Abstract
A gold nanorod (AuNR)-based lateral flow nucleic acid biosensor (LFNAB) is reported for visual detection of DNA with a short test time and high sensitivity. AuNRs with an approximate length of 60 nm were utilized as a colored tag to label the detection DNA probe (Det-DNA). The capture DNA probe (Cap-DNA) was immobilized on the test region of LFNAB. Sandwich-type complex was formed among the AuNR-Det-DNA, target DNA (Tar-DNA), and Cap-DNA on the LFNAB by Watson-Crick base pairing. In the presence of Tar-DNA, AuNRs were thus seized on the test region of LFNAB, and the accumulation of AuNRs subsequently produced a characteristic colored band. The optimized LFNAB was able to detect 10 pM Tar-DNA without instrumentation. Quantitative analysis could be established by measuring the intensity of test band using a portable strip reader, and the detection limit of 2 pM target DNA was achieved on the LFNAB without signal amplification. The detection limit of the AuNR-based LFNAB is 250-fold lower than that of gold nanoparticle (AuNP)-based LFNABs. This work unveiled a sensitive, rapid, and economical strategy for the detection of nucleic acids, and simultaneously opening new promising routes for disease diagnosis and clinical applications.
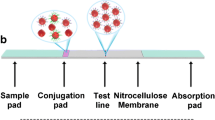
Graphical abstract

Gold nanorods are used as colored tags for lateral flow nucleic acid biosensor.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Corstjens P, Zuiderwijk M, Brink A, Li S, Feindt H, Niedbala RS, Tanke H (2001) Use of up-converting phosphor reporters in lateral-flow assays to detect specific nucleic acid sequences: a rapid, sensitive DNA test to identify human papillomavirus type 16 infection. Clin Chem 47(10):1885–1893
Mao X, Xu H, Zeng Q, Zeng L, Liu G (2009) Molecular beacon-functionalized gold nanoparticles as probes in dry-reagent strip biosensor for DNA analysis. Chem Commun 21:3065–3067
Zhao X, Tapec-Dytioco R, Tan W (2003) Ultrasensitive DNA detection using highly fluorescent bioconjugated nanoparticles. J Am Chem Soc 125(38):11474–11475
Qiu W, Xu H, Takalkar S, Gurung AS, Liu B, Zheng Y, Guo Z, Baloda M, Baryeh K, Liu G (2015) Carbon nanotube-based lateral flow biosensor for sensitive and rapid detection of DNA sequence. Biosens Bioelectron 64:367–372
Sher M, Zhuang R, Demirci U, Asghar W (2017) Paper-based analytical devices for clinical diagnosis: recent advances in the fabrication techniques and sensing mechanisms. Expert Rev Mol Diagn 17(4):351–366
Rahman M, Uddin M, Sultana R, Moue A, Setu M (2013) Polymerase chain reaction (PCR): a short review. Anwer Khan Modern Medical College Journal 4:30–36
Seki Y, Fujiwara Y, Kohno T, Takai E, Sunami K, Goto Y, Horinouchi H, Kanda S, Nokihara H, Watanabe S, Ichikawa H, Yamamoto N, Kuwano K, Ohe Y (2016) Picoliter-droplet digital polymerase chain reaction-based analysis of cell-free plasma DNA to assess EGFR mutations in lung adenocarcinoma that confer resistance to tyrosine-kinase inhibitors. Oncologist 21(2):156–164
Porter-Jordan K, Rosenberg EI, Keiser JF, Gross JD, Ross AM, Nasim S, Garrett CT (1990) Nested polymerase chain reaction assay for the detection of cytomegalovirus overcomes false positives caused by contamination with fragmented DNA. J Med Virol 30(2):85–91
Takalkar S, Baryeh K, Liu G (2017) Fluorescent carbon nanoparticle-based lateral flow biosensor for ultrasensitive detection of DNA. Biosens Bioelectron 98:147–154
Khlebtsov BN, Bratashov DN, Byzova NA, Dzantiev BB, Khlebtsov NG (2019) SERS-based lateral flow immunoassay of troponin I by using gap-enhanced Raman tags. Nano Res 12(2):413–420
Ren W, Mohammed SI, Wereley S, Irudayaraj J (2019) Magnetic focus lateral flow sensor for detection of cervical cancer biomarkers. Anal Chem 91(4):2876–2884
Fu X, Cheng Z, Yu J, Choo P, Chen L, Choo J (2016) A SERS-based lateral flow assay biosensor for highly sensitive detection of HIV-1 DNA. Biosens Bioelectron 78:530–537
He Y, Zeng K, Gurung AS, Baloda M, Xu H, Zhang X, Liu G (2010) Visual detection of single-nucleotide polymorphism with hairpin oligonucleotide-functionalized gold nanoparticles. Anal Chem 82(17):7169–7177
Hwang J, Kwon D, Lee S, Jeon S (2016) Detection of Salmonella bacteria in milk using gold-coated magnetic nanoparticle clusters and lateral flow filters. RSC Adv 6(54):48445–48448
Wen H-W, Borejsza-Wysocki W, DeCory TR, Durst RA (2005) Development of a competitive liposome-based lateral flow assay for the rapid detection of the allergenic peanut protein Ara h1. Anal Bioanal Chem 382(5):1217–1226
Wang J, Cao F, He S, Xia Y, Liu X, Jiang W, Yu Y, Zhang H, Chen W (2018) FRET on lateral flow test strip to enhance sensitivity for detecting cancer biomarker. Talanta 176:444–449
Gao Y, Deng X, Wen W, Zhang X, Wang S (2017) Ultrasensitive paper based nucleic acid detection realized by three-dimensional DNA-AuNPs network amplification. Biosens Bioelectron 92:529–535
Peng T, Wang J, Zhao S, Zeng Y, Zheng P, Liang D, Mari GM, Jiang H (2018) Highly luminescent green-emitting Au nanocluster-based multiplex lateral flow immunoassay for ultrasensitive detection of clenbuterol and ractopamine. Anal Chim Acta 1040:143–149
He Y, Zhang S, Zhang X, Baloda M, Gurung AS, Xu H, Zhang X, Liu G (2011) Ultrasensitive nucleic acid biosensor based on enzyme–gold nanoparticle dual label and lateral flow strip biosensor. Biosens Bioelectron 26(5):2018–2024
Takalkar S, Xu H, Chen J, Baryeh K, Qiu W, Zhao JX, Liu AG (2016) Gold nanoparticle coated silica nanorods for sensitive visual detection of microRNA on a lateral flow strip biosensor. Anal Sci 32(6):617–622
Elahi N, Kamali M, Baghersad MH (2018) Recent biomedical applications of gold nanoparticles: a review. Talanta 184:537–556
Cao J, Sun T, Grattan KTV (2014) Gold nanorod-based localized surface plasmon resonance biosensors: a review. Sensors Actuators B Chem 195:332–351
Locatelli E, Monaco I, Comes Franchini M (2015) Surface modifications of gold nanorods for applications in nanomedicine. RSC Adv 5(28):21681–21699
Xu L, Kuang H, Wang L, Xu C (2011) Gold nanorod ensembles as artificial molecules for applications in sensors. J Mater Chem 21(42):16759–16782
Kabashin AV, Evans P, Pastkovsky S, Hendren W, Wurtz GA, Atkinson R, Pollard R, Podolskiy VA, Zayats AV (2009) Plasmonic nanorod metamaterials for biosensing. Nat Mater 8(11):867–871
Yu C, Irudayaraj J (2007) Multiplex biosensor using gold nanorods. Anal Chem 79(2):572–579
Hao K, He Y, Lu H, Pu S, Zhang Y, Dong H, Zhang X (2017) High-sensitive surface plasmon resonance microRNA biosensor based on streptavidin functionalized gold nanorods-assisted signal amplification. Anal Chim Acta 954:114–120
Li Y, Zhang Y, Zhao M, Zhou Q, Wang L, Wang H, Wang X, Zhan L (2016) A simple aptamer-functionalized gold nanorods based biosensor for the sensitive detection of MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Chem Commun 52(20):3959–3961
Zhu W, Xuan C, Liu G, Chen Z, Wang W (2015) A label-free fluorescent biosensor for determination of bovine serum albumin and calf thymus DNA based on gold nanorods coated with acridine orange-loaded mesoporous silica. Sensors Actuators B Chem 220:302–308
Li C-Z, Male KB, Hrapovic S, Luong JHT (2005) Fluorescence properties of gold nanorods and their application for DNA biosensing. Chem Commun 31:3924–3926
Shakoori Z, Salimian S, Kharrazi S, Adabi M, Saber R (2015) Electrochemical DNA biosensor based on gold nanorods for detecting hepatitis B virus. Anal Bioanal Chem 407(2):455–461
Xu C, Lan L, Yao Y, Ping J, Li Y, Ying Y (2018) An unmodified gold nanorods-based DNA colorimetric biosensor with enzyme-free hybridization chain reaction amplification. Sensors Actuators B Chem 273:642–648
Tao Y, Yang J, Chen L, Huang Y, Qiu B, Guo L, Lin Z (2018) Dialysis assisted ligand exchange on gold nanorods: amplification of the performance of a lateral flow immunoassay for E. coli O157:H7. Microchimica Acta 185(7):350
Nikoobakht B, El-Sayed MA (2003) Preparation and growth mechanism of gold nanorods (NRs) using seed-mediated growth method. Chem Mater 15(10):1957–1962
Sau TK, Murphy CJ (2004) Seeded high yield synthesis of short Au nanorods in aqueous solution. Langmuir 20(15):6414–6420
Vigderman L, Zubarev ER (2013) High-yield synthesis of gold nanorods with longitudinal SPR peak greater than 1200 nm using hydroquinone as a reducing agent. Chem Mater 25(8):1450–1457
Mao X, Ma Y, Zhang A, Zhang L, Zeng L, Liu G (2009) Disposable nucleic acid biosensors based on gold nanoparticle probes and lateral flow strip. Anal Chem 81(4):1660–1668
Baeumner AJ, Pretz J, Fang S (2004) A universal nucleic acid sequence biosensor with nanomolar detection limits. Anal Chem 76(4):888–894
Gao X, Xu H, Baloda M, Gurung AS, Xu L-P, Wang T, Zhang X, Liu G (2014) Visual detection of microRNA with lateral flow nucleic acid biosensor. Biosens Bioelectron 54:578–584
Funding
This study received funding from the Natural Science Foundation of Anhui province (Nos. 1808085QH264, 1908085MB54), Key Research and Development Projects of Anhui Province (No. 202004a07020018), Major project of Anhui Provincial Department of Education (No. KJ2019ZD58), and Wanjiang Scholar Award of Anhui Province, National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 31700735, 21890740, 21890742, 21727815). Projects of Anhui Science and Technology University for Talent introduction (SKYJ201903).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
ESM 1
(DOCX 384 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, Q., Zhang, J., Qiu, W. et al. Gold nanorods-based lateral flow biosensors for sensitive detection of nucleic acids. Microchim Acta 188, 133 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-021-04788-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-021-04788-z