Abstract
A dual-channel ratiometric fluorometric assay is described for the determination of the activity of the enzyme tyrosinase (TYR). It is making use of blue-emitting nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dots (bQDs) and of red-emitting dopamine-modified CdTe quantum dots (DA-rQDs). A mixture of the two kinds of quantum dots was prepared, with the ratiometric fluorescence intensity of red to blue adjusted to 5:1. The dopamine on the rQDs is catalytically oxidized by TYR to form dopamine quinone, and this leads to a reduction of the intensity of red fluorescence (peaking at 644 nm). The emission of the bQDs (peaking at 440 nm) represents a stable reference signal. After adding different activities of TYR, the color of the fluorescence of the system continuously changes from red to blue. This can also be visually observed. The ratio of luminescence intensities (at 644/440 nm) can be used to quantify the activity of TYR, and the detection limit is 4.5 mU mL−1. In addition, a test strip is described based on the above method.

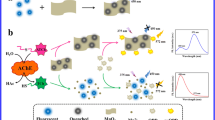
Schematic representation of the ratiometric fluorometric method for determination of the activity of tyrosinase (TYR). (The full name of the abbreviation in the Scheme: 1-ethyl-3-[3-(dimethylamino)-propyl] carbodiimide hydrochloride (EDC), dopamine (DA), N-hydroxysuccinimide (NHS), nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dots (bQDs), CdTe quantum dots (rQDs)).







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Claus H, Decker H (2006) Bacterial tyrosinases. Syst Appl Microbiol 29(1):3–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.syapm.2005.07.012
Yoruk R, Marshall MR (2003) Physicochemical properties and function of plant polyphenol oxidase: a review. J Food Biochem 27(5):361–422. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-4514.2003.tb00289.x
Chang T-S (2009) An updated review of Tyrosinase inhibitors. Int J Mol Sci 10(6):2440–2475. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms10062440
Halaouli S, Asther M, Sigoillot JC, Hamdi M, Lomascolo A (2006) Fungal tyrosinases: new prospects in molecular characteristics, bioengineering and biotechnological applications. J Appl Microbiol 100(2):219–232. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2672.2006.02866.x
Garcia P, Ramallo IA, Furlan RLE (2017) Reverse phase compatible TLC-bioautography for detection of Tyrosinase inhibitors. Phytochem Anal 28(2):101–105. https://doi.org/10.1002/pca.2655
Kim H-r (2014) Recent advances in Tyrosinase research as an industrial enzyme. The Korean Society for Biotechnology and Bioengineering 29(1):1–8
Tessari I, Bisaglia M, Valle F, Samori B, Bergantino E, Mammi S, Bubacco L (2008) The reaction of alpha-synuclein with tyrosinase - possible implications for Parkinson disease. J Biol Chem 283(24):16808–16817. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M709014200
Wang L, Gan Z-F, Guo D, Xia H-L, Patrice FT, Hafez ME, Li D-W (2019) Electrochemistry-regulated recyclable SERS sensor for sensitive and selective detection of Tyrosinase activity. Anal Chem 91(10):6507–6513. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.8b05341
Li S, Mao L, Tian Y, Wang J, Zhou N (2012) Spectrophotometric detection of tyrosinase activity based on boronic acid-functionalized gold nanoparticles. Analyst 137(4):823–825. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2an16085d
Lin T-E, Cortes-Salazar F, Lesch A, Qiao L, Bondarenko A, Girault HH (2015) Multiple scanning electrochemical microscopy mapping of tyrosinase in micro-contact printed fruit samples on polyvinylidene fluoride membrane. Electrochim Acta 179:57–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2015.03.224
Liu X, Yan R, Zhu J, Zhang J, Liu X (2015) Growing TiO2 nanotubes on graphene nanoplatelets and applying the nanonanocomposite as scaffold of electrochemical tyrosinase biosensor. Sensors Actuators B Chem 209:328–335. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2014.11.124
Niu W-J, Shan D, Zhu R-H, Deng S-Y, Cosnier S, Zhang X-J (2016) Dumbbell-shaped carbon quantum dots/AuNCs nanohybrid as an efficient ratiometric fluorescent probe for sensing cadmium (II) ions and L-ascorbic acid. Carbon 96:1034–1042. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2015.10.051
Qiao J, Hwang Y-H, Chen C-F, Qi L, Dong P, Mu X-Y, Kim D-P (2015) Ratiometric fluorescent polymeric thermometer for thermogenesis investigation in living cells. Anal Chem 87(20):10535–10541. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.5b02791
Zhang K, Zhou H, Mei Q, Wang S, Guan G, Liu R, Zhang J, Zhang Z (2011) Instant visual detection of trinitrotoluene particulates on various surfaces by Ratiometric fluorescence of dual-emission quantum dots hybrid. J Am Chem Soc 133(22):8424–8427. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja2015873
Wang K, Qian J, Jiang D, Yang Z, Du X, Wang K (2015) Onsite naked eye determination of cysteine and homocysteine using quencher displacement-induced fluorescence recovery of the dual-emission hybrid probes with desired intensity ratio. Biosens Bioelectron 65:83–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2014.09.093
Chai L, Zhou J, Feng H, Tang C, Huang Y, Qian Z (2015) Functionalized carbon quantum dots with dopamine for Tyrosinase activity monitoring and inhibitor screening: in vitro and intracellular investigation. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7(42):23564–23574. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.5b06711
Liu J, Dong Y, Ma Y, Han Y, Ma S, Chen H, Chen X (2018) One-step synthesis of red/green dual-emissive carbon dots for ratiometric sensitive ONOO− probing and cell imaging. Nanoscale 10(28):13589–13598. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8nr04596h
Zhang Y, Cui P, Zhang F, Feng X, Wang Y, Yang Y, Liu X (2016) Fluorescent probes for "off-on" highly sensitive detection of Hg2+ and L-cysteine based on nitrogen-doped carbon dots. Talanta 152:288–300. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2016.02.018
Song Y, Li Y, Liu Z, Liu L, Wang X, Su X, Ma Q (2014) A novel ultrasensitive carboxymethyl chitosan-quantum dot-based fluorescence "turn on-off" nanosensor for lysozyme detection. Biosens Bioelectron 61:9–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2014.04.036
Yu J, Song N, Zhang Y-K, Zhong S-X, Wang A-J, Chen J (2015) Green preparation of carbon dots by Jinhua bergamot for sensitive and selective fluorescent detection of Hg2+ and Fe3+. Sensors Actuators B Chem 214:29–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2015.03.006
Shi B, Zhang L, Lan C, Zhao J, Su Y, Zhao S (2015) One-pot green synthesis of oxygen-rich nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dots and their potential application in pH-sensitive photoluminescence and detection of mercury (II) ions. Talanta 142:131–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2015.04.059
Huang X, Zhou Y, Liu C, Zhang R, Zhang L, Du S, Liu B, Han M-Y, Zhang Z (2016) A single dual-emissive nanofluorophore test paper for highly sensitive colorimetry-based quantification of blood glucose. Biosens Bioelectron 86:530–535. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2016.07.021
Li H, Liu J, Guo S, Zhang Y, Huang H, Liu Y, Kang Z (2015) Carbon dots from PEG for highly sensitive detection of levodopa. J Mater Chem B 3(11):2378–2387. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4tb01983k
Zhu X, Hu J, Zhao Z, Sun M, Chi X, Wang X, Gao J (2015) Kinetic and sensitive analysis of Tyrosinase activity using Electron transfer complexes: in vitro and intracellular study. Small 11(7):862–870. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.201401595
Qian L, Hong H, Han M, Xu C, Wang S, Guo Z, Yan D (2019) A ketone-functionalized carbazolic porous organic framework for sensitive fluorometric determination of p-nitroaniline. Microchim Acta 186(7):457. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3581-8
Zu F, Yan F, Bai Z, Xu J, Wang Y, Huang Y, Zhou X (2017) The quenching of the fluorescence of carbon dots: a review on mechanisms and applications. Microchim Acta 184(7):1899–1914. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2318-9
Teng Y, Jia X, Li J, Wang E (2015) Ratiometric fluorescence detection of Tyrosinase activity and dopamine using thiolate-protected gold nanoclusters. Anal Chem 87(9):4897–4902. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.5b00468
Yuan J, Cen Y, Kong X-J, Wu S, Liu C-L, Yu R-Q, Chu X (2015) MnO2-Nanosheet-modified Upconversion Nanosystem for sensitive turn-on fluorescence detection of H2O2 and glucose in blood. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7(19):10548–10555. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.5b02188
Hu J-J, Bai X-L, Liu Y-M, Liao X (2017) Functionalized carbon quantum dots with dopamine for tyrosinase activity analysis. Anal Chim Acta 995:99–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2017.09.038
Ma X, Gao W, Halawa MI, Lan Y, Li J, Xu G (2019) Lucigenin fluorescent assay of tyrosinase activity and its inhibitor screening. Sensors Actuators B Chem 280:41–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2018.10.044
Liu B-W, Huang P-C, Li J-F, Wu F-Y (2017) Colorimetric detection of tyrosinase during the synthesis of kojic acid/silver nanoparticles under illumination. Sensors Actuators B Chem 251:836–841. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2017.05.129
Wu X, Li L, Shi W, Gong Q, Ma H (2016) Near-infrared fluorescent probe with new recognition moiety for specific detection of Tyrosinase activity: design, synthesis, and application in living cells and zebrafish. Ange Chem Int Ed 55(47):14728–14732. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201609895
Xu Q, Yoon J (2011) Visual detection of dopamine and monitoring tyrosinase activity using a pyrocatechol violet-Sn4+ complex. Chem Commun 47(46):12497–12499. https://doi.org/10.1039/c1cc15587c
Lei C, Zhao X-E, Sun J, Yan X, Gao Y, Gao H, Zhu S, Wang H (2017) A simple and novel colorimetric assay for tyrosinase and inhibitor screening using 3, 3 ', 5, 5 '-tetramethylbenzidine as a chromogenic probe. Talanta 175:457–462. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2017.07.070
Yang X, Luo Y, Zhuo Y, Feng Y, Zhu S (2014) Novel synthesis of gold nanoclusters templated with L-tyrosine for selective analyzing tyrosinase. Anal Chim Acta 840:87–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2014.05.050
Qu Z, Na W, Liu X, Liu H, Su X (2018) A novel fluorescence biosensor for sensitivity detection of tyrosinase and acid phosphatase based on nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dots. Anal Chim Acta 997:52–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2017.10.010
Yan X, Hu T, Wang L, Zhang L, Su X (2016) Near-infrared fluorescence nanoprobe for enzyme-substrate system sensing and in vitro imaging. Biosens Bioelectron 79:922–929. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2016.01.001
Sidhu JS, Singh A, Garg N, Kaur N, Singh N (2018) A highly selective naphthalimide-based ratiometric fluorescent probe for the recognition of tyrosinase and cellular imaging. Analyst 143(18):4476–4483. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8an01136b
Sun JY, Mel H, Wang SF, Gao F (2016) Two-photon semiconducting polymer dots with dual-emission for Ratiometric fluorescent sensing and bioimaging of Tyrosinase activity. Anal Chem 88(14):7372–7377. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.6b01929
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21173102 and 21473072).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 856 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qu, Z., Yu, T. & Bi, L. A dual-channel ratiometric fluorescent probe for determination of the activity of tyrosinase using nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dots and dopamine-modified CdTe quantum dots. Microchim Acta 186, 635 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3733-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3733-x