Abstract
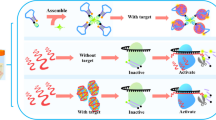
A rapid and ultrasensitive method is described for the detection of staphylococcal enterotoxin B (SEB). It is based on the formation of a dendritic DNA superstructure by integrating (a) target-induced triggering of DNA release with (b) signal amplification by a hybridization chain reaction. Partially complementary pairing of aptamer and trigger DNA forms a duplex structure. The capture DNA is then placed on the surface of a gold electrode through gold-thiol chemistry. In the presence of SEB, the aptamer-target conjugate is compelled to form. This causes the release of trigger DNA owing to a strong competition with SEB. The trigger DNA is subsequently hybridized with the partial complementary sequences of the capture DNA to trigger HCR with three auxiliary DNA sequances (referred to as H1, H2, H3). Finally, the dendritic DNA superstructure is bound to hexaammineruthenium(III) cation by electrostatic adsorption and assembled onto the modified gold electrode. This produces an amplified electrochemical signal that is measured by chronocoulometry. Under optimal conditions, the charge difference increases linearly with the logarithm of the SEB concentrations in the range from 5 pg·mL−1 to 100 ng·mL−1 with a detection limit as low as 3 pg·mL−1 (at S/N = 3).

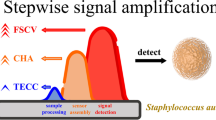
An electrochemical switching strategy is presented for the sensitive detection of Staphylococcus enterotoxin B based on target-triggered assembly of dendritic nucleic acid nanostructures.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Singh PK, Agrawal R, Kamboj DV, Gupta G, Boopathi M, Goel AK, Singh L (2010) Construction of a single-chain variable-fragment antibody against the superantigen staphylococcal enterotoxin B. Appl Environ Microbiol 76:8184–8191. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.01441-10
Nunes MM, Caldas ED (2017) Preliminary quantitative microbial risk assessment for staphylococcus enterotoxins in fresh minas cheese, a popular food in Brazil. Food Control 73:524–531. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2016.08.046
Fisher EL, Otto M, Cheung GYC (2018) Basis of virulence in enterotoxin-mediated staphylococcal food poisoning. Front Microbiol 9:436. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2018.00436
Wu LY, Gao B, Zhang F, Sun XL, Zhang YZ, Li ZJ (2013) A novel electrochemical immunosensor based on magnetosomes for detection of staphylococcal enterotoxin B in milk. Talanta 106:360–366. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2012.12.053
Pinchuk IV, Beswick EJ, Reyes VE (2010) Staphylococcal enterotoxins. Toxins 2:2177–2197. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins2082177
Wang WB, Wang WW, Liu LQ, Xu LG, Kuang H, Zhu JP, Xu CL (2016) Nanoshell-enhanced Raman spectroscopy on a microplate for staphylococcal enterotoxin B sensing. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8:15591–15597. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.6b02905
Wu SJ, Duan N, Gu HJ, Hao LL, Ye H, Gong WH, Wang ZP (2016) A review of the methods for detection of staphylococcus aureus enterotoxins. Toxins 8(7). https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8070176
Rodriguez A, Gordillo R, Andrade MJ, Cordoba JJ, Rodriguez M (2016) Development of an efficient real-time PCR assay to quantify enterotoxin-producing staphylococci in meat products. Food Control 60:302–308. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2015.07.040
Ludwig S, Jimenez-Bush I, Brigham E, Bose S, Diette G, McCormack MC, Matsui EC, Davis MF (2017) Analysis of home dust for staphylococcus aureus and staphylococcal enterotoxin genes using quantitative PCR. Sci Total Environ 581:750–755. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.01.003
Zhou DD, Xie GM, Cao XQ, Chen XP, Zhang X, Chen H (2016) Colorimetric determination of staphylococcal enterotoxin B via DNAzyme-guided growth of gold nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 183:2753–2760. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-016-1919-z
Mondal B, Ramlal S, Lavu PS, Bhavanashri N, Kingston J (2018) Highly sensitive colorimetric biosensor for staphylococcal enterotoxin B by a label-free aptamer and gold nanoparticles. Front Microbiol 9:179. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2018.00179
Andjelkovic M, Tsilia V, Rajkovic A, De Cremer K, Van Loco J (2016) Application of LC-MS/MS MRM to determine staphylococcal enterotoxins (SEB and SEA) in milk. Toxins 8:118. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8040118
Huang YK, Zhang H, Chen XJ, Wang XL, Duan N, Wu SJ, Xu BCWZP (2015) A multicolor time-resolved fluorescence aptasensor for the simultaneous detection of multiplex staphylococcus aureus enterotoxins in the milk. Biosens Bioelectron 74:170–176. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2015.06.046
Wang XL, Huang YK, Wu SJ, Duan N, Xu BC, Wang ZP (2016) Simultaneous detection of staphylococcus aureus and salmonella typhimurium using multicolor time-resolved fluorescence nanoparticles as labels. Int J Food Microbiol 237:172–179. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2016.08.028
Hwang J, Lee S, Choo J (2016) Application of a SERS-based lateral flow immunoassay strip for the rapid and sensitive detection of staphylococcal enterotoxin B. Nanoscale 8:11418–11425. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5nr07243c
Farka Z, Juriik T, Kovaar D, Trnkova L, Sklaadal P (2017) Nanoparticle-based immunochemical biosensors and assays: recent advances and challenges. Chem Rev 117:9973–10042. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrev.7b00037
Shahdordizadeh M, Taghdisi SM, Ansari N, Langroodi FA, Abnous K, Ramezani M (2017) Aptamer based biosensors for detection of Staphylococcus aureus. Sensors Actuators B Chem 241:619–635. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2016.10.088
Kumari S, Tiwari M, Das P (2019) Multi format compatible visual and fluorometric detection of SEB toxin in nanogram range by carbon dot-DNA and acriflavine nano-assembly. Sensors Actuators B Chem 279:393–399. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2018.09.110
Chen XY, Shi XP, Liu Y, Lu LX, Lu YC, Xiong X, Liu YJ, Xiong XH (2018) Impedimetric determination of staphylococcal enterotoxin B using electrochemical switching with DNA triangular pyramid frustum nanostructure. Microchim Acta 185:460. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-2983-3
Hou T, Li W, Liu XJ, Li F (2015) Label-free and enzyme-free homogeneous electrochemical biosensing strategy based on hybridization chain reaction: a facile, sensitive, and highly specific microRNA assay. Anal Chem 87:11368–11374. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.5b02790
Ge L, Wang WX, Sun XM, Hou T, Li F (2016) Affinity-mediated homogeneous electrochemical aptasensor on a graphene platform for ultrasensitive biomolecule detection via exonuclease-assisted target-analog recycling amplification. Anal Chem 88:2212–2219. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.5b03844
Wang XZ, Jiang AW, Hou T, Li HY, Li F (2015) Enzyme-free and label-free fluorescence aptasensing strategy for highly sensitive detection of protein based on target-triggered hybridization chain reaction amplification. Biosens Bioelectron 70:324–329. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2015.03.053
Huang DJ, Huang ZM, Xiao HY, Wu ZK, Tang LJ, Jiang JH (2018) Protein scaffolded DNA tetrads enable efficient delivery and ultrasensitive imaging of miRNA through crosslinking hybridization chain reaction. Chem Sci 9:4892–4897. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8sc01001c
Yan MM, Bai WH, Zhu C, Huang YF, Yan J, Chen AL (2017) Design of nuclease-based target recycling signal amplification in aptasensors. Biosens Bioelectron 77:613–623. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2015.10.015
Shuai HL, Wu X, Huang KJ, Zhai ZB (2017) Ultrasensitive electrochemical biosensing platform based on spherical silicon dioxide/molybdenum selenide nanohybrids and triggered hybridization chain reaction. Biosens Bioelectron 94:616–625. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2017.03.058
Yang DW, Tang YG, Miao P (2017) Hybridization chain reaction directed DNA superstructures assembly for biosensing applications. TrAC Trends Anal Chem 94:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2017.06.011
Shimron S, Wang F, Orbach R, Willner I (2012) Amplified detection of DNA through the enzyme-free autonomous assembly of hemin/G-quadruplex DNAzyme nanowires. Anal Chem 84:1042–1048. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac202643y
Li CX, Wang HM, Shang JH, Liu XQ, Yuan BF, Wang F (2018) Highly sensitive assay of methyltransferase activity based on an autonomous concatenated DNA circuit. ACS Sens 3:2359–2366. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssensors.8b00738
Xu N, Lei JP, Wang QB, Yang QH, Ju HX (2016) Dendritic DNA-porphyrin as mimetic enzyme for amplified fluorescent detection of DNA. Talanta 150:661–665. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2016.01.005
Temur E, Zengin A, Boyaci IH, Dudak FC, Torul H, Tamer U (2012) Attomole sensitivity of staphylococcal enterotoxin B detection using an aptamer-modified surface-enhanced Raman scattering probe. Anal Chem 84:10600–10606. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac301924f
Han JH, Kim HJ, Sudheendra L, Gee SJ, Hammock BD, Kennedy IM (2013) Photonic crystal lab-on-a-chip for detecting staphylococcal enterotoxin B at low attomolar concentration. Anal Chem 85:3104–3109. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac303016h
Xiong XH, Shi XP, Liu YJ, Lu LX, You JJ (2018) An aptamer-based electrochemical biosensor for simple and sensitive detection of staphylococcal enterotoxin B in milk. Anal Methods 10:365–370. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7ay02452e
Mudili V, Makam SS, Sundararaj N, Siddaiah C, Gupta VK, Rao PVL (2015) A novel IgY-aptamer hybrid system for cost-effective detection of SEB and its evaluation on food and clinical samples. Sci Rep 5:15151. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep15151
Acknowledgements
The project was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (No. 2018YFC1602800), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21804071), Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province of China (No. BK20180688), and the University Science Research Project of Jiangsu Province in China (16KJB550005).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 112 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, X., Liu, Y., Lu, Y. et al. Chronocoulometric aptamer based assay for staphylococcal enterotoxin B by target-triggered assembly of nanostructured dendritic nucleic acids on a gold electrode. Microchim Acta 186, 109 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3236-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3236-9