Abstract
Four CeO2 nanomaterials with the morphologies of a nanoplate (CeO2-p), a nanocube (CeO2-c), a porous triangular microplate (CeO2-t), and of a porous hierarchical rod-stacked nanobundle (CeO2-b) were synthesized using a hydrothermal method. They were characterized by scanning and transmission electron microscopies, X-ray diffraction and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. Electrochemical characterizations reveal the tuning of their morphology and the presence of exposed crystal planes of CeO2 that can be realized by changing the alkali sources. Among these materials, the CeO2-b features the largest specific surface and lowest electron transfer resistance towards the redox probe Fe(CN)63-/4-. The best voltammetric response to dopamine and epinephrine is thus achieved by using the Nafion-CeO2-b coated electrode. A sensitive and selective method was developed that can voltammetrically detect dopamine (with a peak near 0.13 V vs. SCE), and epinephrine (with a peak near 0.25 V vs. SCE). The detection limits are 2.9 and 0.67 nM, respectively.

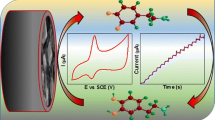
Schematic representation of morphology tailoring of CeO2 and electrochemical sensing of dopamine and epinephrine on these CeO2 samples with different morphologies






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhou X, Zhu A, Shi G (2015) Selective extraction and analysis of catecholamines in rat blood microdialysate by polymeric ionic liquid-diphenylboric acid-packed capillary column and fast separation in high-performance liquid chromatography-electrochemical detector. J Chromatogr A 1409:125–131
Zhao Y, Zhao S, Huang J, Ye F (2011) Quantum dot-enhanced chemiluminescence detection for simultaneous determination of dopamine and epinephrine by capillary electrophoresis. Talanta 85:2650–2654
Tufi S, Lamoree M, de Boer J, Leonards P (2015) Simultaneous analysis of multiple neurotransmitters by hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography coupled to tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 1395:79–87
Li Y, Shen W (2014) Morphology-dependent nanocatalysts: Rod-shaped oxides. Chem Soc Rev 43:1543–1574
Zheng G, Bao Z, Pérez-Justec J, Du R, Liu W, Dai J, Zhang W, Lee LYS, Wong K (2018) Tuning the Morphology and chiroptical properties of discrete gold nanorods with amino acids. Angew Chem Int Ed 57:16452–16457
Wang J, Ma Q, Wang Y, Li Z, Li Z, Yuan Q (2018) New insights into the structure-performance relationships of mesoporous materials in analytical science. Chem Soc Rev 47:8766–8803
Gan T, Wang Z, Gao J, Sun J, Wu K, Wang H, Liu Y (2019) Morphology–dependent electrochemical activity of Cu2O polyhedrons and construction of sensor for simultaneous determination of phenolic compounds with graphene oxide as reinforcement. Sensors Actuators B Chem 282:549–558
Gan T, Wang Z, Shi Z, Zheng D, Sun J, Liu Y (2018) Graphene oxide reinforced core–shell structured Ag@Cu2O with tunable hierarchical morphologies and their morphology–dependent electrocatalytic properties for bio-sensing applications. Biosens Bioelectron 112:23–30
Zhang Y, Yan P, Wan Q, Wu K, Yang N (2016) Morphology-dependent electrochemistry of FeOOH nanostructures. Electrochem Commun 68:10–14
Yu J, Zhang Y, Li H, Wan Q, Li Y, Yang N (2018) Electrochemical properties and sensing applications of nanocarbons: a comparative study. Carbon 129:301–309
Rodriguez JA, Grinter DC, Liu Z, Palomino RM, Senanayake SD (2017) Ceria-based model catalysts: fundamental studies on the importance of the metal-ceria interface in CO oxidation, the water-gas shift, CO2 hydrogenation, and methane and alcohol reforming. Chem Soc Rev 46:1824–1841
Werner K, Weng X, Calaza F, Sterrer M, Kropp T, Paier J, Sauer J, Wilde M, Fukutani K, Shaikhutdinov S, Freund H (2017) Toward an understanding of selective alkyne hydrogenation on ceria: on the impact of O vacancies on H2 interaction with CeO2(111). J Am Chem Soc 139:17608–17616
Yang Z, Ren S, Zhuo Y, Yuan R, Chai Y (2017) Cu/Mn Double-doped CeO2 nanocomposites as signal tags and signal amplifiers for sensitive electrochemical detection of procalcitonin. Anal Chem 89:13349–11335
Lu F, Meng F, Wang L, Luo J, Sang Y (2012) Morphology-selective synthesis method of nanopolyhedra and square-like CeO2 nanoparticles. Mater Lett 73:154–156
Zhang C, Meng F, Wang L, Zhang M, Ding Z (2014) Morphology-selective synthesis method of gear-like CeO2 microstructures and their optical properties. Mater Lett 130:202–205
Yang S, Li G, Yin Y, Yang R, Li J, Qu L (2013) Nano-sized copper oxide/multi-wall carbon nanotube/Nafion modified electrode for sensitive detection of dopamine. J Electroanal Chem 703:45–51
Ensafi AA, Saeid F, Rezaei B, Allafchian AR (2014) NiFe2O4 nanoparticles decorated with MWCNTs as a selective and sensitive electrochemical sensor for the determination of epinephrine using differential pulse voltammetry. Anal Methods 6:6885–6892
Li N, Ren W, Luo H (2008) Simultaneous voltammetric measurement of ascorbic acid and dopamine on poly(caffeic acid)-modified glassy carbon electrode. J Solid State Electrochem 12:693–699
Wang Y, Chen Z (2009) A novel poly(taurine) modified glassy carbon electrode for the simultaneous determination of epinephrine and dopamine. Colloid Surface B 74:322–327
Zhou Y, He M, Huang C, Dong S, Zheng J (2012) A novel and simple biosensor based on poly(indoleacetic acid) film and its application for simultaneous electrochemical determination of dopamine and epinephrine in the presence of ascorbic acid. J Solid State Electrochem 16:2203–2210
Zhang Y, Ren W, Zhang S (2013) Simultaneous determination of epinephrine, dopamine, ascorbic acid and uric acid by polydopamine-nanogold composites modified electrode. Int J Electrochem Sci 8:6839–6850
Cincotto F, Canevari T, Campos A, Landers R, Machado SAS (2014) Simultaneous determination of epinephrine and dopamine by electrochemical reduction on the hybrid material SiO2/graphene oxide decorated with Ag nanoparticles. Analyst 139:4634–4640
Figueiredo-Filho LCS, Silva TA, Vicentini FC, Fatibello-Filho O (2014) Simultaneous voltammetric determination of dopamine and epinephrine in human body fluid samples using a glassy carbon electrode modified with nickel oxide nanoparticles and carbon nanotubes within a dihexadecylphosphate film. Analyst 139:2842–2849
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 61701352 and 21675175), the Open Foundation of Key Laboratory of Analytical Chemistry of the State Ethnic Affairs Commission (KLACOF201704) and Graduate Innovative Fund of Wuhan Institute of Technology (CX2018153 and CX2018160).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 2357 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, C., Zhang, Y., Li, C. et al. Tailoring the CeO2 morphology and its electrochemical reactivity for highly sensitive and selective determination of dopamine and epinephrine. Microchim Acta 187, 143 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-4100-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-4100-7