Abstract
This work describes an anti-ovalbumin antibody-based lateral flow immunoassay (LFI) for T-2 toxin. The antibody uses a coating antigen as a bifunctional element for universality and introduces preincubation to improve the detection limits of the method. T-2 toxin and ovalbumin-modified T-2 toxin competitively binds on the anti-T-2 toxin monoclonal antibody modified on CdSe/ZnS quantum dot beads during preincubation. The modified T-2 toxin acts as a bifunctional element that forms immuno complexes during preincubation and combines with anti-ovalbumin antibody coated in the test line through the ovalbumin terminal. Fluorescence is detected at 610 nm on the test zone following photoexcitation at 365 nm. It has a reverse dose-effect relationship with the amount of T-2 toxin. The calibration plot is linear in the 20–110 fg mL−1 T-2 toxin concentration range, and the limit of detection (LOD) is 10 fg mL−1, which is lower by 8-fold than that of the traditional LFI system (LOD 80 fg mL−1) and one order of magnitude than those of LFIs with labels of colloidal gold nanoparticles (LOD 150 fg mL−1) or fluorophores (LOD 190 ng mL−1). Universality was verified through aflatoxin B1 detection using the established ovalbumin antibody-based LFI system (LOD 10 fg mL−1). The performance of the method was compared with that of established systems and a commercial ELISA kit (LOD 360 fg mL−1).

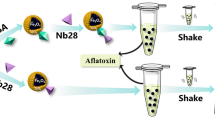
Schematic representation of ovalbumin antibody-based immunochromatographic lateral flow assay for T-2 toxin. Preincubation is introduced for high sensitivity. T-2- anti-ovalbumin acts as a bi-functional element for universality. CdSe/ZnS quantum dot beads act as label. Fluorometric signal is detected at 610 nm.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anfossi L, Di Nardo F, Cavalera S, Giovannoli C, Baggiani C (2019) Multiplex lateral flow immunoassay: an overview of strategies towards high-throughput point-of-need testing. Biosensors 9:2–14. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios9010002
Zhao S, Wang S, Zhang S, Liu J, Dong Y (2018) State of the art: lateral flow assay (LFA) biosensor for on-site rapid detection. Chin Chem Lett 29:1567–1577. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cclet.2017.12.008
Wu C, Hu L, Xia J, Xu G, Luo K, Liu D, Duan H, Cheng S, Xiong Y, Lai W (2017) Comparison of immunoassays based on fluorescent microsphere and quantum-dot submicrobead for quantitative detection of aflatoxin M1 in milk. J Dairy Sci 100:2501–2511. https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.2016-12065
Sheng W, Li S, Liu Y, Wang J, Zhang Y, Wang S (2017) Visual and rapid lateral flow immunoassay for enrofloxacin using dyed polymer microspheres and quantum dots. Mikrochim Acta 184:4313–4321. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2474-y
Luo K, Hu L, Guo Q, Wu C, Wu S, Liu D, Xiong Y, Lai W (2017) Comparison of 4 label-based immunoassays for the detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7 in milk. J Dairy Sci 100:5176–5187. https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.2017-12554
Xing KY, Peng J, Liu DF, Hu LM, Wang C, Li GQ, Zhang GG, Huang Z, Cheng S, Zhu FF, Liu NM, Lai WH (2018) Novel immunoassay based on Eu (III)-doped polystyrene nanoparticle-linker-monoclonal antibody for sensitive detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7. Anal Chim Acta 998:52–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2017.10.027
Yan L, Dou L, Bu T, Huang Q, Wang R, Yang Q, Huang L, Wang J, Zhang D (2018) Highly sensitive furazolidone monitoring in milk by a signal amplified lateral flow assay based on magnetite nanoparticles labeled dual-probe. Food Chem 261:131–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.04.016
Han J, Zhang L, Hu L, Xing K, Lu X, Huang Y, Zhang J, Lai W, Chen T (2018) Nanozyme-based lateral flow assay for the sensitive detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7 in milk. J Dairy Sci 101:5770–5779. https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.2018-14429
Bu T, Huang Q, Yan L, Huang L, Zhang M, Yang Q, Yang B, Wang J, Zhang D (2018) Ultra technically-simple and sensitive detection for Salmonella Enteritidis by immunoassay based on gold growth. Food Control 84:536–543. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2017.08.036
Zhou J, Nie W, Chen Y, Yang C, Gong L, Zhang C, Chen Q, He L, Feng X (2018) Quadruplex gold immunoassay for four families of antibiotic residues in milk. Food Chem 256:304–310. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.02.002
Cheng N, Song Y, Zeinhom MMA, Chang YC, Sheng L, Li H, Du D, Li L, Zhu MJ, Luo Y, Xu W, Lin Y (2017) Nanozyme-mediated dual immunoassay integrated with smartphone for use in simultaneous detection of pathogens. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9:40671–40680. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.7b12734
Zhong YH, Chen YJ, Yao L, Zhao DP, Zheng L, Liu GD, Ye Y, Chen WW (2016) Gold nanoparticles based lateral flow immunoassay with largely amplified sensitivity for rapid melamine screening. Mikrochim Acta 183:1989–1994. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-016-1812-9
Qiu WW, Baryeh K, Takalkar S, Chen W, Liu GD (2019) Carbon nanotube-based lateral flow immunoassay for ultrasensitive detection of proteins: application to the determination of IgG. Microchim Acta 186(7):436–444. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3508-4
Lu XW, Mei T, Guo Q, Zhou WJ, Li XM, Chen JT, Zhou XK, Sun N, Fang ZY (2019) Improved performance of lateral flow immunoassays for alpha-fetoprotein and vanillin by using silica shell-stabilized gold nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 186(1):2–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-3107-9
Anfossi L, Di Nardo F, Cavalera S, Giovannoli C, Spano G, Speranskaya ES, Goryacheva IY, Baggiani C (2018) A lateral flow immunoassay for straightforward determination of fumonisin mycotoxins based on the quenching of the fluorescence of CdSe/ZnS quantum dots by gold and silver nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 185(2):94–104. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2642-0
Sheng W, Chang Q, Shi YJ, Duan WX, Zhang Y, Wang S (2018) Visual and fluorometric lateral flow immunoassay combined with a dual-functional test mode for rapid determination of tetracycline antibiotics. Microchim Acta 185(9):404–414. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-2945-9
Chen L, Tian Y, Sun B, Wang J, Tong Q, Jin Z (2017) Rapid, accurate, and simultaneous measurement of water and oil contents in the fried starchy system using low-field NMR. Food Chem 233:525–529. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2017.04.147
Zou Z, He Z, Li H, Han P, Tang J, Xi C, Li Y, Zhang L, Li X (2012) Development and application of a method for the analysis of two trichothecenes: Deoxynivalenol and T-2 toxin in meat in China by HPLC-MS/MS. Meat Sci 90:613–617. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.meatsci.2011.10.002
Sun Y, Zhang G, Zhao H, Zheng J, Hu F, Fang B (2014) Liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry method for toxicokinetics, tissue distribution, and excretion studies of T-2 toxin and its major metabolites in pigs. J Chromatogr B 958:75–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchromb.2014.03.010
Ler S, Lee F, Gopalakrishnakone P (2006) Trends in detection of warfare agents: detection methods for ricin, staphylococcal entertoxin B and T-2 toxin. J Chromatogr A 1133:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2006.08.078
Deng Q, Qiu M, Wang Y, Lv P, Wu C, Sun L, Ye R, Xu D, Liu Y, Gooneratne R (2017) A sensitive and validated immunomagnetic- bead based enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for analyzing total T-2 (free and modified) toxins in shrimp tissues. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 142:441–447. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.04.037
Khan IM, Zhao S, Niazi S, Mohsin A, Shoaib M, Duan N, Wu S, Wang Z (2018) Silver nanoclusters based FRET aptasensor for sensitive and selective fluorescent detection of T-2 toxin. Sensors Actuators B Chem 277:328–335. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2018.09.021
Porricelli ACR, Lippolis V, Valenzano S, Cortese M, Suman M, Zanardi S, Pascale M (2016) Optimization and validation of a fluorescence polarization immunoassay for rapid detection of T-2 and HT-2 toxins in cereals and cereal-based products. Food Anal Methods 9:3310–3318. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-016-0527-1
Wang C, Li X, Peng T, Wang Z, Wen K, Jiang H (2017) Latex bead and colloidal gold applied in a multiplex immunoassay for high-throughput detection of three classes of antibiotic residues in milk. Food Control 77:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2017.01.016
Kong D, Liu L, Song S, Suryoprabowo S, Li A, Kuang H, Wang L, Xu C (2016) A gold nanoparticle-based semi-quantitative and quantitative ultrasensitive paper sensor for the detection of twenty mycotoxins. Nanoscale 8:5245–5253. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5NR09171C
Bilan R, Fleury F, Nabiev I, Sukhanova A (2015) Quantum dot surface chemistry and functionalization for cell targeting and imaging. Bioconjug Chem 26:609–624. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.bioconjchem.5b00069
Ren M, Xu H, Huang X, Kuang M, Xiong Y, Xu H, Xu Y, Chen H, Wang A (2014) Immunoassay for ultrasensitive detection of Aflatoxin B1 in Maizi by highly luminescent quantum dot beads. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 6:14215–14222. https://doi.org/10.1021/am503517s
Zhang P, Lu H, Chen J, Han H, Ma W (2014) Simple and sensitive detection of HBsAg by using a quantum dots Nanobeads based dot-blot immunoassay. Theranostics 4:307–315. https://doi.org/10.7150/thno.8007
Qie ZW, Liu QQ, Yan WL, Gao ZC, Meng W, Xiao R, Wang SQ (2019) Universal and ultrasensitive Immunochromatographic assay by using an antigen as a Bifunctional element and Antialbumin antibody on a test line. Anal Chem 91(15):9530–9537. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.9b00673
He D, Wu Z, Cui B, Xu E, Jin Z (2019) Building a fluorescent Aptasensor based on exonuclease-assisted target recycling strategy for one-step detection of T-2 toxin. Food Anal Methods 12:625–632. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-018-1392-x
Li C, Luo W, Xu H, Zhang Q, Xu H, Aguilar ZP, Lai W, Wei H, Xiong Y (2013) Development of an immunoassay for rapid and quantitative detection of Clenbuterol in swine urine. Food Control 34:725–732. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2013.06.021
Semenova V, Schiffer J, Steward-Clark E, Soroka S, Schmidt D, Brawner M, Lyde F, Thompson R, Brown N, Foster L (2012) Validation and long term performance characteristics of a quantitative enzyme linked Immunosorbent assay (ELISA) for human anti-PA IgG. J Immunol Methods 376:97–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jim.2011.12.002
Bai Y, Liu Z, Bi Y, Wang X, Jin Y, Sun L, Wang H, Zhang C, Xu S (2012) Preparation of polyclonal antibodies and development of a direct competitive enzyme-linked Immunosorbent assay to detect residues of Phenylethanolamine a in urine samples. J Agric Food Chem 60:11618–11624. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf3036066
Michalet X, Pinaud FF, Bentolila LA, Tsay JM, Doose S, Li JJ, Sundaresan G, Wu AM, Gambhir SS, Weiss S (2005) Quantum dots for live cells, in vivo imaging, and diagnostic. Science. 307(5709):538–544. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1104274
Acknowledgments
We thank colleagues for making great efforts to this manuscript. This work was supported by Major Infectious Diseases such as AIDS and Viral Hepatitis Prevention and Control Technology Major Projects (2018ZX10712-001) and the Major Projects (No. AWS16J020).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic Supporting Material
ESM 1
An Electronic Supporting Material about parameters optimization of the LFI system: (a) labeling amount of anti-T-2-mAb on QB, (b) T-2-OVA concentration in preincubation, (c) sample pH value, (d) ionic strength, (e) anti-OVA antibody concentration, (f) Tween-20 concentration, (g) incubation time, and (h) LFI time. (DOCX 806 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qie, Z., Yan, W., Gao, Z. et al. Ovalbumin antibody-based fluorometric immunochromatographic lateral flow assay using CdSe/ZnS quantum dot beads as label for determination of T-2 toxin . Microchim Acta 186, 816 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3964-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3964-x