Abstract
An effective surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) method is presented for the rapid identification and drug sensitivity analysis of pathogens in blood. In a first step, polyethyleneimine-modified magnetic microspheres (Fe3O4@PEI) were used to enrich bacteria from blood samples. Next, the Fe3O4@PEI@bacteria complex was cultured on both ordinary and drug-sensitive plates. Lastly, the SERS spectra of single colonies were acquired in order to identify different pathogens and their resistant strains by comparison with established standardized bacterial SERS spectras and orthogonal partial least squares discriminant analysis (OPLS-DA) method. Staphylococcus aureus, Acinetobacter baumannii, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and their resistant strains were used to evaluate the performance of the SERS method. The results demonstrate that the method can accurately detect and identify all the tested sensitive and drug-resistant strains of bacteria, including 77 clinical blood infection samples. The method provides a way for rapid identification and susceptibility test of pathogens, and has great potential to replace currently used time-consuming methods.

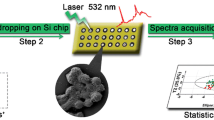
Schematic presentation of a method for the rapid identification and drug sensitivity analysis of pathogens in blood. It is based on a combination of magnetic separation, SERS fingerprint analysis and orthogonal partial least squares discriminant analysis (OPLS-DA).






Similar content being viewed by others
References
David MZ, Daum RS (2010) Community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: epidemiology and clinical consequences of an emerging epidemic. Clin Microbiol Rev 23(3):616–687
Cataldo MA, Taglietti F, Petrosillo N (2010) Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: a community health threat. Postgrad Med 122(6):16–23
Ball CA, Dolinski K, Dwight SS, Harris MA, Issel-Tarver L, Kasarskis A, Scafe CR, Sherlock G, Binkley G, Jin H, Kaloper M, Orr SD, Schroeder M, Weng S, Zhu Y, Botstein D, Cherry JM (2000) Integrating functional genomic information into the Saccharomyces genome database. Nucleic Acids Res 28(1):77–80
Moriel DG, Beatson SA, Wurpel DJ, Lipman J, Nimmo GR, Paterson DL, Schembri MA (2013) Identification of novel vaccine candidates against multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. PLoS One 8(10):e77631
Ferri M, Ranucci E, Romagnoli P, Giaccone V (2017) Antimicrobial resistance: a global emerging threat to public health systems. Crit Rev Food Sci 57(13):2857–2876
Zhang C, Wang C, Xiao R, Tang L, Huang J, Wu D, Liu S, Wang Y, Zhang D, Wang S, Chen X (2018) Sensitive and specific detection of clinical bacteria via vancomycin-modified Fe3O4@Au nanoparticles and aptamer-functionalized SERS tags. J Mater Chem B 6(22):3751–3761
Li J, Wang C, Kang H, Shao L, Hu L, Xiao R, Wang S, Gu B (2018) Label-free identification carbapenem-resistant Escherichia coli based on surface-enhanced resonance Raman scattering. RSC Adv 8(9):4761–4765
Avci E, Kaya NS, Ucankus G, Culha M (2015) Discrimination of urinary tract infection pathogens by means of their growth profiles using surface enhanced Raman scattering. Anal Bioanal Chem 407(27):8233–8241
Shao L, Zhang A, Rong Z, Wang C, Jia X, Zhang K, Xiao R, Wang S (2018) Fast and non-invasive serum detection technology based on surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy and multivariate statistical analysis for liver disease. Nanomed-Nanotechnol 14(2):451–459
Flemming HC, Wingender J (2010) The biofilm matrix. Nat Rev Microbiol 8(9):623–633
Zhang Z, Fang Y, Wang W, Chen L, Sun M (2016) Propagating surface plasmon polaritons: towards applications for remote-excitation surface catalytic reactions. Adv Sci 3(1):1500215
Lin W, Xu X, Quan J, Sun M (2018) Propagating surface plasmon polaritons for remote excitation surface-enhanced Raman scattering spectroscopy. Appl Spectrosc Rev 53(10):771–782
Zhang Z, Xu P, Yang X, Liang W, Sun M (2016) Surface plasmon-driven photocatalysis in ambient, aqueous and high-vacuum monitored by SERS and TERS. J Photochem Photobiol C 100(27):100–112
Magee JT (1993) Whole-organism fingerprinting. Handbook of new bacterial systematics. Academic Press, London, pp 383–427
Mungroo NA, Oliveira G, Neethirajan S (2016) SERS based point-of-care detection of food-borne pathogens. Microchim Acta 183(2):697–707
Wang C, Wang J, Li M, Qu X, Zhang K, Rong Z, Xiao R, Wang S (2016) A rapid SERS method for label-free bacteria detection using polyethylenimine-modified Au-coated magnetic microspheres and Au@Ag nanoparticles. Analyst 141(22):6226–6238
Premasiri WR, Lee JC, Sauer-Budge A, Théberge R, Costello CE, Ziegler LD (2016) The biochemical origins of the surface-enhanced Raman spectra of bacteria: a metabolomics profiling by SERS. Anal Bioanal Chem 408(17):4631–4647
Wu X, Huang YW, Park B, Tripp RA, Zhao Y (2015) Differentiation and classification of bacteria using vancomycin functionalized silver nanorods array based surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy and chemometric analysis. Talanta 139:96–103
Jolayemi OS, Ajatta MA, Adegeye AA (2018) Geographical discrimination of palm oils (Elaeis guineensis) using quality characteristics and UV-visible spectroscopy. Food Sci Nutr 6(4):773–782
Liu J, Che R, Chen H, Zhang F, Xia F, Wu Q, Wang M (2012) Microwave absorption enhancement of multifunctional composite microspheres with spinel Fe3O4 cores and anatase TiO2 shells. Small 8(8):1214–1221
Wang C, Xu J, Wang J, Rong Z, Li P, Xiao R, Wang S (2015) Polyethylenimine-interlayered silver-shell magnetic-core microspheres as multifunctional SERS substrates. J Mater Chem C 3(33):8684–8693
Wang C, Li M, Li Q, Zhang K, Wang C, Xiao R, Wang S (2017) Polyethyleneimine-mediated seed growth approach for synthesis of silver-shell silica-core nanocomposites and their application as a versatile SERS platform. RSC Adv 7(22):13138–13148
Lemma T, Saliniemi A, Hynninen V, Hytönen VP, Toppari JJ (2016) SERS detection of cell surface and intracellular components of microorganisms using nano-aggregated Ag substrate. Vib Spectrosc 83:36–45
Scheffers DJ, Pinho MG (2005) Bacterial cell wall synthesis: new insights from localization studies. Microbiol Mol Biol R : MMBR 69(4):585–607
Zhao Q, Wang M, Yang H, Shi D, Wang YZ (2018) Preparation, characterization and the antimicrobial properties of metal ion-doped TiO2 nano-powders. Ceram Int 44(5):5145–5154
Lee MK, Park KY, Jin T, Kim JH, Seo SJ (2017) Rapid detection of Staphylococcus aureus and methicillin-Resistant S. aureus in atopic dermatitis by using the BD max StaphSR assay. Ann Lab Med 37(4):320–322
Parvez MAK, Shibata H, Nakano T (2008) No relationship exists between PBP 2a amounts expressed in different MRSA strains obtained clinically and their β-lactam MIC values. J Med Investig 55(3, 4):246–253
Mahmood ZA (2015) Microbial amino acids production. In: Harzevili FD and Chen H (ed) Microb biotechnol: progress and trends. CRC Press - Taylor and Francis Group, Boca Raton Florida, pp 187–212
Eliopoulos GM, Maragakis LL, Perl TM (2008) Acinetobacter baumannii: epidemiology, antimicrobial resistance, and treatment options. Clin Infect Dis 46(8):1254–1263
Woods DD (1947) Bacterial metabolism. Annu Rev Microbiol 1(1):115–140
Matos ECO, Andriolo RB, Rodrigues YC, Lima PDL, Carneiro I, Lima KVB (2018) Mortality in patients with multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections: a meta-analysis. Rev Soc Bras Med Trop 51(4):415–420
Huang WE, Ward AD, Whiteley AS (2009) Raman tweezers sorting of single microbial cells. Environ Microbiol Rep 1(1):44–49
Walter A, Marz A, Schumacher W, Rosch P, Popp J (2011) Towards a fast, high specific and reliable discrimination of bacteria on strain level by means of SERS in a microfluidic device. Lab Chip 11(6):1013–1021
Liu Y, Zhou H, Hu Z, Yu G, Yang D, Zhao J (2017) Label and label-free based surface-enhanced Raman scattering for pathogen bacteria detection: a review. Biosens Bioelectron 94:131–140
Martins VV, Pitondo-Silva A, de Melo ML, Falcao JP, Freitas SDS, da Silverira WD, Stehling EG (2014) Pathogenic potential and genetic diversity of environmental and clinical isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. APMIS 122(2):92–100
Mansour AS, Wagih GES, Morgan SD, Elhariri M, EI-Shabrawy MA, Abuelnaga AS, Elgabry EA (2017) Detection of Staphylococcus aureus enterotoxigenic strains in bovine raw milk by reversed passive latex agglutination and multiplex polymerase chain reaction. Vet World 10(8):843–847
Bartual SG, Seifert H, Hippler C, Luzon MA, Wisplinghoff H, Rodriguez-Valera F (2005) Development of a multilocus sequence typing scheme for characterization of clinical isolates of Acinetobacter baumannii. J Clin Microbiol 43(9):4382–4390
Wang J, Wu X, Wang C, Shao N, Dong P, Xiao R, Wang S (2015) Magnetically assisted surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy for the detection of Staphylococcus aureus based on aptamer recognition. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7(37):20919–20929
Wang H, Zhou Y, Jiang X, Sun B, Zhu Y, Wang H, Su Y, He Y (2015) Simultaneous capture, detection, and inactivation of bacteria as enabled by a surface-enhanced Raman scattering multifunctional chip. Angew Chem 54(17):5132–5136
Liu CY, Han YY, Shih PH, Lian WN, Wang HH, Lin CH, Hsueh PR, Wang JK, Wang YL (2016) Rapid bacterial antibiotic susceptibility test based on simple surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopic biomarkers. Sci Rep 6:23375
Gao W, Li B, Yao R, Li Z, Wang X, Dong X, Qu H, Li Q, Li N, Chi H, Zhou B, Xia Z (2017) Intuitive label-free SERS detection of Bacteria using aptamer-based in situ silver nanoparticles synthesis. Anal Chem 89(18):9836–9842
Wang C, Gu B, Liu Q, Pang Y, Xiao R, Wang S (2018) Combined use of vancomycin-modified Ag-coated magnetic nanoparticles and secondary enhanced nanoparticles for rapid surface-enhanced Raman scattering detection of bacteria. Int J Nanomedicine 13:1159–1178
Xu X, Ma X, Wang H, Wang Z (2018) Aptamer based SERS detection of Salmonella typhimurium using DNA-assembled gold nanodimers. Microchim Acta 185(7):325
Chen X, Tang M, Liu Y, Huang J, Liu Z, Tian H, Zheng Y, de la Chapelle ML, Zhang Y, Fu W (2019) Surface-enhanced Raman scattering method for the identification of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus using positively charged silver nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 186(2):102
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No 81471994, 81830101), Jiangsu Provincial Medical Talent (ZDRCA2016053), Six talent peaks project of Jiangsu Province (WSN-135), Advanced health talent of six-one project of Jiangsu Province (LGY2016042), Infectious diseases major project(2018ZX10712001-010).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOC 1958 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, J., Wang, C., Shi, L. et al. Rapid identification and antibiotic susceptibility test of pathogens in blood based on magnetic separation and surface-enhanced Raman scattering. Microchim Acta 186, 475 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3571-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3571-x