Abstract
Three-dimensional Cu@Cu2O aerogels with excellent electrocatalytic activity were prepared and used as electrode matrix for constructing novel electrochemical glucose sensors. The aerogels were obtained by adding a fresh solution of NaBH4 into a mixture of CuCl2 and NaOH aqueous solutions under stirring at room temperature. The aerogels were assembled with Cu or Cu2O nanoparticles. The materials show superfine spongy-like structures with large surface-to-volume ratio, numerous active sites and good solubility. The Cu@Cu2O aerogels show highly efficient electrochemical activity toward glucose oxidation with a relatively low-onset potential (0.25 V) in 0.1 M NaOH solution. This non-enzymatic glucose sensor offers a low detection limit of 0.6 μM (S/N = 3), a high sensitivity (195 mA M−1 cm−2), and two wide linear ranges (0.001–5.2 mM, 5.2–17.1 mM) at a working voltage of 0.6 V (vs. Ag/AgCl) in alkaline solution. While in neutral pH values, the respective data are a linear analytical range from 0.1 to 10 mM; a detection limit of 54 μM (S/N = 3) and a sensitivity of 12 mA M−1 cm−2 at scan rate of 100 mV s−1. The sensor possesses high selectivity, good reproducibility and long-time stability. It was utilized to determine glucose levels in (spiked) human serum samples, and satisfactory results were obtained.

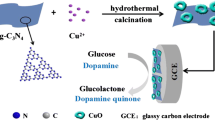
Schematic presentation of a glassy carbon electrode modified with 3D porous Cu@Cu2O aerogels. The aerogels were obtained by a reduction reaction at room temperature (Scheme 1A). The aerogel networks were used to develop a highly sensitive electrochemical sensing platform for the detection of glucose (Scheme 1B).








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pei YJ, Hu M, Tu FH, Tang XY, Huang W, Chen S, Li ZL, Xia Y (2018) Ultra-rapid fabrication of highly surface-roughened nanoporous gold film from AuSn alloy with improved performance for nonenzymatic glucose sensing. Biosens Bioelectron 117:758–765
Dhara K, Mahapatra DR (2018) Electrochemical nonenzymatic sensing of glucose using advanced nanomaterials. Microchim Acta 185(1):49
Karra S, Wooten M, Griffith W, Gorski W (2016) Morphology of gold nanoparticles and electrocatalysis of glucose oxidation. Electrochim Acta 218:8–14
Gao F, Zhou F, Yao Y, Zhang Y, Du L, Geng D, Wang P (2017) Ordered assembly of platinum nanoparticles on carbon nanocubes and their application in the non-enzymatic sensing of glucose. J Electroanal Chem 803:165–172
Nantaphol S, Watanabe T, Nomura N, Siangproh W, Chailapakul O, Einaga Y (2017) Bimetallic Pt-Au nanocatalysts electrochemically deposited on boron-doped diamond electrodes for nonenzymatic glucose detection. Biosens Bioelectron 98:76–82
Shi L, Zhu X, Liu T, Zhao H, Lan M (2016) Encapsulating Cu nanoparticles into metal-organic frameworks for nonenzymatic glucose sensing. Sensors Actuators B Chem 227:583–590
Sun S, Zhang X, Sun Y, Yang S, Song X, Yang Z (2013) Facile water-assisted synthesis of cupric oxide nanourchins and their application as nonenzymatic glucose biosensor. Acs Appl Mater Interfaces 5(10):4429–4437
Chen J, Xu Q, Shu Y, Hu X (2018) Synthesis of a novel Au nanoparticles decorated Ni-MOF/Ni/NiO nanocomposite and electrocatalytic performance for the detection of glucose in human serum. Talanta 184:136–142
Madhu R, Veeramani V, Chen SM, Manikandan A, Lo AY, Chueh YL (2015) Honeycomb-like porous carbon-cobalt oxide nanocomposite for high-performance enzyme less glucose sensor and supercapacitor applications. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7(29):15812–15820
Arachchige IU, Brock SL (2006) Sol-gel assembly of CdSe nanoparticles to form porous aerogel networks. J Am Chem Soc 128(24):7964–7971
Antonietti M, Fechler N, Fellinger TP (2014) Carbon aerogels and monoliths: control of porosity and nanoarchitecture via sol-gel routes. Chem Mater 26(1):196–210
Liu W, Herrmann AK, Bigall NC, Rodriguez P, Wen D, Oezaslan M, Schmidt TJ, Gaponik N, Eychmueller A (2015) Noble metal aerogels-synthesis, characterization, and application as electrocatalysts. Acc Chem Res 48(2):154–162
Bag S, Trikalitis PN, Chupas PJ, Armatas GS, Kanatzidis MG (2007) Porous semiconducting gels and aerogels from chalcogenide clusters. Science 317(5837):490–493
Wen D, Liu W, Haubold D, Zhu C, Oschatz M, Holzschuh M, Wolf A, Simon F, Kaskel S, Eychmueller A (2016) Gold aerogels: three-dimensional assembly of nanoparticles and their use as electrocatalytic interfaces. ACS Nano 10(2):2559–2567
Cai B, Dianat A, Huebner R, Liu W, Wen D, Benad A, Sonntag L, Gemming T, Cuniberti G, Eychmueller A (2017) Multimetallic hierarchical aerogels: shape engineering of the building blocks for efficient electrocatalysis. Adv Mater 29(11)
Zhang Y, Su L, Manuzzi D, De Los Monteros HVE, Jia W, Huo D, Hou C, Lei Y (2012) Ultrasensitive and selective non-enzymatic glucose detection using copper nanowires. Biosens Bioelectron 31(1):426–432
Huang TK, Lin KW, Tung SP, Cheng TM, Chang IC, Hsieh YZ, Lee CY, Chiu HT (2009) Glucose sensing by electrochemically grown copper nanobelt electrode. J Electroanal Chem 636(1–2):123–127
Gao Z, Liu J, Chang J, Wu D, He J, Wang K, Xu F, Jiang K (2012) Mesocrystalline Cu2O hollow nanocubes: synthesis and application in non-enzymatic amperometric detection of hydrogen peroxide and glucose. Crystengcomm 14(20):6639–6646
Ling P, Zhang Q, Cao T, Gao F (2018) Versatile three-dimensional porous Cu@Cu2O aerogel networks as electrocatalysts and mimicking peroxidases. Angew Chem Int Ed 57(23):6819–6824
Martin L, Martinez H, Poinot D, Pecquenard B, Le Cras F (2013) Comprehensive X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy study of the conversion reaction mechanism of CuO in Lithiated thin film electrodes. J Phys Chem C 117(9):4421–4430
Svintsitskiy DA, Stadnichenko AI, Demidov DV, Koscheev SV, Boronin AI (2011) Investigation of oxygen states and reactivities on a nanostructured cupric oxide surface. Appl Surf Sci 257(20):8542–8549
Ai Z, Zhang L, Lee S, Ho W (2009) Interfacial hydrothermal synthesis of Cu@Cu2O core-shell microspheres with enhanced visible-light-driven photocatalytic activity. J Phys Chem C 113(49):20896–20902
Chen F, Zhao X, Liu H, Qu J (2014) Reaction of Cu(CN)3 2− with H2O2 in water under alkaline conditions: cyanide oxidation, Cu+/Cu2+ catalysis and H2O2 decomposition. Appl Catal B Environ 158:85–90
Chusuei CC, Brookshier MA, Goodman DW (1999) Correlation of relative X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy shake-up intensity with CuO particle size. Langmuir 15(8):2806–2808
Shu J, Qiu Z, Lv S, Zhang K, Tang D (2017) Cu2+-doped SnO2 Nanograin/Polypyrrole Nanospheres with synergic enhanced properties for ultrasensitive room-temperature H2S gas sensing. Anal Chem 89(20):11135–11142
Qian Y, Ye F, Xu J, Le ZG (2012) Synthesis of cuprous oxide (Cu2O) nanoparticles/graphene composite with an excellent electrocatalytic activity towards glucose. Int J Electrochem Sci 7(10):10063–10073
Wang J, Zhang WD (2011) Fabrication of CuO nanoplatelets for highly sensitive enzyme-free determination of glucose. Electrochim Acta 56(22):7510–7516
Khan R, Ahmad R, Rai P, Jang LW, Yun JH, Yu YT, Hahn YB, Lee IH (2014) Glucose-assisted synthesis of Cu2O shuriken-like nanostructures and their application as nonenzymatic glucose biosensors. Sensors Actuators B Chem 203:471–476
Faranak F, Mansour R, Mohammad JH, Hasuck K (2018) Microwave-assisted synthesis of graphene modified CuO nanoparticles for voltammetric enzyme-free sensing of glucose at biological pH values. Microchim Acta 185(1):57
Somasekhar RC, Ilhwan P, Sungbo C (2018) Nonenzymatic determination of glucose at near neutral pH values based on the use of nafion and platinum black coated microneedle electrode array. Microchim Acta 185(5):250
Nikolaev KG, Ermakov SS, Offenhäusser A, Mourzina Y (2018) Nonenzymatic determination of glucose on electrodes prepared by directed electrochemical nanowire assembly (DENA). J Anal Chem 72(4):371–374
Thiruppathi M, Thiyagarajan N, Gopinathan M, Chang JL, Zen JM (2017) A dually functional 4-aminophenylboronic acid dimer for voltammetric detection of hypochlorite, glucose and fructose. Microchim Acta 184(10):4073–4080
Zhao YX, Li YP, He ZY, Yan ZF (2013) Facile preparation of Cu-Cu2O nanoporous nanoparticles as a potential catalyst for non-enzymatic glucose sensing. RSC Adv 3(7):2178–2181
Wang AJ, Feng JJ, Li ZH, Liao QC, Wang ZZ, Chen JR (2012) Solvothermal synthesis of Cu/Cu2O hollow microspheres for non-enzymatic amperometric glucose sensing. Crystengcomm 14(4):1289–1295
Li S, Zheng Y, Qin GW, Ren Y, Pei W, Zuo L (2011) Enzyme-free amperometric sensing of hydrogen peroxide and glucose at a hierarchical Cu2O modified electrode. Talanta 85(3):1260–1264
Acknowledgments
The funding of this work was provided by National Natural Science Foundation of China (no. 31371806 and 21575125). In addition, much thanks to The Testing Center of Yangzhou University due to all the characterizations.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Highlights
• The Cu@Cu2O aerogels were obtained with a one-step reduction method.
• The aerogel were firstly prepared to construct electrochemical glucose sensor.
• The electrochemical glucose sensor showed a wide linear range, a low detection limit and a high sensitivity in alkaline detection condition.
• This research provided a promising platform for sensing applications.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOC 311 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, Y., Yang, F., Yu, Q. et al. Three-dimensional porous Cu@Cu2O aerogels for direct voltammetric sensing of glucose. Microchim Acta 186, 192 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3263-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3263-6