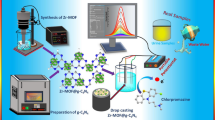
Abstract
A glassy carbon electrode was functionalized by MoO2 nanoparticle–decorated multiwalled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) and examined as a working electrode in oxyfluorfen (OXY) detection by differential pulse stripping voltammetry (DPSV). Measurement parameters were as follows: initial potential − 0.1 V, end potential + 0.5 V, accumulation potential − 0.15 V, accumulation time 80 s, and scan rate 50 mV s−1. A stripping potential of + 0.315 V vs. Ag/AgCl was employed. The pPesticide oxyfluorfen was determined in model samples by DPSV with good reproducibility (RSD <2.4%) in the concentration range 2.5 to 34.5 ng mL−1, with r = 0.99 and a limit of detection of 1.5 ng mL−1. These results are in the same range as those of HPLC/DAD, which is used as the comparative method. Recovery for OXY determination in a real river water sample was 102%. Analyses in Briton-Robinson buffer has shown to be pH dependent with the best response at pH 6.0. Structural characterization of MoO2-MWCNT by Raman spectroscopy, field emission scanning electron microscopy, high-resolution transmission electron microscopy, and X-ray crystallography revealed a preserved MWCNT structure decorated with firmly attached clusters of MoO2 nanoparticles.

Glassy carbon electrode functionalized by MoO2 nanoparticle–decorated multiwalled carbon nanotubes is used as a working electrode in the voltammetric determination of pesticide oxyfluorfen in water.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jha N, Ramaprabhu S (2010) Development of Au nanoparticles dispersed carbon nanotube-based biosensor for the detection of paraoxon. Nanoscale 2:806–810. https://doi.org/10.1039/b9nr00336c
Trojanowicz M (2006) Analytical applications of carbon nanotubes: a review. TrAC Trends Anal Chem 25:480–489. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2005.11.008
Merkoçi A (2006) Carbon nanotubes in analytical sciences. Microchim Acta 152:157–174. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-005-0439-z
Liu G, Riechers SL, Mellen MC, Lin Y (2005) Sensitive electrochemical detection of enzymatically generated thiocholine at carbon nanotube modified glassy carbon electrode. Electrochem Commun 7:1163–1169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.elecom.2005.08.025
Agüí L, Yáñez-Sedeño P, Pingarrón JM (2008) Role of carbon nanotubes in electroanalytical chemistry. Anal Chim Acta 622:11–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2008.05.070
Yavuz E, Özdokur KV, Çakar İ, Koçak S, Ertaş FN (2015) Electrochemical preparation, characterization of molybdenum-oxide/platinum binary catalysts and its application to oxygen reduction reaction in weakly acidic medium. Electrochim Acta 151:72–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2014.11.006
Özdokur KV, Tatlı AY, Yılmaz B, Koçak S, Ertaş FN (2016) Development of pulsed deposited manganese and molybdenum oxide surfaces decorated with platinum nanoparticles and their catalytic application for formaldehyde oxidation. Int J Hydrog Energy 41:5927–5933. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2016.02.127
Çakar İ, Özdokur KV, Demir B, Yavuz E, Demirkol DO, Koçak S, Timur S, Ertaş FN (2013) Molybdenum oxide/platinum modified glassy carbon electrode: a novel electrocatalytic platform for the monitoring of electrochemical reduction of oxygen and its biosensing applications. Sensors Actuators B Chem 185:331–336. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2013.04.106
Bhaskar A, Deepa M, Narasinga Rao T (2013) MoO 2 /multiwalled carbon nanotubes (MWCNT) hybrid for use as a Li-ion battery anode. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 5:2555–2566. https://doi.org/10.1021/am3031536
Li X, Jiang Y, Jia L, Wang C (2016) MoO2 nanoparticles on reduced graphene oxide/polyimide-carbon nanotube film as efficient hydrogen evolution electrocatalyst. J Power Sources 304:146–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2015.11.013
dos Santos EV, Sáez C, Martínez-Huitle CA, Cañizares P, Rodrigo MA (2016) Removal of oxyfluorfen from ex-situ soil washing fluids using electrolysis with diamond anodes. J Environ Manag 171:260–266. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2016.01.027
(1984) EEB Chemical Profile: Oxyfluorfen. Washington, DC
Chmiel T, Mieszkowska A, Kempińska-Kupczyk D, Kot-Wasik A, Namieśnik J, Mazerska Z (2019) The impact of lipophilicity on environmental processes, drug delivery and bioavailability of food components. Microchem J 146:393–406. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2019.01.030
Humburg NE, Colby SR, Lym RG et al (1989) Herbicide handbook of the Weed Science Society of America, 6th edn. Weed Science Society of America, Champaign
Zhang Q, Zhang L, Wang H, Jiang Q, Zhu X (2018) Simultaneous efficient removal of oxyfluorfen with electricity generation in a microbial fuel cell and its microbial community analysis. Bioresour Technol 250:658–665. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.11.091
Wu C, Liu X, Wu X, Dong F, Xu J, Zheng Y (2019) Sorption, degradation and bioavailability of oxyfluorfen in biochar-amended soils. Sci Total Environ 658:87–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.12.059
Barba S, Villaseñor J, Cañizares P, Rodrigo MA (2019) Strategies for the electrobioremediation of oxyfluorfen polluted soils. Electrochim Acta 297:137–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2018.11.195
Carboneras MB, Villaseñor J, Fernández-Morales FJ, Rodrigo MA, Cañizares P (2018) Biological treatment of wastewater polluted with an oxyfluorfen-based commercial herbicide. Chemosphere 213:244–251. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.09.054
Fenoll J, Hellín P, Flores P, Sotomayor JA, Nicolás MI (2008) Determination of oxadiazon and oxyfluorfen in thyme by gas chromatography with electron-capture detection and gas chromatography/mass spectrometry. Int J Environ Anal Chem 88:663–670. https://doi.org/10.1080/03067310802030699
Wu X, Xu J, Dong F, Liu X, Zheng Y (2013) Simultaneous determination of metolachlor, pendimethalin and oxyfluorfen in bulb vegetables using gas chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Anal Methods 5:6389. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3ay41332b
Tsang C, Dananjay A, Kim J, Manthiram A (1996) Synthesis of lower valent molybdenum oxides by an ambient temperature reduction of aqueous K 2 MoO 4 by KBH 4. Inorg Chem 35:504–509. https://doi.org/10.1021/ic950955w
Chen A, Li C, Tang R, Yin L, Qi Y (2013) MoO2–ordered mesoporous carbon hybrids as anode materials with highly improved rate capability and reversible capacity for lithium-ion battery. Phys Chem Chem Phys 15:13601–13610. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3cp51255j
Funding
The research was funded by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technological Development of the Republic of Serbia.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 1398 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Milićević, J.S., Ranđelović, M.S., Momčilović, M.Z. et al. Multiwalled carbon nanotubes modified with MoO2 nanoparticles for voltammetric determination of the pesticide oxyfluorfen. Microchim Acta 187, 429 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-020-04406-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-020-04406-4