultrasensitive detection of antibiotics. Biosens Bioelectron 132:8–16
Jia C, Mi Y, Liu Z, Zhou W, Gao H, Zhang S, Lu R (2020) Attapulgite modified with covalent organic frameworks as the sorbent in dispersive solid phase extraction for the determination of pyrethroids in environmental water samples. Microchem J 153:104522
Ma TT, Shen XF, Yang C, Qian HL, Pang YH, Yan XP (2019) Covalent immobilization of covalent organic framework on stainless steel wire for solid-phase microextraction GC-MS/MS determination of sixteen polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in grilled meat samples. Talanta 201:413–418
Lohse MS, Stassin T, Naudin G, Wuttke S, Ameloot R, Vos DD, Medina DD, Bein T (2016) Sequential pore wall modification in a covalent organic framework for application in lactic acid adsorption. Chem Mater 28:626–631
Qian HL, Yang CX, Yan XP (2016) Bottom-up synthesis of chiral covalent organic frameworks and their bound capillaries for chiral separation. Nat Commun 7:12104–12107
Zeng H, Rice PM, Wang SX, Sun SH (2004) Shape-controlled synthesis and shape-induced texture of MnFe2O4 nanoparticles. J Am Chem Soc 126:11458–11459
Paul B, Purkayastha DD, Dhar SS (2016) Size-controlled synthesis of NiFe2O4 nanospheres via a PEG assisted hydrothermal route and their catalytic properties in oxidation of alcohols by periodic acid. Appl Surf Sci 370:469–475
Xia Y, He Z, Su J, Tang B, Hu K, Lu Y, Sun S, Li X (2018) Fabrication of magnetically separable NiFe2O4/BiOI nanocomposites with enhanced photocatalytic performance under visible-light irradiation. RSC Adv 8:4284–4294
Zhou P, Zheng R, Zhang W, Liu W, Li Y, Wang H, Wang X (2019) Development of an effervescent tablet microextraction method using NiFe2O4-based magnetic nanoparticles for preconcentration/extraction of heavy metals prior to ICP-MS analysis of seafood. J Anal At Spectrom 34:598–606
Simonin JP (2016) On the comparison of pseudo-first order and pseudo-second order rate laws in the modeling of adsorption kinetics. Chem Eng J 300:254–263
Mohammadi M, Ghaemi A, Torab-Mostaedi M, Asadollahzadeh M, Hemmati A (2013) Adsorption of cadmium (II) and nickel (II) on dolomite powder. Desalin Water Treat 53:149–157
Li N, Wu D, Hu N, Fan G, Li X, Sun J, Chen X, Suo Y, Li G, Wu Y (2018) Effective enrichment and detection of trace polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in food samples based on magnetic covalent organic framework hybrid microspheres. J Agric Food Chem 66:3572–3580
Wang XM, Wang H, Lu MX, Teng RJ, Du XZ (2017) Facile synthesis of phenyl-modified magnetic graphene/mesoporous silica with hierarchical bridge-pore structure for efficient adsorption of pesticides. Mater Chem Phys 198:393–400
Rampey AM, Umpleby RJ, Rushton GT, Iseman JC, Shah RN, Shimizu KD (2004) Characterization of the imprint effect and the influence of imprinting conditions on affinity, capacity, and heterogeneity in molecularly imprinted polymers using the Freundlich isotherm-affinity distribution analysis. Anal Chem 76:1123–1133
de Escobar CC, Fisch A, dos Santos JH (2015) Effectof a sol–gel route on the preparationof silica-based sorbent materials synthesized by molecular imprinting for the adsorption of dyes. Ind Eng Chem Res 54:254–262
Ge Y, Li Z (2018) Application of lignin and its derivatives in adsorption of heavy metal ions in water: a review. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 6:7181–7192
Yang D, Li X, Meng D, Wang M, Yang Y (2017) Supramolecular solvents combined with layered double hydroxide-coated magnetic nanoparticles for extraction of bisphenols and 4-tert-octylphenol from fruit juices. Food Chem 237:870–876
Regueiro J, Wenzl T (2015) Determination of bisphenols in beverages by mixed-mode solid-phase extraction and liquid chromatography coupled to tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 1422:230–238
Zhang Z, Zhang J, Wang Y, Tong Y, Zhang L (2017) Controlled synthesis of hollow porous carbon spheres for enrichment and simultaneous determination of nine bisphenols from real samples. Talanta 167:428–435
Wang X, Liu J, Liu A, Liu Q, Du X, Jiang G (2012) Preparation and evaluation of mesoporous cellular foams coating of solid-phase microextraction fibers by determination of tetrabromobisphenol A, tetrabromobisphenol S and related compounds. Anal Chim Acta 753:1–7
Vinas P, Pastor-Belda M, Torres A, Campillo N, Hernandez-Cordoba M (2016) Use of oleic-acid functionalized nanoparticles for the magnetic solid-phase microextraction of alkylphenols in fruit juices using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Talanta 151:217–223
Li J, Zhang X, Liu Y, Tong H, Xu Y, Liu S (2013) Preparation of a hollow porous molecularly imprinted polymer using tetrabromobisphenol a as a dummy template and its application as SPE sorbent for determination of bisphenol a in tap water. Talanta 117:281–287
Yang D, Li X, Meng D, Yang Y (2018) Carbon quantum dots-modified ferrofluid for dispersive solid-phase extraction of phenolic compounds in water and milk samples. J Mol Liq 261:155–161
Acknowledgements
This work was generously supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21467028 and 21777129); the Program for Innovative Research Group of Gansu Province, China (Grant No.1210RJIA001); Special fund project for the central government to guide local science and technology development (2020); Key Laboratory of Polymer Materials of Gansu Province; and the Key Laboratory of Ecological Environment Related Polymer Materials of the Ministry of Education.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There authors declare that they have no competing interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(DOCX 1120 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, X., Ji, H., Wang, F. et al. NiFe2O4-based magnetic covalent organic framework nanocomposites for the efficient adsorption of brominated flame retardants from water. Microchim Acta 188, 161 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-021-04809-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-021-04809-x