Abstract
A fibrous magnetic boron nitride nanocomposite was synthesized and is shown to be a viable adsorbent for the magnetic solid phase extraction of pesticides prior to their quantitation by gas chromatography with electron capture detection. The optimum conditions were obtained by both single factor optimization and response surface analysis (Box-Behnken design). Under the optimized conditions, the response to the ten pesticides (dicofol, α-endosulfan, p,p’-DDE, nitrofen, β-endosulfan, p,p’-DDD, p,p’-DDT, bifenthrin, permethrin and fenvalerate) is linear in the 0.03–40 ng·mL−1 concentration range with the coefficients of determination ranging from 0.9970 to 0.9992. The relative standard deviations at concentration levels of 0.5 ng·mL−1, 20 ng·mL−1 and 40 ng·mL−1 were below 8.7%. The recoveries of the analytes from spiked tea water and tea beverage samples varied between 84.5% and 122%, with relative standard deviations ranging from 4.8 to 12%. The limits of detection are between 0.01 and 0.05 ng·mL−1. The adsorbent can be reused over 50 times without significant loss of extraction efficiency.

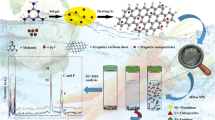
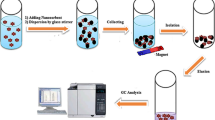
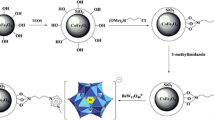
A novel fibrous-shape magnetic boron nitride nanocomposite (Fe3O4@f-BN) was used as the adsorbent for the magnetic solid phase extraction (MSPE) of ten pesticides from tea water and tea beverage samples prior to their determination by gas chromatography (GC).


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liu D, Min S (2012) Rapid analysis of organochlorine and pyrethroid pesticides in tea samples by directly suspended droplet microextraction using a gas chromatography-electron capture detector. J Chromatogr A 1235:166–173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2012.02.070
Lozano A, Rajski L, Belmonte-Valles N, Ucles A, Ucles S, Mezcua M, Fernandez-Alba AR (2012) Pesticide analysis in teas and chamomile by liquid chromatography and gas chromatography tandem mass spectrometry using a modified QuEChERS method: validation and pilot survey in real samples. J Chromatogr A 1268:109–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2012.10.013
Cao Y, Tang H, Chen D, Li L (2015) A novel method based on MSPD for simultaneous determination of 16 pesticide residues in tea by LC-MS/MS. J Chromatogr B Anal Technol Biomed Life Sci 998-999:72–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchromb.2015.06.013
Ji J, Deng C, Zhang H, Wu Y, Zhang X (2007) Microwave-assisted steam distillation for the determination of organochlorine pesticides and pyrethroids in Chinese teas. Talanta 71(3):1068–1074. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2006.05.087
Zeng Y, Li B, Ma W, Zhou K, Fan H, Wang H (2011) Discussion on current pollution status and legislation of environmental hormone in China. Procedia Environ Sci 11:1267–1277. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proenv.2011.12.190
Mehdinia A, Einollahi S, Jabbari A (2016) Magnetite nanoparticles surface-modified with a zinc(II)-carboxylate Schiff base ligand as a sorbent for solid-phase extraction of organochlorine pesticides from seawater. Microchim Acta 183(9):2615–2622. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-016-1894-4
Chen G, Cao P, Liu R (2011) A multi-residue method for fast determination of pesticides in tea by ultra performance liquid chromatography–electrospray tandem mass spectrometry combined with modified QuEChERS sample preparation procedure. Food Chem 125(4):1406–1411. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2010.10.017
Huo F, Tang H, Wu X, Chen D, Zhao T, Liu P, Li L (2016) Utilizing a novel sorbent in the solid phase extraction for simultaneous determination of 15 pesticide residues in green tea by GC/MS. J Chromatogr B Anal Technol Biomed Life Sci 1023-1024:44–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchromb.2016.04.053
Zhou Q, Zhu L, Xia X, Tang H (2016) The water-resistant zeolite imidazolate framework 67 is a viable solid phase sorbent for fluoroquinolones while efficiently excluding macromolecules. Microchim Acta 183(6):1839–1846. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-016-1814-7
Asgharinezhad AA, Ebrahimzadeh H (2016) A simple and fast method based on mixed hemimicelles coated magnetite nanoparticles for simultaneous extraction of acidic and basic pollutants. Anal Bioanal Chem 408(2):473–486. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-015-9114-3
Aziz-Zanjani MO, Mehdinia A (2014) A review on procedures for the preparation of coatings for solid phase microextraction. Microchim Acta 181(11–12):1169–1190. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-014-1265-y
Farajzadeh MA, Mohebbi A (2018) Development of magnetic dispersive solid phase extraction using toner powder as an efficient and economic sorbent in combination with dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction for extraction of some widely used pesticides in fruit juices. J Chromatogr A 1532:10–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2017.11.048
Santos LO, Anjos JP, Ferreira SLC, Andrade JB (2017) Simultaneous determination of PAHS, nitro-PAHS and quinones in surface and groundwater samples using SDME/GC-MS. Microchem J 133:431–440. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2017.04.012
Safari M, Yamini Y, Tahmasebi E, Latifeh F (2015) Extraction and preconcentration of formaldehyde in water by polypyrrole-coated magnetic nanoparticles and determination by high-performance liquid chromatography. J Sep Sci 38(19):3421–3427. https://doi.org/10.1002/jssc.201500420
Dargahi R, Ebrahimzadeh H, Asgharinezhad AA, Hashemzadeh A, Amini MM (2018) Dispersive magnetic solid-phase extraction of phthalate esters from water samples and human plasma based on a nanosorbent composed of MIL-101(Cr) metal-organic framework and magnetite nanoparticles before their determination by GC-MS. J Sep Sci 41(4):948–957. https://doi.org/10.1002/jssc.201700700
Yang R, Liu Y, Yan X, Liu S (2016) Simultaneous extraction and determination of phthalate esters in aqueous solution by yolk-shell magnetic mesoporous carbon-molecularly imprinted composites based on solid-phase extraction coupled with gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Talanta 161:114–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2016.08.037
Safari M, Yamini Y, Mani-Varnosfaderani A, Asiabi H (2016) Synthesis of Fe3O4@PPy–MWCNT nanocomposite and its application for extraction of ultra-trace amounts of PAHs from various samples. J Iran Chem Soc 14(3):623–634. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13738-016-1012-x
Asgharinezhad AA, Ebrahimzadeh H (2015) Coextraction of acidic, basic and amphiprotic pollutants using multiwalled carbon nanotubes/magnetite nanoparticles@polypyrrole composite. J Chromatogr A 1412:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2015.07.087
Jiao C, Ma R, Li M, Hao L, Wang C, Wu Q, Wang Z (2017) Magnetic cobalt-nitrogen-doped carbon microspheres for the preconcentration of phthalate esters from beverage and milk samples. Microchim Acta 184(8):2551–2559. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2251-y
Lin J, Xu L, Huang Y, Li J, Wang W, Feng C, Liu Z, Xu X, Zou J, Tang C (2016) Ultrafine porous boron nitride nanofibers synthesized via a freeze-drying and pyrolysis process and their adsorption properties. RSC Adv 6(2):1253–1259. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5ra23426c
Huang C, Chen C, Zhang M, Lin L, Ye X, Lin S, Antonietti M, Wang X (2015) Carbon-doped BN nanosheets for metal-free photoredox catalysis. Nat Commun 6:7698-7704. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms8698
Fei H, Ye R, Ye G, Gong Y, Peng Z, Fan X, Samuel ELG, Ajayan PM, Tour JM (2014) Boron- and Nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dots/graphene hybrid nanoplatelets as efficient electrocatalysts for oxygen reduction. ACS Nano 8(10):10837–10843. https://doi.org/10.1021/nn504637y
Duan Z, Liu Y, Xie X, Ye X, Zhu X (2016) h-BN nanosheets as 2D substrates to load 0D Fe3O4 nanoparticles: a hybrid anode material for lithium-ion batteries. Chemistry-An Asian J 11(6):828–833. https://doi.org/10.1002/asia.201501439
Kiho K, Hyun J, Jooheon K (2016) Surface modification of BN/Fe3O4 hybrid particle to enhance interfacial affinity for high thermal conductive material. Polymer 91:74–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymer.2016.03.066
Wu Q, Cheng S, Li Z, Chen H (2016) Highly sensitive mass spectrometric detection of flunitrazepam using magnetic graphene framework enrichment. Anal Methods 8(32):6168–6175. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6ay01280a
Zang X, Chang Q, Hou M, Wang C, Wang Z (2015) Graphene grafted magnetic microspheres for solid phase extraction of bisphenol A and triclosan from water samples followed by gas chromatography-mass spectrometric analysis. Anal Methods 7(20):8793–8800. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5ay01578b
Song T, Yu C, He X, Lin J, Liu Z, Yang X, Zhang Y, Huang Y, Tang C (2018) Synthesis of magnetically separable porous BN microrods@Fe3O4 nanocomposites for Pb(II) adsorption. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 537:508–515. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2017.10.060
Stefanelli P, Santilio A, Cataldi L, Dommarco R (2009) Multiresidue analysis of organochlorine and pyrethroid pesticides in ground beef meat by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. J Environ Sci Health, Part B 44(4):350–356. https://doi.org/10.1080/03601230902801000
Gao L, Chen L (2013) Preparation of magnetic carbon nanotubes for separation of pyrethroids from tea samples. Microchim Acta 18:423–430. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-013-0947-1
Wu L, Song C, Zhao Y, He Z, Zhou G, Lu W, Wang B (2015) Determination of organochlorine pesticides in tea beverage by directly suspended droplet microextraction combined with GC-ECD. Food Anal Methods 8(1): 147–153. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-014-9882-y
Acknowledgements
Financial supports from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31471643, 31571925 and 31671930), the Hebei “Double First Class Discipline” Construction Foundation for the Discipline of Food Science and Engineering of Hebei Agricultural University (2016SPGCA18), the Natural Science Foundation of Hebei Province (C2018204076), the Youth Scientific and Technological Research Foundation of the Department of Education of Hebei for Hebei Provincial Universities (QN2017085) and the Natural Science Foundation of Agricultural University of Hebei (LG201810) are gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOC 1936 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pang, Y., Zang, X., Wang, M. et al. Fibrous boron nitride nanocomposite for magnetic solid phase extraction of ten pesticides prior to the quantitation by gas chromatography. Microchim Acta 185, 561 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-3103-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-3103-0