Abstract
A metal organic framework (MOF) based adsorbent of type UiO-66 was hydrothermally prepared and applied to simultaneous sensing and removal of the asthma drug clenbuterol. The MOF possesses a large specific surface area (1460 cm2·g−1) and a stable structure, and has a large adsorption capacity for clenbuterol (160 mg·g−1). If clenbuterol binds to the MOF, the fluorescence of the sorbent (best measured at excitation/emission wavelengths of 290/396 nm) is quenched by up to 88%. Based on these findings, a fluorometric assay has been developed for the rapid determination of clenbuterol. The adsorption equilibrium of UiO-66 for CLB can be achieved at 60 min and the adsorption efficiency is above 80%. The method has a linear response in the 4.0 to 40 ng·mL−1 concentration range, and the lower limit of detection is 0.17 μM. All of this indicates that UiO-66 is promising for simultaneous detection and the removal of CLB in water.

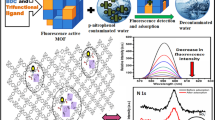
Schematic presentation of the detection and removal of clenbuterol in water medium by a stable fluorescent Zr(IV)-based metal organic framework. This method exhibited a large adsorption capacity for clenbuterol (160 mg/g) and low limit of detection (0.17 μM)





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Prezelj A, Obreza A, Pecar S (2003) Abuse of Clenbuterol and its detection. Curr Med Chem 10(4):281–290
He P, Shen L, Liu R, Luo Z, Li Z (2011) Direct detection of β-agonists by use of gold nanoparticle-based colorimetric assays. Anal Chem 83(18):6988–6995
Shellaiah M, Simon T, Venkatesan P, Sun KW, Ko F, Wu S (2018) Nanodiamonds conjugated to gold nanoparticles for colorimetric detection of clenbuterol and chromium(III) in urine. Mikrochimica Acta 185(1)
Bui QA, Vu TH, Ngo VK, Kennedy IR, Lee NA, Allan RD (2016) Development of an ELISA to detect clenbuterol in swine products using a new approach for hapten design. Anal Bioanal Chem 408(22):6045–6052
Wang R, Zhang W, Wang P, Su X (2018) A paper-based competitive lateral flow immunoassay for multi β-agonist residues by using a single monoclonal antibody labelled with red fluorescent nanoparticles. Mikrochimica Acta 185(3)
Zhang Z, Duan F, He L, Peng D, Yan F, Wang M et al (2016) Electrochemical clenbuterol immunosensor based on a gold electrode modified with zinc sulfide quantum dots and polyaniline. Mikrochimica Acta 183(3):1089–1097
Ji R, Chen S, Xu W, Qin Z, Qiu JF, Li CR (2018) A voltammetric immunosensor for clenbuterol based on the use of a MoS 2 -AuPt nanocomposite. Mikrochimica Acta 185(4)
Ge Y, Camarada MB, Xu L, Qu M, Liang H, Zhao E et al (2018) A highly stable black phosphorene nanocomposite for voltammetric detection of clenbuterol. Mikrochimica Acta 185(12)
Guo R, Xu Q, Wang D, Hu X (2008) Trace determination of clenbuterol with an MWCNT-Nafion nanocomposite modified electrode. Mikrochimica Acta 161:265–272
Zhao J, Yuan H, Peng Y, Hong Q, Liu M (2017) Detection of Ractopamine and Clenbuterol hydrochloride residues in pork using surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy. J Appl Spectrosc 84(1):76–81
Lin RB, Chen B (2017) A microporous metal–organic framework for selective C2H2 and CO2 separation. J Solid State Chem 252:138–141
Kreno LE, Leong K, Farha OK, Allendorf MD, Van Duyne RP, Hupp JT (2012) Metal-organic framework materials as chemical sensors. Chem Rev 112(2):1105–1125
Hu Z, Deibert BJ, Li J (2014) Luminescent metal–organic frameworks for chemical sensing and explosive detection. Chem Soc Rev 43(16):5815–5840
Zhang X, Li C, Gao J, Hou J, Jing X et al (2018) A bi-functional luminescent Zn(II)-MOF for detection of nitroaromatic explosives and Fe 3+ ions. Sensors and Actuators B-chemical:207–213
Wu Y, Feng J, Xie B, Zou L, Li Y, Li Z (2017) An extremely stable 2D zinc(II) coordination polymer exhibiting high sensing ability and photocatalytic degradation activities of dyes. J Inorg Organomet Polym Mater 27(5):1–9
De Voorde BV, Bueken B, Denayer JF, De Vos DE (2014) Adsorptive separation on metal–organic frameworks in the liquid phase. Chem Soc Rev 43(16):5766–5788
Dong Y, Zhang H, Lei F, Liang M, Qian X, Shen P et al (2017) Benzimidazole-functionalized Zr-UiO-66 nanocrystals for luminescent sensing of Fe3+ in water. J Solid State Chem 245:160–163
Germain ME, Knapp MJ (2009) Optical explosives detection: from color changes to fluorescence turn-on. Chem Soc Rev 38(9):2543–2555
Ahmaruzzaman M (2008) Adsorption of phenolic compounds on low-cost adsorbents : a review. Adv Colloid Interf Sci 143(1):48–67
Collins DJ, Zhou H (2007) Hydrogen storage in metal-organic frameworks. J Mater Chem 17(30):3154–3160
Ferey G (2008) Hybrid porous solids: past, present, future. Chem Soc Rev 37(1):191–214
Li Y, Yang RT (2006) Significantly enhanced hydrogen storage in metal−organic frameworks via spillover. J Am Chem Soc 128(3):726–727
Shahat A, Hassan HM, Azzazy HM (2013) Optical metal-organic framework sensor for selective discrimination of some toxic metal ions in water. Anal Chim Acta 793:90–98
Kumar P, Kim K, Deep A (2015) Recent advancements in sensing techniques based on functional materials for organophosphate pesticides. Biosens Bioelectron 70:469–481
Schaate A, Roy P, Godt A, Lippke J, Waltz F, Wiebcke M, Behrens P (2011) Modulated synthesis of Zr-based metal–organic frameworks: from Nano to single crystals. Chemistry: A European Journal 17(24):6643–6651
Bai Y, Dou Y, Xie L, Rutledge W, Li J, Zhou H (2016) Zr-based metal–organic frameworks: design, synthesis, structure, and applications. Chem Soc Rev 45(8):2327–2367
Rosi NL, Kim J, Eddaoudi M, Chen B, Okeeffe M, Yaghi OM (2005) Rod packings and metal−organic frameworks constructed from rod-shaped secondary building units. J Am Chem Soc 127(5):1504–1518
Yuan S, Liu T, Feng D, Tian J, Wang K, Qin J et al (2015) A single crystalline porphyrinic titanium metal–organic framework. Chem Sci 6(7):3926–3930
Wang B, Lv X, Feng D, Xie L, Zhang J, Li M et al (2016) Highly stable Zr(IV)-based metal–organic frameworks for the detection and removal of antibiotics and organic explosives in water. J Am Chem Soc 138(19):6204–6216
Yang Q, Wang J, Chen X, Yang W, Pei H, Hu N et al (2018) The simultaneous detection and removal of organophosphorus pesticides by a novel Zr-MOF based smart adsorbent. J Mater Chem 6(5):2184–2192
He T, Zhang Y, Kong X, Yu J, Lv X, Wu Y, Guo Z, Li J (2018) Zr(IV)-based metal-organic framework with T-shaped ligand: unique structure, high stability, selective detection, and rapid adsorption of CrO in water. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 10(19):16650–16659
Katz MJ, Brown ZJ, Colon YJ, Siu PW, Scheidt KA, Snurr RQ et al (2013) A facile synthesis of UiO-66, UiO-67 and their derivatives. Chem Commun 49(82):9449–9451
Mu X, Jiang J, Chao F, Lou Y, Chen J (2017) Ligand modification of UiO-66 with an unusual visible light photocatalytic behavior for RhB degradation. Dalton Trans 47(6):1895–1902
Hu Z, Lustig WP, Zhang J, Zheng C, Wang H, Teat SJ et al (2015) Effective detection of mycotoxins by a highly luminescent metal-organic framework. J Am Chem Soc 137(51):16209–16215
Nagarkar SS, Joarder B, Chaudhari AK, Mukherjee S, Ghosh SK (2013) Highly selective detection of nitro explosives by a luminescent metal–organic framework. Angew Chem 52(10):2881–2885
Pleadin J, Vulic A, Persi N, Milic D, Vahcic N (2011) Ractopamine and Clenbuterol urinary residues in pigs as food-producing animals. Food Technol Biotechnol 49(4):517–522
Ramachandra S, Schuermann KC, Edafe F, Belser P, Nijhuis CA, Reus WF et al (2011) Luminescent ruthenium tripod complexes: properties in solution and on conductive surfaces. Inorg Chem 50(5):1581–1591
Xu B, Wu X, Li H, Tong H, Wang L (2011) Selective detection of TNT and picric acid by conjugated polymer film sensors with donor–acceptor architecture. Macromolecules 44(13):5089–5092
Chen C, Chen D, Xie S, Quan H, Luo X, Guo L (2017) Adsorption behaviors of organic micropollutants on zirconium metal–organic framework UiO-66: analysis of surface interactions. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9(46):41043–41054
Embaby MS, Elwany SD, Setyaningsih W, Saber MR (2017) The adsorptive properties of UiO-66 towards organic dyes: a record adsorption capacity for the anionic dye Alizarin Red S. Chin J Chem Eng 26(4):731–739
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the China National Key R&D Program (2017YFC1601604), NSFC (No.21777189) and China Central Basic Research Program (Y2018PT23) for financially supporting this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 460 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, H., Wang, B., Cheng, J. et al. Determination and removal of clenbuterol with a stable fluorescent zirconium(IV)-based metal organic framework. Microchim Acta 186, 454 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3586-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3586-3