Abstract
A glassy carbon electrode was modified with carbon black and CdTe quantum dots in a chitosan film to obtained a sensor for norfloxacin (NOR) in the presence of dopamine, caffeine, and uric acid. The morphological, structural and electrochemical characteristics of the nanostructured material were evaluated using spectrophotometry, X-ray diffraction, transmission electronic microscopy and voltammetry. The high electrochemical activity, fast electron transfer rate and high surface area enhanced the oxidation peak currents and shifted the peak potentials of NOR for more negative values (typically at 0.95 V vs. Ag/AgCl). Electrochemical determination of NOR was carried out using square-wave adsorptive anodic stripping voltammetry (SWAdASV). Response is linear in the 0.2 to 7.4 μmol L−1 NOR concentration range, and the detection limit is as low as 6.6 nmol L−1. The method was successfully applied to the determination of norfloxacin in pharmaceutical formulation, synthetic urine and spiked serum.

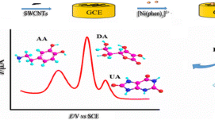
Schematic presentation of a voltammetric method using a glassy carbon electrode modified with carbon black and CdTe quantum dots in a chitosan film for the determination of norfloxacin in serum and urine samples.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Goyal RN, Rana ARS, Chasta H (2012) Electrochemical sensor for the sensitive determination of norfloxacin in human urine and pharmaceuticals. Bioelectrochemistry 83:46–51
Menday AP (2002) Symptomatic vaginal candidiasis after pivmecillinam and norfloxacin treatment of acute uncomplicated lower urinary tract infection. Int J Antimicrob Agents 20:297–300
Stein GE (1987) Review of the bioavailability and pharmacokinetics of oral norfloxacin. Am J Med 82:18–21
Bharti AR, Nally JE, Ricaldi JN, Matthias MA, Diaz MM, Lovett MA, Levett PN, Gilman RH, Willig MR, Gotuzzo E, Vinetz JM (2003) Leptospirosis: a zoonotic disease of global importance. Lancet Infect Dis 3:757–771
Drlica K (1999) Mechanism of fluoroquinolone action. Curr Opin Microbiol 2:504–508
Stratton C (1992) Fluoroquinolone antibiotics - properties of the class and individual agents. Clin Ther 14:348–375
Leeming JP, Diamond JP, Trigg R, White L, Hoh HB, Easty DL (1994) Ocular penetration of topical ciprofloxacin and norfloxacin drops and their effect upon eyelid flora. Br J Ophthalmol 78:546–548
Vilchez JL, Ballesteros O, Taoufiki J, Sanchez-Palencia G, Navalon A (2001) Determination of the antibacterial norfloxacin in human urine and serum samples by solid-phase spectrofluorimetry. Anal Chim Acta 444:279–286
Yi YN, Li GR, Wang YS, Zhou YZ, Zhu HM (2011) Simultaneous determination of norfloxacin and lomefloxacin in milk by first derivative synchronous fluorescence spectrometry using Al (III) as an enhancer. Anal Chim Acta 707:128–134
Nilghaz A, Lu X (2019) Detection of antibiotic residues in pork using paper-based microfluidic device coupled with filtration and concentration. Anal Chim Acta 1046:163–169
da Silva H, Pacheco J, Silva J, Viswanathan S, Delerue-Matos C (2015) Molecularly imprinted sensor for voltammetric detection of norfloxacin. Sensors Actuators B Chem 219:301–307
Pérez-Ruiz T, Martínez-Lozano C, Tomás V, Carpena J (1997) Determination of norfloxacin in real samples by different spectrofluorimetric techniques. Analyst 122:705–708
Kowalski C, Roliński Z, Sławik T, Głód BK (2005) Determination of norfloxacin in chicken tissues by HPLC with fluorescence detection. J Liq Chromatogr Relat Technol 28:121–135
Espinosa-Mansilla A, Pena AM, Gomez DG, Salinas F (2005) HPLC determination of enoxacin, ciprofloxacin, norfloxacin and ofloxacin with photoinduced fluorimetric (PIF) detection and multiemission scanning: application to urine and serum. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci 822:185–193
Ghoneim MM, Radi A, Beltagi AM (2001) Determination of Norfloxacin by square-wave adsorptive voltammetry on a glassy carbon electrode. J Pharm Biomed Anal 25:205–210
Huang K-J, Liu X, Xie W-Z, Yuan H-X (2008) Electrochemical behavior and voltammetric determination of norfloxacin at glassy carbon electrode modified with multi walled carbon nanotubes/Nafion. Colloids Surf B 64:269–274
Huang J-Y, Bao T, Hu T-X, Wen W, Zhang X-H, Wang S-F (2017) Voltammetric determination of levofloxacin using a glassy carbon electrode modified with poly(o-aminophenol) and graphene quantum dots. Microchim Acta 184:127–135
Santos AM, Wong A, Fatibello-Filho O (2018) Simultaneous determination of salbutamol and propranolol in biological fluid samples using an electrochemical sensor based on functionalized-graphene, ionic liquid and silver nanoparticles. J Electroanal Chem 824:1–8
Martin Santos A, Wong A, Araújo Almeida A, Fatibello-Filho O (2017) Simultaneous determination of paracetamol and ciprofloxacin in biological fluid samples using a glassy carbon electrode modified with graphene oxide and nickel oxide nanoparticles. Talanta 174:610–618
Lu L, Zhang F, Xia J, Wang Z, Liu X, Yuan Y (2015) Conductive carbon black-graphene composite for sensitive sensing of rutin. Int J Electrochem Sci 10:1646–1657
Prathish KP, Barsan MM, Geng D, Sun X, Brett CMA (2013) Chemically modified graphene and nitrogen-doped graphene: electrochemical characterisation and sensing applications. Electrochim Acta 114:533–542
Canevari TC, Cincotto FH, Gomes D, Landers R, Toma HE (2017) Magnetite nanoparticles bonded carbon quantum dots magnetically confined onto screen printed carbon electrodes and their performance as electrochemical sensor for NADH. Electroanalysis 29:1968–1975
Cincotto FH, Fava EL, Moraes FC, Fatibello-Filho O, Faria RC (2019) A new disposable microfluidic electrochemical paper-based device for the simultaneous determination of clinical biomarkers. Talanta 195:62–68
Silva TA, Moraes FC, Janegitz BC, Fatibello-Filho O (2017) Electrochemical biosensors based on nanostructured carbon black: a review. J Nanomater 2017:1–14
Wong A, Santos AM, Fatibello-Filho O (2018) Simultaneous determination of paracetamol and levofloxacin using a glassy carbon electrode modified with carbon black, silver nanoparticles and PEDOT:PSS film. Sensors Actuators B Chem 255:2264–2273
Long CM, Nascarella MA, Valberg PA (2013) Carbon black vs. black carbon and other airborne materials containing elemental carbon: physical and chemical distinctions. Environ Pollut 181:271–286
Algar WR, Tavares AJ, Krull UJ (2010) Beyond labels: a review of the application of quantum dots as integrated components of assays, bioprobes, and biosensors utilizing optical transduction. Anal Chim Acta 673:1–25
Yu KH, Lu GH, Mao S, Chen KH, Kim H, Wen ZH, Chen JH (2011) Selective deposition of CdSe nanoparticles on reduced graphene oxide to understand photoinduced charge transfer in hybrid nanostructures. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 3:2703–2709
Gu ZG, Yang SP, Li ZJ, Sun XL, Wang GL, Fang YJ, Liu JK (2011) An ultrasensitive electrochemical biosensor for glucose using CdTe-CdS core-shell quantum dot as ultrafast electron transfer relay between graphene-gold nanocomposite and gold nanoparticle. Electrochim Acta 56:9162–9167
Cincotto FH, Moraes FC, Machado SAS (2014) Graphene Nanosheets and quantum dots: a smart material for electrochemical applications. Chem Eur J 20:4746–4753
Laube N, Mohr B, Hesse A (2001) Laser-probe-based investigation of the evolution of particle size distributions of calcium oxalate particles formed in artificial urines. J Cryst Growth 233:367–374
Dey D, Nayak SK, Chopra D (2019) CHAPTER 3 Intermolecular interactions in in situ cryocrystallized compounds. In: Understanding Intermolecular Interactions in the Solid State: Approaches and Techniques. RSC, pp 98–129
Mobedi N, Marandi M, Bidaki HZ (2014) Effect of hydrazine hydrate on the luminescence properties of MPA capped CdTe nanocrystals in hot injection method. J Lumin 156:235–239
Yu WW, Qu LH, Guo WZ, Peng XG (2003) Experimental determination of the extinction coefficient of CdTe, CdSe, and CdS nanocrystals. Chem Mater 15:2854–2860
Devaraj M, Deivasigamani RK, Jeyadevan S (2013) Enhancement of the electrochemical behavior of CuO nanoleaves on MWCNTs/GC composite film modified electrode for determination of norfloxacin. Colloids Surf B 102:554–561
Madhusudana Reddy T, Balaji K, Jayarama Reddy S (2007) Voltammetric behavior of some fluorinated quinolone antibacterial agents and their differential pulse voltammetric determination in drug formulations and urine samples using a β-cyclodextrin-modified carbon-paste electrode. J Anal Chem 62:168–175
Ye Z, Wang L, Wen J (2015) A simple and sensitive method for determination of Norfloxacin in pharmaceutical preparations. Braz J Pharm Sci 51:429–437
Liu ZP, Jin ML, Cao JP, Wang J, Wang X, Zhou GF, van den Berg A, Shui LL (2018) High-sensitive electrochemical sensor for determination of Norfloxacin and its metabolism using MWCNT-CPE/pRGO-ANSA/Au. Sensors Actuators B Chem 257:1065–1075
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support granted by Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq) process number (160150/2015-9, 405546/2018-1 and 429462/2018-2) and FAPESP process number 2016/16565-5, 2016/12926-3 and 2017/10118-0.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 291 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Santos, A.M., Wong, A., Cincotto, F.H. et al. Square-wave adsorptive anodic stripping voltammetric determination of norfloxacin using a glassy carbon electrode modified with carbon black and CdTe quantum dots in a chitosan film. Microchim Acta 186, 148 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3268-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3268-1