Abstract
The extraordinary fluorescence quenching capability of graphene oxide (GO) was coupled to the specific recognition capability of aptamers to design a four-color fluorescent nanoprobe for multiplexed detection and imaging of tumor-associated proteins in living cells. Specifically, alpha-fetoprotein (AFP), vascular endothelial growth factor-165 (VEGF165), carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA), and human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) were detected. Due to strong π interaction, the fluorescence of labeled aptamers is quenched by GO. Four fluorophore-labeled aptamers that bind the tumor-associated proteins were adsorbed on GO to form the four-color nanoprobe with quenched fluorescence. The nanoprobes were internalized into cells via endocytosis, where the aptamer/GO nanoprobes bind the intracellular tumor-associated proteins. The aptamer-protein complexes thus formed detach from GO, and fluorescence recovers. Each analyte has its typical color (AFP: blue; VEGF165: green; CEA: yellow; HER2: red). As a result, simultaneous detection and imaging of multiple tumor-associated proteins in living cells were achieved. This nanoprobe has a fast response and is highly specific and biocompatible. The linear ranges for AFP, VEGF165, CEA, and HER2 are 0.8 nM–160 nM, 0.5 nM–100 nM, 1.0 nM–200 nM, and 1.2 nM–240 nM, respectively. Detection limits were 0.45 nM for AFP, 0.30 nM for VEGF165, 0.62 nM for CEA, and 0.96 nM for HER2. The probe allows for a fast distinction between tumor cells and normal cells via imaging.

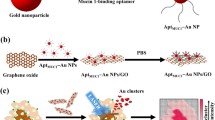
Schematic presentation of the development of a four-color fluorometic method based on aptamer and graphene oxide for simultaneous detection and imaging of alpha-fetoprotein, vascular endothelial growth factor-165, carcinoembryonic antigen and human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 in living cells.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chikkaveeraiah BV, Bhirde AA, Morgan NY, Eden HS, Chen X (2012) Electrochemical immunosensors for detection of cancer protein biomarkers. ACS Nano 6:6546–6561
Fu X, Chen L, Choo J (2017) Optical nanoprobes for ultrasensitive immunoassay. Anal Chem 89:124–137
Xu H, Li Q, Wang L, He Y, Shi J, Tang B, Fan C (2014) Nanoscale optical probes for cellular imaging. Chem Soc Rev 43:2650–2661
Huang D, Huang Z, Xiao H, Wu Z, Tang L, Jiang J (2018) Protein scaffolded DNA tetrads enable efficient delivery and ultrasensitive imaging of miRNA through crosslinking hybridization chain reaction. Chem Sci 9:4892–4897
Pan W, Zhang T, Yang H, Diao W, Li N, Tang B (2013) Multiplexed detection and imaging of intracellular mRNAs using a four-color nanoprobe. Anal Chem 85:10581–10588
Borra R, Dong D, Elnagar AY, Woldemariam GA, Camarero JA (2012) In-cell fluorescence activation and labeling of proteins mediated by FRET-quenched split inteins. J Am Chem Soc 134:6344–6353
Ji H, Guan Y, Wu L, Ren J, Miyoshi D, Sugimoto N, Qu X (2015) A fluorescent probe for detection of an intracellular prognostic indicator in early-stage cancer. Chem Commun 51:1479–1482
Liang H, Chen S, Li P, Wang L, Li J, Li J, Yang H, Tan W (2018) Nongenetic approach for imaging protein dimerization by aptamer recognition and proximity-induced DNA assembly. J Am Chem Soc 140:4186–4190
Liu Y, Zhang X, Chen W, Tan YL, Kelly JW (2015) Fluorescence turn-on folding sensor to monitor proteome stress in live cells. J Am Chem Soc 137:11303–11311
Mizusawa K, Takaoka Y, Hamachi I (2012) Specific cell surface protein imaging by extended self-assembling fluorescent turn-on nanoprobes. J Am Chem Soc 134:13386–13395
Tang Y, Wang Z, Yang X, Chen J, Liu L, Zhao W, Le XC, Li F (2015) Constructing real-time, wash-free, and reiterative sensors for cell surface proteins using binding-induced dynamic DNA assembly. Chem Sci 6:5729–5733
Wu B, Wang H, Chen J, Yan X (2011) Fluorescence resonance energy transfer inhibition assay for α-fetoprotein excreted during cancer cell growth using functionalized persistent luminescence nanoparticles. J Am Chem Soc 133:686–688
Yoshii T, Mizusawa K, Takaoka Y, Hamachi I (2014) Intracellular protein-responsive supramolecules: protein sensing and in-cell construction of inhibitor assay system. J Am Chem Soc 136:16635–16642
Yu W, Wu T, Huang C, Chen I, Tan K (2016) Protein sensing in living cells by molecular rotor-based fluorescence-switchable chemical probes. Chem Sci 7:301–307
Zhao B, Wu P, Zhang H, Cai C (2015) Designing activatable aptamer probes for simultaneous detection of multiple tumor-related proteins in living cancer cells. Biosens Bioelectron 68:763–770
Wu Z, Liu G, Yang X, Jiang J (2015) Electrostatic nucleic acid nanoassembly enables hybridization chain reaction in living cells for ultrasensitive mRNA imaging. J Am Chem Soc 137:6829–6836
Li N, Chang C, Pan W, Tang B (2012) A multicolor nanoprobe for detection and imaging of tumor-related mRNAs in living cells. Angew Chem Int Ed 51:7426–7430
Chen D, Feng H, Li J (2012) Graphene oxide: preparation, functionalization, and electrochemical applications. Chem Rev 112:6027–6053
Pumera M (2011) Graphene in biosensing. Mater Today 14:308–315
Chang H, Tang L, Wang Y, Jiang J, Li J (2010) Graphene fluorescence resonance energy transfer aptasensor for the thrombin detection. Anal Chem 82:2341–2346
Lu C, Li J, Lin M, Wang Y, Yang H, Chen X, Chen G (2010) Amplified aptamer-based assay through catalytic recycling of the analyte. Angew Chem Int Ed 49:8454–8457
Dong H, Zhang J, Ju H, Lu H, Wang S, Jin S, Hao K, Du H, Zhang X (2012) Highly sensitive multiple microRNA detection based on fluorescence quenching of graphene oxide and isothermal strand-displacement polymerase reaction. Anal Chem 84:4587–4593
Pan W, Liu B, Gao X, Yu Z, Liu X, Li N, Tang B (2018) A graphene-based fluorescent nanoprobe for simultaneous monitoring of miRNA and mRNA in living cells. Nanoscale 10:14264–14271
Ryoo SR, Lee J, Yeo J, Na HK, Kim YK, Jang H, Lee JH, Han SW, Lee Y, Kim VN, Min DH (2013) Quantitative and multiplexed microRNA sensing in living cells based on peptide nucleic acid and nano graphene oxide (PANGO). ACS Nano 7:5882–5891
Liu H, Tian T, Ji D, Ren N, Ge S, Yan M, Yu J (2016) A graphene-enhanced imaging of microRNA with enzyme-free signal amplification of catalyzed hairpin assembly in living cells. Biosens Bioelectron 85:909–914
Li L, Feng J, Liu H, Li Q, Tong L, Tang B (2016) Two-color imaging of microRNA with enzyme-free signal amplification via hybridization chain reactions in living cells. Chem Sci 7:1940–1945
Yang L, Liu B, Wang M, Li J, Pan W, Gao X, Li N, Tang B (2018) A highly sensitive strategy for fluorescence imaging of microRNA in living cells and in vivo based on graphene oxide-enhanced signal molecules quenching of molecular beacon. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 10:6982–6990
Shao C, Liang J, He S, Luan T, Yu J, Zhao H, Xu J, Tian L (2017) pH-responsive graphene oxide-DNA nanosystem for live cell imaging and detection. Anal Chem 89:5445–5452
Yang L, Li J, Pan W, Wang H, Li N, Tang B (2018) Fluorescence and photoacoustic dual-mode imaging of tumor-related mRNA with a covalent linkage-based DNA nanoprobe. Chem Commun 54:3656–3659
Wang Y, Li Z, Weber TJ, Hu D, Lin CT, Li J, Lin Y (2013) In situ live cell sensing of multiple nucleotides exploiting DNA/RNA aptamers and graphene oxide nanosheets. Anal Chem 85:6775–6782
Wang Y, Li Z, Hu D, Lin CT, Li J, Lin Y (2010) Aptamer/graphene oxide nanocomplex for in situ molecular probing in living cells. J Am Chem Soc 132:9274–9276
Yi M, Yang S, Peng Z, Liu C, Li J, Zhong W, Yang R, Tan W (2014) Two-photon graphene oxide/aptamer nanosensing conjugate for in vitro or in vivo molecular probing. Anal Chem 86:3548–3554
Chen T, Tian X, Liu C, Ge J, Chu X, Li Y (2015) Fluorescence activation imaging of cytochrome c released from mitochondria using aptameric nanosensor. J Am Chem Soc 137:982–989
Wang H, Zhang Q, Chu X, Chen T, Ge T, Yu R (2011) Graphene oxide-peptide conjugate as an intracellular protease sensor for caspase-3 activation imaging in live cells. Angew Chem Int Ed 123:7203–7207
Tian J, Ding L, Wang Q, Hu Y, Jia L, Yu J, Ju H (2015) Folate receptor-targeted and cathepsin B-activatable nanoprobe for in situ therapeutic monitoring of photosensitive cell death. Anal Chem 87:3841–3848
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundations of China (No. 21864005, 81460544) and the Natural Science Foundations of Guangxi Province (No. 2015GXNSFGA139003) as well as BAGUI Scholar Program and the project of State Key Laboratory for Chemistry and Molecular Engineering of Medicinal Resources (CMEMR2015-A08).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOC 4681 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, J., Chen, W., Shi, M. et al. An aptamer-based four-color fluorometic method for simultaneous determination and imaging of alpha-fetoprotein, vascular endothelial growth factor-165, carcinoembryonic antigen and human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 in living cells. Microchim Acta 186, 204 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3312-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3312-1