Abstract
A sensitive aptamer/protein binding-triggered sandwich assay for thrombin is described. It is based on electrochemical-chemical-chemical redox cycling using a glassy carbon electrode (GCE) that was modified with WSe2 and gold nanoparticles (AuNPs). The AuNPs are linked to thrombin aptamer 1 via Au-S bonds. Thrombin is first captured by aptamer 1 and then sandwiched through the simultaneous interaction with AuNPs modified with thrombin-specific aptamer 2 and signalling probe. Subsequently, the DNA-linked AuNP hybrids result in the capture of streptavidin-conjugated alkaline phosphatase onto the modified GCE through the specific affinity reaction for further signal enhancement. As a result, a linear range of 0–1 ng mL−1 and a detection limit as low as 190 fg mL−1 are accomplished. The specificity for thrombin is excellent. Conceivably, this strategy can be easily expanded to other proteins by using the appropriate aptamer.

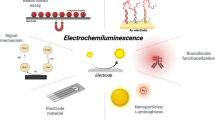
Schematic presentation of an electrochemical biosensor for thrombin based on WSe2 and gold nanoparticles, aptamer-thrombin-aptamer sandwiching, redox cycling, and signal enhancement by alkaline phosphatase.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tan Z, Feagin TA, Heemstra JM (2016) Temporal control of aptamer biosensors using covalent self-caging to shift equilibrium. J Am Chem Soc 138(20):6328–6331. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.6b00934
Bock LC, Griffin LC, Latham JA, Vermaas EH, Toole JJ (1992) Selection of single-stranded DNA molecules that bind and inhibit human thrombin. Nature 355(6360):564–566. https://doi.org/10.1038/355564a0
Zhang Y, Xia J, Zhang F, Wang Z, Liu Q (2018) Ultrasensitive label-free homogeneous electrochemical aptasensor based on sandwich structure for thrombin detection. Sensors Actuators B Chem 267:412–418. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2018.04.053
Yang Y, Yang Z, Lv J, Yuan R, Chai Y (2017) Thrombin aptasensor enabled by Pt nanoparticles-functionalized co-based metal organic frameworks assisted electrochemical signal amplification. Talanta 169:44–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2017.03.037
He B (2018) Sandwich electrochemical thrombin assay using a glassy carbon electrode modified with nitrogen-and sulfur-doped graphene oxide and gold nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 185(7):344. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-2872-9
Li Y, Li Y, Xu N, Pan J, Chen T, Chen Y, Gao W (2017) Dual-signal amplification strategy for electrochemiluminescence sandwich biosensor for detection of thrombin. Sensors Actuators B Chem 240:742–748. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2016.09.043
Wang X, Sun D, Tong Y, Zhong Y, Chen Z (2017) A voltammetric aptamer-based thrombin biosensor exploiting signal amplification via synergetic catalysis by DNAzyme and enzyme decorated AuPd nanoparticles on a poly (o-phenylenediamine) support. Microchim Acta 184(6):1791–1799. https://doi.org/10.1007/s0060
Zhao X, Li S, Xu L, Ma W, Wu X, Kuang H, Xu C (2015) Up-conversion fluorescence “off-on” switch based on heterogeneous core-satellite assembly for thrombin detection. Biosens Bioelectron 70:372–375. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2015.03.068
Liang G, Cai S, Zhang P, Peng Y, Chen H, Zhang S, Kong J (2011) Magnetic relaxation switch and colorimetric detection of thrombin using aptamer-functionalized gold-coated iron oxide nanoparticles. Anal Chim Acta 689(2):243–249. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2011.01.046
Chen YX, Zhang WJ, Huang KJ, Zheng M, Mao YC (2017) An electrochemical microRNA sensing platform based on tungsten diselenide nanosheets and competitive RNA-RNA hybridization. Analyst 142(24):4843–4851. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7an01244f
Karfa P, Madhuri R, Sharma PK (2017) Multifunctional fluorescent chalcogenide hybrid nanodots (MoSe2: CdS and WSe2: CdS) as electro catalyst (for oxygen reduction/oxygen evolution reactions) and sensing probe for lead. J Mater Chem A 5(4):1495–1508. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6TA08172J
Xu Q, Wang G, Zhang M, Xu G, Lin J, Luo X (2018) Aptamer based label free thrombin assay based on the use of silver nanoparticles incorporated into self-polymerized dopamine. Microchim Acta 185(5):253. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-2787-5
Shuai HL, Huang KJ, Xing LL, Chen YX (2016) Ultrasensitive electrochemical sensing platform for microRNA based on tungsten oxide-graphene composites coupling with catalyzed hairpin assembly target recycling and enzyme signal amplification. Biosens Bioelectron 86:337–345. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2016.06.057
Zhang H, Guo Z, Dong H, Chen H, Cai C (2017) An electrochemiluminescence assay for sensitive detection of methyltransferase activity in different cancer cells by hybridization chain reaction coupled with a G-quadruplex/hemin DNAzyme biosensing strategy. Analyst 142(11):2013–2019. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7AN00486A
Wang W, Xu DD, Pang DW, Tang HW (2017) Fluorescent sensing of thrombin using a magnetic nano-platform with aptamer-target-aptamer sandwich and fluorescent silica nanoprobe. J Lumin 187:9–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jlumin.2017.02.059
Wang XQ, Chen YF, Qi F, Zheng BJ, He JR, Li Q, Li PJ, Zhang WL, Li YR (2016) Interwoven WSe 2 /CNTs hybrid network: A highly efficient and stable electrocatalyst for hydrogen evolution. Electrochem Commun 72:74–78
Zou ML, Zhang JF, Zhu H, Du ML, Wang QF, Zhang M, Zhang XW (2015) A 3D dendritic WSe2catalyst grown on carbon nanofiber mats for efficient hydrogen evolution. J Mater Chem A 3:12149–12153
Henckel DA, Lenz O, Cossairt BM (2017) Effect of Ligand Coverage on Hydrogen Evolution Catalyzed by Colloidal WSe2. ACS Catal 7:2815–2820
Wang XQ, Chen YF, Zheng BJ, Qi F, He JR, Li Q, Li PJ, Zhang WL (2017) Graphene-like WSe 2 nanosheets for efficient and stable hydrogen evolution. J Alloys Compd 691:698–704
Hussain S, Patil SA, Vikraman D, Arbab AA, Jeong SH, Kim HS, Jung J (2017) Growth of a WSe 2 /W counter electrode by sputtering and selenization annealing for high-efficiency dye-sensitized solar cells. Appl Surf Sci 406:84–90
Chen YX, Zhang WJ, Huang KJ, Zheng Ming B, Mao YC (2017) An electrochemical microRNA sensing platform based on tungsten diselenide nanosheets and competitive RNA–RNA hybridization. Analyst 142:4843–4851. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7an01244f
Wang X, Chen Y, Zheng B, Qi F, He J, Li Q, Zhang W (2017) Graphene-like WSe2 nanosheets for efficient and stable hydrogen evolution. J Alloy Compd 691:698–704. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.08.305
Chen YX, Huang KJ, Lin F, Fang LX (2017) Ultrasensitive electrochemical sensing platform based on graphene wrapping SnO2 nanocorals and autonomous cascade DNA duplication strategy. Talanta 175:168–176. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2017.07.042
Radi AE, Acero Sánchez JL, Baldrich E, O'Sullivan CK (2005) Reusable impedimetric aptasensor. Anal Chem 77(19):6320–6323. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac0505775
Wang Y, Zhang Y, Yan T, Fan D, Du B, Ma H, Wei Q (2016) Ultrasensitive electrochemical aptasensor for the detection of thrombin based on dual signal amplification strategy of Au@GS and DNA-CoPd NPs conjugates. Biosens Bioelectron 80:640–646. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2016.02.042
Zheng Y, Yuan Y, Chai Y, Yuan R (2015) A label-free electrochemical aptasensor based on the catalysis of manganese porphyrins for detection of thrombin. Biosens Bioelectron 66:585–589. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2014.12.022
Yang J, Dou B, Yuan R, Xiang Y (2016) Proximity binding and metal ion-dependent DNAzyme cyclic amplification-integrated aptasensor for label-free and sensitive electrochemical detection of thrombin. Anal Chem 88(16):8218–8223. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.6b02035
Umrao S, Jain V, Chakraborty B, Roy R (2018) Protein-induced fluorescence enhancement as aptamer sensing mechanism for thrombin detection. Sensors Actuators B Chem 267:294–301. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2018.04.039
Cao Y, Wang Z, Cao J, Mao X, Chen G, Zhao J (2017) A general protein aptasensing strategy based on untemplated nucleic acid elongation and the use of fluorescent copper nanoparticles: application to the detection of thrombin and the vascular endothelial growth factor. Microchim Acta 184:3697–3704. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2393-y
He J, Li G, Hu Y (2017) Aptamer-involved fluorescence amplification strategy facilitated by directional enzymatic hydrolysis for bioassays based on a metal-organic framework platform: highly selective and sensitive determination of thrombin and oxytetracycline. Microchim Acta 184:2365–2373. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2263-7
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21475115), Henan Provincial Science and technology innovation team (C20150026), Nanhu Scholars Program of XYNU and Henan Science and Technology Cooperation Project (172106000064).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOC 375 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, YH., Xia, H., Huang, KJ. et al. Ultrasensitive determination of thrombin by using an electrode modified with WSe2 and gold nanoparticles, aptamer-thrombin-aptamer sandwiching, redox cycling, and signal enhancement by alkaline phosphatase. Microchim Acta 185, 502 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-3028-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-3028-7