Abstract
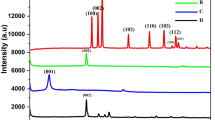
A glassy carbon electrode (GCE) was modified by electropolymerization of curcumin on MnO2-Gr nanosheets to obtain a detection method for Hg(II) and for the anions fluoride and cyanide. The complexation by curcumin can be monitored by potentiometry. The results revealed a cathodic shift for the simultaneous detection of fluoride and cyanide and an anodic shift for the mercury(II) sensing, with peak potentials of −0.24, 0.12 and 0.82 V, respectively (vs. Ag/AgCl). The modified GCE is fairly selective, reproducible and repeatable. The detection limits are 19.2 nM for Hg(II), 17.2 nM for fluoride, and 28.3 nM for cyanide (LOD, S/N = 3). The method was successfully applied to the analysis of spiked samples of tap water, river water and petrochemical refinery wastewater.

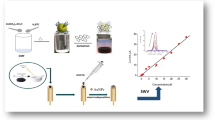
Schematic of an electrochemical curcumin-MnO2-graphene nanosheet platform for the simultaneous assay of fluoride, cyanide and mercury(II) in the ppb concentration range in various natural and wastewater samples.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kruse P (2018) Review on water quality sensors. J Phys D Appl Phys 51:203002
Schwarzenbach RP, Egli T, Hofstetter TB, Gunten UV, Wehrli B (2010) Global water pollution and human health. Annu Rev Environ Resour 35:109–136
Zulkifli SN, Abdulrahim H, Lau WJ (2018) Detection of contaminants in water supply: a review on state-of-the-art monitoring technologies and their applications. Sensor Actuat B-Chem 255:2657–2689
Hanrahan G, Patil DG, Wang J (2004) Electrochemical sensors for environmental monitoring: design, development and applications. J Environ Monit 6:657–664
Wang Q, Kim D, Dionysiou D, Sorial G, Timberlake D (2004) Sources and remediation for mercury contamination in aquatic systems – a literature review. Environ Pollut 131:323–336
Kjeldsen P (1999) Behaviour of cyanides in soil and groundwater: a review. Water Air Soil Pollut 115:279–308
González-Horta C, Ballinas-Casarrubias L, Sánchez-Ramírez B, Ishida MC, Barrera-Hernández A, Gutiérrez-Torres D, Zacarias OL, Saunders RJ, Drobná Z, Mendez MA, García-Vargas G, Loomis D, Stýblo M, Del Razo LM (2015) A concurrent exposure to arsenic and fluoride from drinking water in Chihuahua, Mexico. Int J Environ Res Public Health 12:4587–4601
Karmakar A, Kumar N, Samanta P, Desai AV, Ghosh SK (2016) A post-synthetically modified MOF for selective and sensitive aqueous-phase detection of highly toxic cyanide ions. Chem Eur J 22:864–868
Frisbie SH, Mitchell EJ, Sarkar B (2015) Urgent need to revaluate the latest World Health Organization guidelines for toxic inorganic substances in drinking water. Environ Health 14:1–15
Ratner N, Mandler D (2015) Electrochemical detection of low concentrations of mercury in water using gold nanoparticles. Anal Chem 87:5148–5155
Borthakur P, Darabdhara G, Das MR, Boukherroub R, Szunerits S (2017) Solvothermal synthesis of CoS/reduced porous graphene oxidenanocomposite for selective colorimetric detection of Hg(II) ion inaqueous medium. Sens Actuat B-Chem 244:684–692
Wan L, Shu Q, Zhu J, Jin S, Li N, Chen X, Chen S (2016) A new multifunctional Schiff-based chemosensor for mask free fluorimetric and colorimetric sensing of F− and CN. Talanta 152:39–44
Shu Q, Birlenbach L, Schmittel M (2012) A bis(ferrocenyl)phenanthroline iridium (III) complex as a Lab-on-a-molecule for cyanide and fluoride in aqueous solution. Inorg Chem 51:13123–13127
Amjadi M, Hassanzadeh J, Manzoori JL (2014) Determination of cyanide using a chemiluminescencesystem composed of permanganate, rhodamine B, and gold nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 181:1851–1856
Amalraj A, Pius A, Gopi S, Gopi S (2017) Biological activities of curcuminoids, other biomolecules from turmeric and their derivatives – A review. J Tradit Complement Med 7:205–233
Ponnuvel K, Santhiya K, Padmini V (2016) Curcumin based chemosensor for selective detection of fluoride and cyanide anions in aqueous media. Photochem Photobiol Sci 15:1536–1543
Wu FY, Sun MZ, Xiang YL, Wu YM, Tong DQ (2010) Curcumin as a colorimetric and fluorescent chemosensor for selective recognition of fluoride ion. J Lumin 130:304–308
Pourreza N, Golmohammadi H, Rastegarzadeh S (2016) Highly selective and portable chemosensor for mercury determination in water samples using curcumin nanoparticles in a paper based analytical device. RSC Adv 6:69060–69066
Feng X, Zhang Y, Song J, Chen N, Zhou J, Huang Z, Ma Y, Zhang L, Wang L (2014) MnO2/graphene nanocomposites for nonenzymatic electrochemical detection of hydrogen peroxide. Electroanalysis 26:1–8
Mars A, Hamami M, Bechnak L, Patra D, Raouafi N (2018) Curcumin-graphene quantum dots for dual mode sensing platform : electrochemical and fluorescence detection of APOe4, responsible of Alzheimer’s disease. Anal Chim Acta, in press 1036:141–146
Devadas B, Rajkumar M, Chen SC (2014) Electropolymerization of curcumin on glassy carbon electrode and its electrocatalytic application for the voltammetric determination of epinephrine and p-acetoaminophenol. Colloid Surface B 116:674–680
Naumis GG, Barraza-Lopez S, Oliva-Leyva M, Terrones H (2017) Electronic and optical properties of strained graphene and other strained 2D materials: a review. Rep Prog Phys 80:1–63
Kuila T, Bose S, Khanra P, Mishra AK, Kim NH, Lee JH (2011) Recent advances in graphene-based biosensors. Biosens Bioelectron 26:4637–4648
Shao Y, Wang J, Wu H, Liu J, Aksay IA, Lin Y (2010) Graphene based electrochemical sensors and biosensors: a review. Electroanalysis 22:1027–1036
Qui G, Huang H, Dharmarathna S, Benbow E, Stafford L, Suib SL (2011) Hydrothermal synthesis of manganese oxide nanomaterials and their catalytic and electrochemical properties. Chem Mater 23:3892–3901
Zhang J, Jiang J, Zhao XS (2011) Synthesis and capacitive properties of manganese oxide nanosheets dispersed on functionalized graphene sheets. J Phys Chem C 115:6448–6454
Patil SK, Ghosh R, Kennedy P, Mobin SM, Das D (2016) Potential anion sensing properties by a redox and substitution series of [Ru(bpy)3-n(Hdpa)n]2+,n=1-3; Hdpa=2,2′-dipyridylamine: selectiverecognition and stoichiometric binding with cyanide and fluoride ions. RSC Adv 6(67):62310–62319
Beer PD, Chen Z, Drew MGB, Pilgrim AJ (1994) Electrochemical recognition of group 1 and 2 metal cations by redox-active ionophores. Inorg Chim Acta 225:137–144
Puneet P, Vedarajan R, Matsumi N (2016) Alternating poly(borosiloxane) for solid state Ultrasensitivity toward fluoride ions in aqueous media. ACS Sens 1(10):1198–1202
Bhanjana G, Dilbaghi N, Bhalla V, Kim K-H, Kumar S (2017) Direct ultrasensitive redox sensing of mercury using a nanogold platform. J Mol Liq 225:598–605
Lee S, Nam YS, Choi SH, Lee Y, Lee KB (2016) Highly sensitive photometric determination of cyanide based on selective etching of gold nanorods. Microchim Acta 183:3035–3041
Yin Z, Wu J, Yang Z (2010) A sensitive mercury (II) sensor based on CuO nanoshuttles/poly(thionine) modified glassy carbon electrode. Microchim Acta 170:307–312
Gu JA, Lin YJ, Chia YM, Lin HY, Huang ST (2013) Colorimetric and bare-eye determination of fluoride using gold nanoparticle agglomeration probes. Microchim Acta 180:801–806
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to thank the Tunisian Ministry of High Education and Scientific Research for financial support of this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 1.36 mb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mejri, A., Mars, A., Elfil, H. et al. Graphene nanosheets modified with curcumin-decorated manganese dioxide for ultrasensitive potentiometric sensing of mercury(II), fluoride and cyanide. Microchim Acta 185, 529 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-3064-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-3064-3