Abstract
Two kinds of electrochemical impedimetric biosensors for the detection of E. coli O157:H7 are described and compared. They were fabricated using self-assembled layers of thiolated protein G (PrG-thiol) on (i) planar gold electrodes and (ii) gold nanoparticles (Au NPs) modified gold electrodes. The fabrications of the biosensors were characterized using cyclic voltammetry, electrochemical impedance spectroscopy, scanning electron microscopy and atomic force microscopy techniques. The modification of the planar gold electrode by Au NPs via self-assembled monolayer of 1,6-hexadithiol as a linker molecule increased the electrochemically active surface area by about 2.2 times. The concentration of PrG-thiol and its incubation time, as well as the concentration of IgG were optimized. The Au NP-based biosensor exhibited a limit of detection of 48 colony forming unit (cfu mL−1) which is 3 times lower than that of the planar gold electrode biosensor (140 cfu mL−1). It also showed a wider dynamic range (up to 107 cfu mL−1) and sensitivity. The improved analytical performance of the Au NP-modified biosensor is ascribed to the synergistic effect between the Au NPs and the PrG-thiol scaffold. The biosensor exhibited high selectivity for E. coli O157:H7 over other bacteria such as Staphylococcus aureus and Salmonella typhimurium.

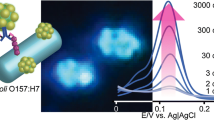
Schematic representations of sensor fabrication using Au NP-modified electrode (HKEC = heat- killed E. coli O157:H7).






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Majowicz SE, Scallan E, Jones-Bitton A, Sargeant JM, Stapleton J, Angulo FJ, Yeung DH, Kirk MD (2014) Global incidence of human Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli infections and deaths: a systematic review and knowledge synthesis. Foodborne Pathog Dis 11:447–455
Tokarskyy O, Marshall DL (2008) Immunosensors for rapid detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7 — perspectives for use in the meat processing industry. Food Microbiol 25:1–12
Velusamy V, Arshak K, Korostynska O, Oliwa K, Adley C (2010) An overview of foodborne pathogen detection: in the perspective of biosensors. Biotechnol Adv 28:232–254
Mayer CL, Leibowitz CS, Kurosawa S, Stearns-Kurosawa DJ (2012) Shiga toxins and the pathophysiology of hemolytic uremic syndrome in humans and animals. Toxins 4:1261–1287
Fung F, Wang H-S, Menon S (2018) Food safety in the 21st century. Biom J 41:88–95
Varadi L, Luo JL, Hibbs DE, Perry JD, Anderson RJ, Orenga S, Groundwater PW (2017) Methods for the detection and identification of pathogenic bacteria: past, present, and future. Chem Soc Rev 46:4818–4832
Amiri M, Bezaatpour M, Jafari H, Boukherroub R, Szunerits S (2018) Electrochemical methodologies for the detection of pathogens. ACS Sensors 3:1069–1086
Chen Y, Wang Z, Liu Y, Wang X, Li Y, Ma P, Gu B, Li H (2014) Recent advances in rapid pathogen detection method based on biosensors. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 37:1021–1037
Yoo SM, Lee SY (2016) Optical biosensors for the detection of pathogenic microorganisms. Trends Biotechnol 34:7–25
Dong Z-M, Zhao G-C (2015) Label-free detection of pathogenic bacteria via immobilized antimicrobial peptides. Talanta 137:55–61
Xu M, Wang R, Li Y (2017) Electrochemical biosensors for rapid detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7. Talanta 162:511–522
Heo J, Hua SZ (2009) An overview of recent strategies in pathogen sensing. Sensors 9:4483–4502
Chang B-Y, Park S-M (2010) Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. Annu Rev Anal Chem 3:207–229
Zhu C, Yang G, Li H, Du D, Lin Y (2015) Electrochemical sensors and biosensors based on nanomaterials and nanostructures. Anal Chem 87:230–249
Tran TB, Son SJ, Min J (2016) Nanomaterials in label-free impedimetric biosensor: current process and future perspectives. BioChip J 10:318–330
Lin D, Harris KD, Chan NWC, Jemere AB (2018) Nanostructured indium tin oxide electrodes immobilized with toll-like receptor proteins for label-free electrochemical detection of pathogen markers. Sensors Actuators B Chem 257:324–330
Jans H, Huo Q (2012) Gold nanoparticle-enabled biological and chemical detection and analysis. Chem Soc Rev 41:2849–2866
Lin D, Tang T, Harrison DJ, Lee WE, Jemere AB (2015) A regenerating ultrasensitive electrochemical impedance immunosensor for the detection of adenovirus. Biosens Bioelectron 68:129–134
Zhang J, Wang J, Zhu J, Xu J, Chen H, Xu D (2008) An electrochemical impedimetric arrayed immunosensor based on indium tin oxide electrodes and silver-enhanced gold nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 163:63–70
Zhou J, Du L, Zou L, Zou Y, Hu N, Wang P (2014) An ultrasensitive electrochemical immunosensor for carcinoembryonic antigen detection based on staphylococcal protein A—au nanoparticle modified gold electrode. Sensors Actuators B Chem 197:220–227
Wang Y, Ping J, Ye Z, Wu J, Ying Y (2013) Impedimetric immunosensor based on gold nanoparticles modified graphene paper for label-free detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7. Biosens Bioelectron 49:492–498
Yang H, Zhou H, Hao H, Gong Q, Nie K (2016) Detection of Escherichia coli with a label-free impedimetric biosensor based on lectin functionalized mixed self-assembled monolayer. Sensors Actuators B Chem 229:297–304
Geng P, Zhang X, Meng W, Wang Q, Zhang W, Jin L, Feng Z, Wu Z (2008) Self-assembled monolayers-based immunosensor for detection of Escherichia coli using electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. Electrochim Acta 53:4663–4668
Ruan C, Yang L, Li Y (2002) Immunobiosensor chips for detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7 using electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. Anal Chem 74:4814–4820
Maalouf R, Fournier-Wirth C, Coste J, Chebib H, Saikali Y, Vittori O, Errachid A, Cloarec J-P, Martelet C, Jaffrezic-Renault N (2007) Label-free detection of bacteria by electrochemical impedance spectroscopy: comparison to surface plasmon resonance. Anal Chem 79:4879–4886
dos Santos MB, Agusil JP, Prieto-Simon B, Sporer C, Teixeria V, Samitier J (2013) Highly sensitive detection of pathogen Escherichia coli O157:H7 by electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. Biosens Bioelectron 45:174–180
dos Santos MB, Azevedo S, Agusil JP, Prieto-Simon B, Sporer C, Torrents E, Juarez A, Teixeira V, Samitier J (2015) Label-free ITO-based immunosensor for the detection of very low concentrations of pathogenic bacteria. Bioelectrochem 101:146–152
Joung C-K, Nim H-N, Lim M-C, Jeon T-J, Kim H-Y, Kim YR (2013) A nanoporous membrane-based impedimetric immunosensor for label-free detection of pathogenic bacteria in whole milk. Biosens Bioelectron 44:210–215
Fowler JM, Stuart MC, Wong DKY (2007) Self-assembled layer of thiolated protein G as an Immunosensor scaffold. Anal Chem 79:350–354
Kausaite-Minkstimiene A, Ramanaviciene A, Kirlyte J, Ramanavicius A (2010) Comparative study of random and oriented antibody immobilization techniques on the binding capacity of immunosensor. Anal Chem 82:6401–6408
Makaraviciute A, Ramanaviciene A (2013) Site-directed antibody immobilization techniques for immunosensors. Biosens Bioelectron 50:460–471
Trilling AK, Beekwilder J, Zuilhof H (2013) Antibody orientation on biosensor surfaces: a minireview. Analyst 138:1619–1627
Liu Y, Yu J (2016) Oriented immobilization of proteins on solid supports for use in biosensors and biochips: a review. Microchim Acta 183:1–19
Turkova J (1999) Oriented immobilization of biologically active proteins as a tool for revealing protein interactions and function. J Chromatogr B Biomed Sci Appl 722:11–31
Hafaiedh I, Chammem H, Abdelghani A, Ait E, Feldman L, Meilhac O, Mora L (2013) Supported protein G on gold electrode: characterization and immunosensor application. Talanta 116:84–90
Mahmoud AM, Tang T, Harrison DJ, Lee WE, Jemere AB (2014) A regenerating self-assembled gold nanoparticle-containing electrochemical impedance sensor. Biosens Bioelectron 56:328–333
Sun X, Zhu Y, Wang X (2011) Amperometric immunosensor based on a protein A/deposited gold nanocrystals modified electrode for carbofuran detection. Sensors 11:11679–11691
Janek RP, Fawcett WR (1998) Impedance spectroscopy of self-assembled monolayers on Au (111): sodium ferrocyanide charge transfer at modified electrode. Langmuir 14:3011–3018
Shein JB, Lai LMH, Eggers PK, Paddon-Row MN, Gooding JJ (2009) Formation of efficient electron transfer pathways by adsorbing gold nanoparticles to self-assembled monolayer modified electrodes. Langmuir 25:11121–11128
Adams KL, Jena BK, Percival SJ, Zhang B (2011) Highly sensitive detection of exocytotic dopamine release using a gold-nanoparticle-network microelectrode. Anal Chem 83:920–927
Bertok T, Sediva A, Vikartovska A, Tkac J (2014) Comparison of the 2D and 3D nanostructured lectin-based biosensors for in situ detection of sialic acid on glycoproteins. Int J Electrochem Sci 9:890–900
Baccar H, Mejri MB, Hafaiedh I, Ktari T, Aouni M, Abdelghani A (2010) Surface plasmon resonance immunosensor for bacteria detection. Talanta 82:810–814
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the support from the NRC-Nanotechnology Research Centre, Defence Research and Development Canada – Suffield Research Centre, and Defence Research and Development Canada Technology Development Fund.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PPTX 1.15 mb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, D., Pillai, R.G., Lee, W.E. et al. An impedimetric biosensor for E. coli O157:H7 based on the use of self-assembled gold nanoparticles and protein G. Microchim Acta 186, 169 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3282-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3282-3