Abstract
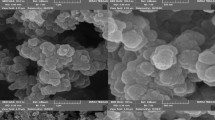
A novel aluminum terephthalate/Fe2O3 nanocomposite was synthesized by the addition of Fe2O3 nanoparticles into a reaction solution containing aluminum terephthalate MOF. The synthesized nanocomposite was successfully used as a fiber coating material for solid-phase microextraction (SPME) of six organophosphorus compounds (OPPs) from river water, grape juice, and tea samples. The effect of different parameters on the efficiency of SPME including desorption temperature and time, extraction temperature and time, salt concentration, pH, and agitation were thoroughly studied. The OPPs were detected and determined using GC-MS. According to the findings, a wide linear range (0.15–800 μg kg−1), low limit of detection (0.04–10 μg kg−1), and high recoveries from spiked samples (87.5–112%) were achieved with low inter-day relative standard deviation (3.2–6.7%, n = 5). The MIL-53(Al)/Fe2O3 nanocomposite showed a high extraction ability towards OPPs, and hence, it can be considered a promising adsorbent for the extraction of various pesticides in complex matrices like tea and juice.
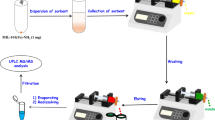
Graphical abstract





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pang Y, Zang X, Li H, Liu J, Chang Q, Zhang S, Wang C, Wang Z (2020) Solid-phase microextraction of organophosphorous pesticides from food samples with a nitrogen-doped porous carbon derived from g-C3N4 templated MOF as the fiber coating. J Hazard Mater 384:121430. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121430
Li ZD, Liu Z, Xu Y, Wang D (2018) Synthesis, characterization of a ternary Cu(II) Schiff base complex with degradation activity of organophosphorus pesticides. Inorg Chim Acta 471:280–289. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ica.2017.11.024
Mol HGJ, Van Dam RCJ, Steijger OM (2003) Determination of polar organophosphorus pesticides in vegetables and fruits using liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry: selection of extraction solvent. J Chromatogr A 1015(1–2):119–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0021-9673(03)01209-3
Amiri A, Tayebee R, Abdar A, Narenji Sani F (2019) Synthesis of a zinc-based metal-organic framework with histamineas an organic linker for the dispersive solid-phase extraction of organophosphorus pesticides in water and fruit juice samples. J Chromatogr A 1597:39–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2019.03.039
Gao L, Liu L, Sun Y, Zhao W, He L (2020) Fabrication of a novel azamacrocycle-based adsorbent for solid-phase extraction of organophosphorus pesticides in tea drinks. Microchem J 153:104364. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2019.104364
Shizuka S-S, Tomoko H, Satoru N, Hiroshi A (2018) Multiresidue determination of pesticides in tea by liquid chromatography-high resolution mass spectrometry: comparison between Orbitrap and time-of-flight mass analyzers. Food Chem 256:140–148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.02.123
Moinfar S, Hosseini MRM (2009) Development of dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction method for the analysis of organophosphorus pesticides in tea. J Hazard Mater 169(1–3):907–911. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.04.030
Moinfar S, Jamil LA, Sami HZ (2020) Determination of organophosphorus pesticides in juice and water by modified continuous sample drop flow microextraction combined with gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. Food Anal Methods 13:1050–1059. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-020-01723-5
Pellicer-Castell E, Belenguer-Sapiña C, Amorós P, El Haskouri J, Herrero-Martínez JM, Mauri-Aucejo A (2018) Study of silica-structured materials as sorbents for organophosphorus pesticides determination in environmental water samples. Talanta 189:560–567. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2018.07.044
Bagheri H, Amanzadeh H, Yamini Y, Masoomi MY, Morsali A, Salar-Amoli J, Hassan J (2018) A nanocomposite prepared from a zinc-based metal-organic framework and polyethersulfone as a novel coating for the headspace solid-phase microextraction of organophosphorous pesticides. Microchim Acta 185:62. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2607-3
Timofeeva I, Shishov A, Kanashina D, Dzema D, Bulatov A (2017) On-line in-syringe sugaring-out liquid-liquid extraction coupled with HPLC-MS/MS for the determination of pesticides in fruit and berry juices. Talanta 167:761–767. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2017.01.008
Alexovič M, Horstkotte B, Solich P, Sabo J (2016) Automation of static and dynamic non-dispersive liquid phase microextraction. Part 1: approaches based on extractant drop-, plug-, film- and microflow-formation. Anal Chim Acta 906:22–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2015.11.038
Xu B, Wang Y, Jin R, Li X, Song D, Zhang H, Sun Y (2015) Magnetic solid-phase extraction based on Fe3O4@polyaniline particles followed by ultrafast liquid chromatography for determination of Sudan dyes in environmental water samples. Anal Methods 7:1606–1614. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4AY02645D
Arthur CL, Pawliszyn (1990) Solid phase microextraction with thermal desorption using fused silica optical fibers. Anal Chem 62(19):2145–2148. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac00218a019
Ghaemmaghami M, Yamini Y, Zavar Mousavi K (2020) Accordion-like Ti3C2Tx MXene nanosheets as a high-performance solid phase microextraction adsorbent for determination of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons using GC-MS. Microchim Acta 187(2):151. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-020-4123-0
Guo Y, He X, Huang C, Chen H, Lu Q, Zhang L (2020) Metal–organic framework-derived nitrogen-doped carbon nanotube cages as efficient adsorbents for solid-phase microextraction of polychlorinated biphenyls. Anal Chim Acta 1095:99–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2019.10.023
Zheng J, Huang J, Yang Q, Ni C, Xie X, Shi Y, Sun J, Zhu F, Ouyang G (2018) Fabrications of novel solid phase microextraction fiber coatings based on new materials for high enrichment capability. TrAC Trends Anal Chem 108:135–153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2018.08.021
Ma T-T, Shen X-F, Yang C, Qian H-L, Pang Y-H, Yan X-P (2019) Covalent immobilization of covalent organic framework on stainless steel wire for solid-phase microextraction GC-MS/MS determination of sixteen polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in grilled meat samples. Talanta 201:413–418. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2019.04.031
Spietelun A, Pilarczyk M, Kloskowski A, Namieśnik J (2010) Current trends in solid-phase microextraction (SPME) fibre coatings. Chem Soc Rev 39(11):4524–4537. https://doi.org/10.1039/C003335A
Chen Y, Xia L, Liang R, Lu Z, Li L, Huo B, Li G, Hu Y (2019) Advanced materials for sample preparation in recent decade. Trends Anal Chem 120:115662. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2019.115652
Qin Z, Jiang Y, Piao H, Li J, Tao S, Ma P, Wang X, Song D, Sun Y (2020) MIL-101(Cr)/MWCNTs-functionalized melamine sponges for solid-phase extraction of triazines from corn samples, and their subsequent determination by HPLC-MS/MS. Talanta 211:120676. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2019.120676
Loiseau T, Taulelle F, Serre C, Henry M, Huguenard C, Bataille T, Fink G, Ferey G (2004) A rationale for the large breathing of the porous aluminum terephthalate (MIL-53) upon hydration. Chem Eur J 10(6):1373–1382. https://doi.org/10.1002/chem.200305413
Xie L, Liu S, Han Z, Jiang R, Zhu F, Xu W, Su C, Ouyang G (2017) Amine-functionalized MIL-53(Al)-coated stainless steel fiber for efficient solid-phase microextraction of synthetic musks and organochlorine pesticides in water samples. Anal Bioanal Chem 409:5239–5247. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-017-0472-x
Chen X-F, Zang H, Wang X, Cheng JG, Zhao RS, Cheng CG, Lu XQ (2012) Metal–organic framework MIL-53(Al) as a solid-phase microextraction adsorbent for the determination of 16 polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in water samples by gas chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. Analyst 137:5411–5419. https://doi.org/10.1039/C2AN35806A
Zhang S, Jiao Z, Yao W (2014) A simple solvothermal process for fabrication of a metal-organic framework with an iron oxide enclosure for the determination of organophosphorus pesticides in biological samples. J Chromatogr A 1371:74–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2014.10.088
Lin K-YA, Chang HA, Hsu CJ (2015) Iron-based metal organic framework, MIL-88A, as a heterogeneous persulfate catalyst for decolorization of Rhodamine B in water. RSC Adv 5:32520–32530. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5RA01447F
Askarinejad A, Bagherzadeh M, Morsali A (2011) Sonochemical fabrication and catalytic properties of α-Fe2O3 nanoparticles. J Exp Nanosci 6(3):217–225. https://doi.org/10.1080/17458080.2010.489583
Wang F, Li L, Feng H, Yang Y, Xiao B, Chen D (2019) An enhanced sensitivity and cleanup strategy for the nontargeted screening and targeted determination of pesticides in tea using modified dispersive solid-phase extraction and cold-induced acetonitrile aqueous two-phase systems coupled with liquid chromatography-high resolution mass spectrometry. Food Chem 275:530–538. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.09.142
Zhu B, Xu X, Luo J, Jin S, Chen W, Liu Z, Tian C (2019) Simultaneous determination of 131 pesticides in tea by on-line GPC-GC–MS/MS using graphitized multi-walled carbon nanotubes as dispersive solid phase extraction sorbent. Food Chem 276:202–208. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.09.152
Pabisiak T, Kiejna A (2019) Incipient adsorption of water and hydroxyl on hematite (0001) surface. J Phys Commun 3:035023. https://doi.org/10.1088/2399-6528/ab0fa7
Deng J, Zhang P, Jin T, Zhou H, Cheng J (2017) Graphene oxide/b-cyclodextrin composite as fiber coating for high efficiency headspace solid phase microextraction of organophosphate ester flame retardants in environmental water. RSC Ad 7:54475–54484. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7RA07903F
FDA (2018) Bioanalytical method validation guidance, FDA. 44. http://www.ich.org/fileadmin/Public WebSite/ICH_Products/Guidelines/Quality/Q2R1/Step4/Q2R1__Guideline.pdf
Shokrollahi M, Seidi S, Fotouhi L (2020) In situ electrosynthesis of a copper-based metal–organic framework as nanosorbent for headspace solid-phase microextraction of methamphetamine in urine with GC-FID analysis. Microchim Acta 187:548. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-020-04535-w
Amini S, Ebrahimzdeh H, Seidi S, Jalilian N (2020) Preparation of electrospun polyacrylonitrile/Ni-MOF-74 nanofibers for extraction of atenolol and captopril prior to HPLC-DAD. 187:508. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-020-04483-5
Xiao Z, He M, Chen B, Hu B (2016) Polydimethylsiloxane/metal-organic frameworks coated stir bar sorptive extraction coupled to gas chromatography-flame photometric detection for the determination of organophosphorus pesticides in environmental water samples. Talanta 156-157:126–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2016.05.001
Cruz Fernandes V, Freitas M, Grosso Pacheco J, Maria Oliveira J, Fernandes Domingues V, Delerue-Matos C (2018) Magnetic dispersive micro solid-phase extraction and gas chromatography determination of organophosphorus pesticides in strawberries. J Chromatogr A 1566:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2018.06.045
Mahpishanian S, Sereshti H (2016) Three-dimensional graphene aerogel-supported iron oxide nanoparticles as an efficient adsorbent for magnetic solid phase extraction of organophosphorus pesticide residues in fruit juices followed by gas chromatographic determination. J Chromatogr A 1443:43–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2016.03.046
Deng X, Guo Q, Chen X, Xue T, Wang H, Yao P (2014) Rapid and effective sample clean-up based on magnetic multiwalled carbon nanotubes for the determination of pesticide residues in tea by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Food Chem 145(15):853–858. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2013.08.137
Wang P, Luo M, Liu D, Zhan J, Liu X, Wang F, Zhou Z, Wang P (2018) Application of a magnetic graphene nanocomposite for organophosphorus pesticide extraction in environmental water samples. J Chromatogr A 1535:9–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2018.01.003
Niu M, Li Z, He W, Zhou W, Lu R, Li J, Gao H, Zhang S, Pan C (2020) Attapulgite modified magnetic metal-organic frameworks for magnetic solid phase extraction and determinations of benzoylurea insecticides in tea infusions. Food Chem 317:126425. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.126425
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
Solutions and chemicals, instrumatations, some experimental results are provided. (DOCX 2015 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moinfar, S., Khodayari, A., Sohrabnezhad, S. et al. MIL-53(Al)/Fe2O3 nanocomposite for solid-phase microextraction of organophosphorus pesticides followed by GC-MS analysis. Microchim Acta 187, 647 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-020-04621-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-020-04621-z