Abstract
An electrochemiluminescence (ECL) analytical platform is constructed based on boron nitride quantum dots (BNQDs) as a novel coreactant of luminol for quantitative assay of concanavalin A (Con A). Different from previous research that mainly focuses on its superior optical properties, BNQDs are used for the first time as a coreactant for boosting ECL intensity of luminol, which has a 10-fold enhancement compared with individual poly(luminol/aniline) nanorods loaded on reduced graphene oxide (PLA-rGO) using GCE. On the basis that BNQDs contain an abundance of active amino, a possible mechanism of amino oxidation facilitating ECL emission is proposed. Firstly, luminol as light spices are oxidized to luminol•− and BNQDs generate an abundance of BNQDs-NH+• via electrochemical oxidization, producing reductive intermediates BNQDs-N• in alkaline conditions. Finally, BNQDs-N• react with luminol•− to obtain the excited species AP2−*, returning to ground state and emitting light. Due to the hindrance effect of Con A, the ECL intensity decreases gradually as various concentrations of Con A are modifying the electrode surface. Therefore, a sensitive ECL biosensor for detecting Con A is constructed exhibiting a wide linear range of 1.0 pg·mL−1 to 1.0 μg·mL−1 and a low detection limit of 0.15 pg·mL−1.

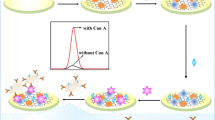
Schematic representation of an electrochemiluminescence (ECL) biosensor based on boron nitride quantum dots (BNQDs) as an efficient coreactant of reduced graphene oxide functionalized poly(luminol/aniline) (PLA-rGO) for quantitative assay of concanavalin A (Con A).





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fan Y, Tan X, Ou X, Lu Q, Chen S, Wei S (2016) A novel “on-off” electrochemiluminescence sensor for the detection of concanavalin A based on Ag-doped g-C3N4. Electrochim Acta 202:90–99
Hardman KD, Ainsworth CF (1972) Structure of concanavalin-A AT 2.4-A resolution. Biochemistry 11:4910–4919
Mann DA, Kanai M, Maly DJ, Kiessling LL (1998) Probing low affinity and multivalent interactions with surface plasmon resonance: ligands for concanavalin A. J Am Chem Soc 120:10575–10582
Li X, Wang Y, Shi L, Ma H, Zhang Y, Du B, Wu D, Wei Q (2017) A novel ECL biosensor for the detection of concanavalin A based on glucose functionalized NiCo2S4 nanoparticles-grown on carboxylic graphene as quenching probe. Biosens Bioelectron 96:113–120
Ou X, Tan X, Liu X, Lu Q, Chen S, Wei S (2015) A signal-on electrochemiluminescence biosensor for detecting Con A using phenoxy dextran-graphite-like carbon nitride as signal probe. Biosens Bioelectron 70:89–97
Pongracz J, Parnell S, Anderson G, Jaffrezou JP, E. Jenkinson, (2003) Con A activates an Akt/PKB dependent survival mechanism to modulate TCR induced cell death in double positive thymocytes. Mol Immunol 39: 1013–1023
Hu Y, Zuo P, Ye BC (2013) Label-free electrochemical impedance spectroscopy biosensor for direct detection of cancer cells based on the interaction between carbohydrate and lectin. Biosens Bioelectron 43:79–83
Zhang M, Liu H, Chen L, Yan M, Ge L, Ge S, Yu J (2013) A disposable electrochemiluminescence device for ultrasensitive monitoring of K562 leukemia cells based on aptamers and ZnO@carbon quantum dots. Biosens Bioelectron 49:79–85
Chen Q, Wei W, Lin JM (2011) Homogeneous detection of concanavalin A using pyrene-conjugated maltose assembled graphene based on fluorescence resonance energy transfer. Biosens Bioelectron 26:4497–4502
Huang CF, Yao GH, Liang RP, Qiu JD (2013) Graphene oxide and dextran capped gold nanoparticles based surface plasmon resonance sensor for sensitive detection of concanavalin A. Biosens Bioelectron 50:305–310
Li Y, Zhang S, Dai H, Hong Z, Lin Y (2016) An enzyme-free photoelectrochemical sensing of concanavalin A based on graphene-supported TiO2 mesocrystal. Sens Actuators B Chem 232:226–233
Hong SA, Kwon J, Kim D, Yang S (2015) A rapid, sensitive and selective electrochemical biosensor with concanavalin A for the preemptive detection of norovirus. Biosens Bioelectron 64:338–344
Li L, Chen Y, Zhu JJ (2017) Recent advances in electrochemiluminescence analysis. Anal Chem 89:358–371
Cao Y, Yuan R, Chai Y, Mao L, Niu H, Liu H, Zhuo Y (2012) Ultrasensitive luminol electrochemiluminescence for protein detection based on in situ generated hydrogen peroxide as coreactant with glucose oxidase anchored AuNPs@MWCNTs labeling. Biosens Bioelectron 31:305–309
Zhang J, Chen S, Ruo Y, Zhong X, Wu X (2015) An ultrasensitive electrochemiluminescent biosensor for the detection of concanavalin A based on poly(ethylenimine) reduced graphene oxide and hollow gold nanoparticles. Anal Bioanal Chem 407:447–453
Hanif S, Han S, John P, Gao W, Kitte SA, Xu G (2016) Electrochemiluminescence of Luminol-Tripropylamine System. Electrochim Acta 196:245–251
Liu W, Chen A, Li S, Peng K, Chai Y, Yuan R (2019) Perylene derivative/luminol nanocomposite as a strong electrochemiluminescence emitter for construction of an ultrasensitive MicroRNA biosensor. Anal Chem 91:1516–1523
Wang C, Chen L, Wang P, Li M, Liu D (2019) A novel ultrasensitive electrochemiluminescence biosensor for glutathione detection based on poly-L-lysine as co-reactant and graphene-based poly(luminol/aniline) as nanoprobes. Biosens Bioelectron 133:154–159
Guo Y, Shang X, Liu F, Hu Y, Li S, Liu J, Wu F (2018) Novel enhancer for luminol-AuNP electrochemiluminescence and decoration on RNA membranes for effective cytosensing. ACS Appl Bio Mater 1:1647–1655
Tang H, Chen W, Li D, Duan X, Ding S, Zhao M, Zhang J (2019) Luminol-based ternary electrochemiluminescence nanospheres as signal tags and target-triggered strand displacement reaction as signal amplification for highly sensitive detection of helicobacter pylori DNA. Sens Actuators B Chem 293:304–311
Yu YQ, Zhang HY, Chai YQ, Yuan R, Zhuo Y (2016) A sensitive electrochemiluminescent aptasensor based on perylene derivatives as a novel co-reaction accelerator for signal amplification. Biosens Bioelectron 85:8–15
Fang D, Pan M, Yi H, Dai H, Hong Z, Zheng X, Lin Y (2019) Enhanced electrochemiluminescence of luminol-DBAE system based on self-assembled mesocrystalline hybrid for the detection of ovarian cancer marker. Sens Actuators B Chem 286:608–615
Lin L, Xu Y, Zhang S, Ross IM, Ong ACM, Allwood DA (2014) Fabrication and luminescence of monolayered boron nitride quantum dots. Small 10:60–65
Li H, Tay RY, Tsang SH, Zhen X, Teo EHT (2015) Controllable synthesis of highly luminescent boron nitride quantum dots. Small 11:6491–6499
Xing H, Zhai Q, Zhang X, Li J, Wang E (2018) Boron nitride quantum dots as efficient coreactant for enhanced electrochemiluminescence of ruthenium(II) tris(2,2′-bipyridyl). Anal Chem 90:2141–2147
Huo B, Liu B, Chen T, Cui L, Xu G, Liu M, Liu J (2017) One-step synthesis of fluorescent boron nitride quantum dots via a hydrothermal strategy using melamine as nitrogen source for the detection of ferric ions. Langmuir 33:10673–10678
Liu B, Yan S, Song Z, Liu M, Ji X, Yang W, Liu J (2016) One-step synthesis of boron nitride quantum dots: simple chemistry meets delicate nanotechnology. Chem Eur J 22:18899–18907
Hu F, Chen S, Wang C, Yuan R, Xiang Y, Wang C (2012) Multi-wall carbon nanotube-polyaniline biosensor based on lectin-carbohydrate affinity for ultrasensitive detection of Con A. Biosens Bioelectron 34:202–207
Fan Y, Tan X, Ou X, Chen S, Wei S (2017) An ultrasensitive electrochemiluminescence biosensor for the detection of concanavalin A based on Au nanoparticles-thiosemicarbazide functionalized PtNi nanocubes as signal enhancer. Biosens Bioelectron 87:802–806
Acknowledgments
We sincerely acknowledge the financial support of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 61503309).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing of interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 3699 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, C., Li, M., Wang, P. et al. An electrochemiluminescence biosensor based on boron nitride quantum dots as novel coreactant for quantitative determination of concanavalin A. Microchim Acta 187, 409 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-020-04385-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-020-04385-6