Abstract
A method is presented for chiral separation of catecholamines present in bovine and mice blood. It combines magnetic solid phase extraction (MSPE) and chiral capillary electrophoresis (ch-CE). A copolymer consisting of poly(3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine) and polyethyleneimine was coated onto magnetic particles (MPs) by co-deposition using the CuSO4/H2O2 system as a polymerization initiator. The coated MPs are spherical and the average diameter is about 168 ± 4 nm. The thickness of the coating is approximately 19 nm. The functional MPs are used as sorbents in MSPE to simultaneously extract the catecholamines epinephrine, norepinephrine and isoprenaline. Under the optimum conditions, the extraction efficiencies for those catecholamines are in the range from 92.3 to 98.3%, with relative standard deviations (RSDs) of <5.3%. The extraction can be performed within 4 min. The extracts were then submitted to ch-CE. A method for field-enhanced sample injection (FESI) was used to enhance the detection sensitivities of the enantiomers. The limits of detection for catecholamine enantiomers range from 400 to 600 pg mL−1. In comparison with the FESI-ch-CE method, the sensitivity enhancement factors of the MSPE/ch-CE method for catecholamines are about 10-fold. The method was applied to the determination of trace levels of catecholamine enantiomers in (spiked) bovine and mice blood. The recoveries ranged from 88.2 to 93.8%, with RSDs of <5.5%. The whole detection procedure takes less than 30 min.

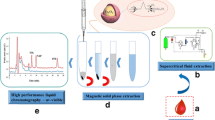
Schematic representation of the separation and detection of catecholamine enantiomers in blood by combination of polyDOPA/PEI-magnetic particles-based solid phase extraction and chiral-capillary electrophoresis.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brunton LL, Hilal-Dandan R, Knollmann BC (2018) Goodman & Gilman’s the pharmacological basis of therapeutics. McGraw-Hill Education, Columbus
Liu S (2011) Adrenergic agents. In: Beale JM Jr, Block JH (eds) Wilson and Gisvold’s textbook of organic medicinal and pharmaceutical chemistry, 12th edn. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia, pp 519–557
Fukushima T, Murayama K, Santa T, Homma H, Imai K (1998) Enantiomeric separation of d−/l-norepinephrine and -epinephrine by high-performance liquid chromatography with a β-cyclodextrin type chiral stationary phase. Biomed Chromatogr 12:1–3. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1099-0801(199801/02)12:1<1::AID-BMC694>3.0.CO;2-W
Lin C-E, Cheng H-T, Fang I-J, Liu Y-C, Kuo C-M, Lin W-Y, Lin C-H (2006) Strategies for enantioseparations of catecholamines and structurally related compounds by capillary zone electrophoresis using sulfated β-cyclodextrins as chiral selectors. Electrophoresis 27:3443–3451. https://doi.org/10.1002/elps.200500658
Pan C, Wang W, Zhang H, Xu L, Chen X (2015) In situ synthesis of homochiral metal-organic framework in capillary column for capillary electrochromatography enantioseparation. J Chromatogr A 1388:207–216. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2015.02.034
Jiang L, Chen Y, Chen Y, Ma M, Tan Y, Tang H, Chen B (2015) Determination of monoamine neurotransmitters in human urine by carrier-mediated liquid-phase microextraction based on solidification of stripping phase. Talanta 144:356–362. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2015.06.068
Zhang X, Xu S, Lim J-M, Lee Y-I (2012) Molecularly imprinted solid phase microextraction fiber for trace analysis of catecholamines in urine and serum samples by capillary electrophoresis. Talanta 99:270–276. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2012.05.050
Zhou X, Zhu A, Shi G (2015) Selective extraction and analysis of catecholamines in rat blood microdialysate by polymeric ionic liquid-diphenylboric acid-packed capillary column and fast separation in high-performance liquid chromatography-electrochemical detector. J Chromatogr A 1409:125–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2015.07.040
Hemmati M, Rajabi M, Asghari A (2018) Magnetic nanoparticle based solid-phase extraction of heavy metal ions: A review on recent advances. Microchim Acta 185:160. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-2670-4
Xiao D, Lu T, Zeng R, Bi Y (2016) Preparation and highlighted applications of magnetic microparticles and nanoparticles: a review on recent advances. Microchim Acta 183:2655–2675. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-016-1928-y
Bouri M, Lerma-García MJ, Salghi R, Zougagh M, Ríos A (2012) Selective extraction and determination of catecholamines in urine samples by using a dopamine magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer and capillary electrophoresis. Talanta 99:897–903. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2012.07.053
Khezeli T, Daneshfar A (2015) Dispersive micro-solid-phase extraction of dopamine, epinephrine and norepinephrine from biological samples based on green deep eutectic solvents and Fe3O4@MIL-100 (Fe) core-shell nanoparticles grafted with pyrocatechol. RSC Adv 5:65264–65273. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5ra08058d
He M, Wang C, Wei Y (2016) Selective enrichment and determination of monoamine neurotransmitters by CU(II) immobilized magnetic solid phase extraction coupled with high-performance liquid chromatography-fluorescence detection. Talanta 147:437–444. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2015.10.017
Ai Y, Nie J, Wu G, Yang D (2014) The DOPA-functionalized bioadhesive with properties of photocrosslinked and thermoresponsive. J Appl Polym Sci 131:41102. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.41102
Guo H, Sun Y, Niu X, Wei N, Pan C, Wang G, Zhang H, Chen H, Yi T, Chen X (2018) The preparation of poly-levodopa coated capillary column for capillary electrochromatography enantioseparation. J Chromatogr A 1578:91–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2018.10.007
Xiao X, Wu J, Li Z, Jia L (2019) Enantioseparation and sensitive analysis of ofloxacin by poly(3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine) functionalized magnetic nanoparticles-based solid phase extraction in combination with on-line concentration capillary electrophoresis. J Chromatogr A 1587:14–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2018.11.026
Vicennati P, Giuliano A, Ortaggi G, Masotti A (2008) Polyethylenimine in medicinal chemistry. Curr Med Chem 15:2826–2839. https://doi.org/10.2174/092986708786242778
Wang J, Zhu J, Tsehaye MT, Li J, Dong G, Yuan S, Li X, Zhang Y, Liu J, Van der Bruggen B (2017) High flux electroneutral loose nanofiltration membranes based on rapid deposition of polydopamine/polyethyleneimine. J Mater Chem A 5:14847–14857. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7ta02661g
Subair R, Tripathi BP, Formanek P, Simon F, Uhlmann P, Stamm M (2016) Polydopamine modified membranes with in situ synthesized gold nanoparticles for catalytic and environmental applications. Chem Eng J 295:358–369. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.02.105
Park JW, Bae KH, Kim C, Park TG (2011) Clustered magnetite nanocrystals cross-linked with PEI for efficient siRNA delivery. Biomacromolecules 12:457–465. https://doi.org/10.1021/bm101244j
Xuan S, Wang Y-XJ, Yu JC, Leung KC-F (2009) Tuning the grain size and particle size of superparamagnetic Fe3O4 microparticles. Chem Mater 21:5079–5087. https://doi.org/10.1021/cm901618m
Tariq M, Al-Badr AA (1985) Isoproterenol. In: Florey K (ed) Analytical profiles of drug substances, vol 14. Academic Press, Salt Lake City, pp 391–422. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0099-5428(08)60586-9
Martín M, Salazar P, Villalonga R, Campuzano S, Pingarrón JM, González-Mora JL (2014) Preparation of core-shell Fe3O4@poly(dopamine) magnetic nanoparticles for biosensor construction. J Mater Chem B 2:739–746. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3tb21171a
Xi Z-Y, Xu Y-Y, Zhu L-P, Wang Y, Zhu B-K (2009) A facile method of surface modification for hydrophobic polymer membranes based on the adhesive behavior of poly(DOPA) and poly(dopamine). J Memb Sci 327:244–253. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2008.11.037
Sui Y, Gao X, Wang Z, Gao C (2012) Antifouling and antibacterial improvement of surface-functionalized poly(vinylidene fluoride) membrane prepared via dihydroxyphenylalanine-initiated atom transfer radical graft polymerizations. J Memb Sci 394–395:107–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2011.12.038
Yiu HHP, Pickard MR, Olariu CI, Williams SR, Chari DM, Rosseinsky MJ (2012) Fe3O4-PEI-RITC magnetic nanoparticles with imaging and gene transfer capability: Development of a tool for neural cell transplantation therapies. Pharm Res 29:1328–1343. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-011-0632-1
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21675056) and the Scientific and Technological Planning Project of Guangzhou City, China (201805010002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
All animal procedures were performed in accordance with the National Institutes of Health (NIH) Guidelines for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals of South China Normal University, and the experiments were approved by the Animal Ethics Committee of South China Normal University. The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 1868 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, J., Li, Z. & Jia, L. Solid phase extraction and capillary electrophoretic separation of racemic catecholamines by using magnetic particles coated with a copolymer prepared from poly(3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine) and polyethyleneimine. Microchim Acta 186, 627 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3731-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3731-z