Abstract
A surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) method is described for the determination of microRNA that is associated with various forms of cancer. The substrate consists of functionalized gold-silver bimetallic structure, and the sensitivity is strongly enhanced by making use of a re-circulated enzymatic amplification system (REAS). Poly-dopamine acts as both a reductant and a protective of the substrates. It was employed to link the gold core and silver satellite. The unique “hot spots” consisting of a Au@PDA@Ag nanocomposite improve the Raman signal and sensitivity. The reductive feature of PDA can prevent the susceptible oxidation of metallic silver to maintain the high Raman activity. To improve the sensitivity of the assays, a re-circulated enzymatic amplification system was developed in which the nicking endonuclease triggers the nucleic acid reaction system to enter an amplified cycle. By integrating the bimetallic nanosubstrate and magnetic separation into the REAS, microRNA can be detected by SERS (best at the Raman band of 1586 cm−1) with a limit of detection as low as 0.2 fM. In our perception, the assay provides an exciting new avenue to study the expression of tumor genes. Thus, it holds vast promise in cancer diagnosis.

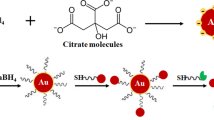
Schematic presentation of the SERS method based on poly-dopamine mediated bimetallic SERS substrate and re-circulated enzymatic amplification.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Crowley E, Di Nicolantonio F, Loupakis F, Bardelli A (2013) Liquid biopsy: monitoring cancer-genetics in the blood. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 10(8):472–484
Raymond CK, Roberts BS, Garrett-Engele P, Lim LP, Johnson JM (2005) Simple, quantitative primer-extension PCR assay for direct monitoring of microRNAs and short-interfering RNAs. RNA 11(11):1737–1744
Thomson JM, Parker J, Perou CM, Hammond SM (2004) A custom microarray platform for analysis of microRNA gene expression. Nat Methods 1(1):47–53
Zhang H, Fu CP, Yi Y, Zhou XD, Zhou CH, Ying GP, Shen YP, Zhu YF (2018) A magnetic-based SERS approach for highly sensitive and reproducible detection of cancer-related serum microRNAs. Anal Methods 10:624–633
Zhou W, Tian YF, Yin BC, Ye BC (2017) Simultaneous surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy detection of multiplexed MicroRNA biomarkers. Anal Chem 89(11):6120–6128
Driskell JD, Tripp RA (2010) Label-free SERS detection of microRNA based on affinity for an unmodified silver nanorod array substrate. Chem Commun 46(19):3298–3300
Su J, Wang D, Norbel L, Shen J, Zhao Z, Dou Y, Peng T, Shi J, Mathur S, Fan C, Song S (2017) Multicolor gold-silver Nano-mushrooms as ready-to-use SERS probes for ultrasensitive and multiplex DNA/miRNA detection. Anal Chem 89(4):2531–2538
Wang Y, Yan B, Chen L (2013) SERS tags: novel optical nanoprobes for bioanalysis. Chem Rev 113(3):1391–1428
Zhu T, Hu Y, Yang K, Dong N, Yu M, Jiang N (2017) A novel SERS nanoprobe based on the use of core-shell nanoparticles with embedded reporter molecule to detect E. coli O157:H7 with high sensitivity. Microchim Acta 185(1)
Yang K, Hu Y, Dong N (2016) A novel biosensor based on competitive SERS immunoassay and magnetic separation for accurate and sensitive detection of chloramphenicol. Biosens Bioelectron 80:373–377
Kneipp K, Kneipp H, Itzkan I, Dasari RR, Feld MS (1999) Ultrasensitive chemical analysis by Raman spectroscopy. Chem Rev 99(10):2957–2976
Campion A, Kambhampati P (1998) Surface-enhanced Raman scattering. Chem Soc Rev 27(4):241–250
Li GC, Zhang YL, Jiang J, Luo Y, Lei DY (2017) Metal-substrate-mediated Plasmon hybridization in a nanoparticle dimer for photoluminescence line-width shrinking and intensity enhancement. ACS Nano 11(3):3067–3080
Yang M, Alvarez-Puebla R, Kim HS, Aldeanueva-Potel P, Liz-Marzan LM, Kotov NA (2010) SERS-active gold lace nanoshells with built-in hotspots. Nano Lett 10(10):4013–4019
Zhao Y, Yang Y, Luo Y, Yang X, Li M, Song Q (2015) Double detection of mycotoxins based on SERS labels embedded ag@au Core–Shell nanoparticles. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7(39):21780–21786
Yang Y, Liu J, Fu ZW, Qin D (2014) Galvanic replacement-free deposition of au on ag for core-shell nanocubes with enhanced chemical stability and SERS activity. J Am Chem Soc 136(23):8153–8156
Cong Y, Xia T, Zou M, Li Z, Peng B, Guo D, Deng Z (2014) Mussel-inspired polydopamine coating as a versatile platform for synthesizing polystyrene/ag nanocomposite particles with enhanced antibacterial activities. J Mater Chem B 2(22):3450–3461
Lee H, Dellatore S, Miller W, Messersmith P (2017) Mussel-inspired surface chemistry for multifunctional coatings. Science 318(5849):426–430
Hong S, Na YS, Choi S, Song IT, Kim WY, Lee H (2012) Non-covalent self-assembly and covalent polymerization co-contribute to Polydopamine formation. Adv Funct Mater 22(22):4711–4717
Dreyer DR, Miller DJ, Freeman BD, Paul DR, Bielawski CW (2012) Elucidating the structure of poly(dopamine). Langmuir 28(15):6428–6435
Ham HO, Liu Z, Lau KHA, Lee H, Messersmith PB (2011) Facile DNA immobilization on surfaces through a catecholamine polymer. Angew Chem Int Ed 50(3):732–736
Lin LS, Cong ZX, Cao JB, Ke KM, Peng QL, Gao JH, Yang HH, Liu G, Chen XY (2014) Multifunctional Fe3O4@Polydopamine Core-Shell nanocomposites for intracellular mRNA detection and imaging-guided Photothermal therapy. ACS Nano 8(4):3876–3883
Lee H, Rho J, Messersmith PB (2009) Facile conjugation of biomolecules onto surfaces via mussel adhesive protein inspired coatings. Adv Mater 21(4):431–434
Yang JR, Tang M, Diao W, Cheng WB, Zhang Y, Yan YR (2016) Electrochemical strategy for ultrasensitive detection of microRNA based on MNAzyme-mediated rolling circle amplification on a gold electrode. Microchim Acta 183(11):3061–3067
Sang Y, Xu YJ, Xu LL, Cheng W, Li XM, Wu JL, Ding SJ (2017) Colorimetric and visual determination of microRNA via cycling signal amplification using T7 exonuclease. Microchim Acta 184(7):2465–2471
Ziegler C, Eychmüller A (2011) Seeded growth synthesis of uniform gold nanoparticles with diameters of 15−300 nm. J Phys Chem C 115(11):4502–4506
Yang K, Hu Y, Dong N, Zhu G, Zhu T, Jiang N (2017) A novel SERS-based magnetic aptasensor for prostate specific antigen assay with high sensitivity. Biosens Bioelectron 94:286–291
Xu W, Xue X, Li T, Zeng H, Liu X (2009) Ultrasensitive and selective colorimetric DNA detection by nicking endonuclease assisted nanoparticle amplification. Angew Chem Int Ed 48(37):6849–6852
Calin GA, Croce CM (2006) MicroRNA signatures in human cancers. Nat Rev Cancer 6(11):857–866
Borghei YS, Hosseini M, Ganjali MR, Ju H (2018) Colorimetric and energy transfer based fluorometric turn-on method for determination of microRNA using silver nanoclusters and gold nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 185(6):286
Zheng J, Bai JHQF, Li JS, Li YH, Yang JF, Yang RH (2015) DNA-templated in situ growth of AgNPs on SWNTs: a new approach for highly sensitive SERS assay of microRNA. Chem Commun 51(2015):6552–6555
Oishi M, Sugiyama S (2016) An efficient particle-based DNA circuit system: catalytic disassembly of DNA/PEG-modified gold nanoparticle-magnetic bead composites for colorimetric detection of miRNA. Small 12(37):5153–5158
Rafiee-Pour HA, Behpour M, Keshavarz M (2016) A novel label-free electrochemical miRNA biosensor using methylene blue as redox indicator: application to breast cancer biomarker miRNA-21. Biosens Bioelectron 77:202–207
Roy S, Soh JH, Gao Z (2011) A microfluidic-assisted microarray for ultrasensitive detection of miRNA under an optical microscope. Lab Chip 11(11):1886–1894
Acknowledgements
This research has been supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) (Grant nos. 21273083 and U1732146) and the Project under Scientific and Technological Planning Grant nos. 201805010002 by Guangzhou City.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOC 4.08 mb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, N., Hu, Y., Wei, W. et al. Detection of microRNA using a polydopamine mediated bimetallic SERS substrate and a re-circulated enzymatic amplification system. Microchim Acta 186, 65 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-3174-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-3174-y