Abstract
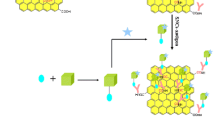
A composite consisting of graphene oxide and gold nanorods (GO-GNRs) was designed for the trace determination of hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) using surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS). GO contains numerous carboxy and hydroxy groups on its surface and therefore can serve as the substrate for decoration with GNRs and for immobilizing antibody against HBsAg. The GNRs (carrying the SERS probe 2-mercaptopyridine) exhibit high SERS activity, and this improves the sensitivity of the biosensor. The antibody on the GO-GNRs binds HBsAg with high specificity, and it results in excellent selectivity. The SERS signal (measured at 1002 cm−1) increases in the 1–1000 pg·mL−1 HBsAg concentrations range, and the limit of detection is 0.05 pg·mL−1 (at an S/N ratio of 3). The immunoassay achieves the sensitive and selective determination of HBsAg in serum and expands the potential application of GO-GNR based SERS tag in clinical research.

A novel graphene oxide-gold nanorod (GO-GNRs) based surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) tag for immunoassay was designed. It allows for sensitive and selective determination of HBsAg in serum. The method is expected to expand the potential application in the environment, in medicine and in food analysis.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yildiz U, Inci F, Wang S, Toy M, Tekin H, Javaid A, Lau D, Demirci U (2015) Recent advances in micro/nanotechnologies for global control of hepatitis B infection. Biotechnol Adv 33(1):178–190
Xi Z, Huang R, Li Z, He N, Wang T, Su E, Deng Y (2015) Selection of HBsAg-specific DNA aptamers based on Carboxylated magnetic nanoparticles and their application in the rapid and simple detection of hepatitis B virus infection. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7(21):11215–11223
Xiang Q, Huang J, Huang H, Mao W, Ye Z (2018) A label-free electrochemical platform for the highly sensitive detection of hepatitis B virus DNA using graphene quantum dots. RSC Adv 8(4):1820–1825
Li X, Zhang S, Yu Z, Yang T (2014) Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopic analysis of Phorate and Fenthion pesticide in apple skin using silver nanoparticles. Appl Spectrosc 68(4):483–487
Hakonen A, Svedendahl M, Ogier R, Yang Z-J, Lodewijks K, Verre R, Shegai T, Andersson PO, Käll M (2015) Dimer-on-mirror SERS substrates with attogram sensitivity fabricated by colloidal lithography. Nanoscale 7(21):9405–9410
Yang D, Chen S, Huang P, Wang X, Jiang W, Pandoli O, Cui D (2010) Bacteria-template synthesized silver microspheres with hollow and porous structures as excellent SERS substrate. Green Chem 12(11):2038–2042
Wang X, Yang D, Huang P, Li M, Li C, Chen D, Cui D (2012) Hierarchically assembled au microspheres and sea urchin-like architectures: formation mechanism and SERS study. Nanoscale 4(24):7766–7772
Cowcher DP, Xu Y, Goodacre R (2013) Portable, quantitative detection of Bacillus bacterial spores using surface-enhanced Raman scattering. Anal Chem 85(6):3297–3302
Chan T, Liu T, Wang K, Tsai K, Chen Z, Chang Y, Tseng Y, Wang C, Wang J, Wang (2015) SERS detection of biomolecules by highly sensitive and reproducible Raman-enhancing nanoparticle array. Nanoscale Res Lett 12(1):344
Qiu Z, Shu J, Tang D (2018) Near-infrared-to-ultraviolet light-mediated Photoelectrochemical Aptasensing platform for Cancer biomarker based on Core–Shell NaYF4:Yb,tm@TiO2 Upconversion microrods. Anal Chem 90(1):1021–1028
Shu J, Qiu Z, Lv S, Zhang K, Tang D (2018) Plasmonic enhancement coupling with defect-engineered TiO2–x: a mode for sensitive Photoelectrochemical biosensing. Anal Chem 90(4):2425–2429
Lin Y, Zhou Q, Tang D (2017) Dopamine-loaded liposomes for in-situ amplified Photoelectrochemical immunoassay of AFB1 to enhance photocurrent of Mn2+-doped Zn3(OH)2V2O7 Nanobelts. Anal Chem 89(21):11803–11810
Shu J, Tang D (2017) Current advances in quantum-dots-based Photoelectrochemical immunoassays. Chem Asian J 12(21):2780–2789
Song C, Min L, Zhou N, Yang Y, Su S, Huang W, Wang L (2014) Synthesis of novel gold Mesoflowers as SERS tags for immunoassay with improved sensitivity. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 6(24):21842–21850
Kamińska A, Witkowska E, Winkler K, Dzięcielewski I, Weyher JL, Waluk J (2015) Detection of hepatitis B virus antigen from human blood: SERS immunoassay in a microfluidic system. Biosens Bioelectron 66:461–467
Zengin A, Tamer U, Caykara T (2017) SERS detection of hepatitis B virus DNA in a temperature-responsive sandwich-hybridization assay. J Raman Spectrosc 48(5):668–672
Gao W, Li B, Yao R, Li Z, Wang X, Dong X, Zhou B (2017) Intuitive label-free SERS detection of Bacteria using aptamer-based in situ ag nanoparticles synthesis. Anal Chem 89(18):9836–9842
Zhou H, Yang D, Ivleva N-P, Mircescu N-E, Niessner R, Haisch C (2014) SERS detection of Bacteria in water by in situ coating with ag nanoparticles. Anal Chem 86(3):1525–1533
Alula MT, Krishnan S, Hendricks NR, Karamchand L, Blackburn JM (2017) Identification and quantitation of pathogenic bacteria via in-situ formation of silver nanoparticles on cell walls, and their detection via SERS. Microchim Acta 184(1):219–227
Fan W, Lee Y, Pedireddy S, Zhang Q, Liu T, Ling X (2014) Graphene oxide and shape-controlled silver nanoparticle hybrids for ultrasensitive single-particle surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) sensing. Nanoscale 6(9):4843–4851
Chua C, Pumera M (2014) Chemical reduction of graphene oxide: a synthetic chemistry viewpoint. Chem Soc Rev 43:291–312
Wang X, Huang P, Feng L, He M, Guo S, Shen G, Cui D (2012) Green controllable synthesis of silver nanomaterials on graphene oxide sheets via spontaneous reduction. RSC Adv 2(9):3816–3822
Yang D, Cui D (2008) Advances and prospects of gold Nanorods. Chem Asian J 3(12):2010–2022
Wang X, Li Y, Wang H, Fu Q, Peng J, Wang Y, Du J, Zhou Y, Zhan L (2010) Gold nanorod-based localized surface plasmon resonance biosensor for sensitive detection of hepatitis B virus in buffer, blood serum and plasma. Biosens Bioelectron 26(2):404–410
Nikoobakht B, El-Sayed M (2003) Preparation and growth mechanism of gold Nanorods (NRs) using seed-mediated growth method. Chem Mater 15(10):1957–1962
Qu F, Liu Y, Kong R, You J (2017) A versatile DNA detection scheme based on the quenching of fluorescent silver nanoclusters by MoS2 nanosheets: application to aptamer-based determination of hepatitis B virus and of dopamine. Microchim Acta 184(11):4417–4424
Hakonen A, Strömberg N (2012) Diffusion consistent calibrations for improved chemical imaging using nanoparticle enhanced optical sensors. Analyst 137(2):315–321
Shen J, Zhou Y, Fu F, Xu H, Lv J, Xiong Y, Wang A (2015) Immunochromatographic assay for quantitative and sensitive detection of hepatitis B virus surface antigen using highly luminescent quantum dot-beads. Talanta 142:145–149
Narang J, Singhal C, Malhotra N, Narang S, Pn AK, Gupta R, Kansal R, Pundir CS (2016) Impedimetric genosensor for ultratrace detection of hepatitis B virus DNA in patient samples assisted by zeolites and MWCNT nanocomposites. Biosens Bioelectron 86:566–574
Babamiri B, Hallaj R, Salimi A (2018) Ultrasensitive electrochemiluminescence immunosensor for determination of hepatitis B virus surface antigen using CdTe@CdS-PAMAM dendrimer as luminescent labels and Fe3O4 nanoparticles as magnetic beads. Sensor Actuat B-Chem 254:551–560
Zhan L, Zhen S-J, Wan X-Y, Gao P-F, Huang C-Z (2016) A sensitive sueface-enhanced Raman scattering enzyme-catalyzed immunoassay of respiratory syncytial virus. Talanta 148:308–312
Kearns H, Goodacre R, Jamieson LE, Graham D, Faulds K (2017) SERS detection of multiple anti-microbial resistant pathogens using nanosensors. Anal Chem 89(23):12666–12673
Huang K, Li J, Liu Y, Cao X, Yu S, Yu M (2012) Disposable immunoassay for hepatitis B surface antigen based on a graphene paste electrode functionalized with gold nanoparticles and a Nafion-cysteine conjugate. Microchim Acta 177(3–4):419–426
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81472001, 31400851), the Minjiang Scholars Program of Fujian Province, the Tongjiang Scholars Program of Quanzhou City, the Fourth Health Education Joint Development Project of Fujian Province (WKJ-2016-2-36). Natural Science Foundation of Fujian Province (2015 J05030).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOC 422 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, M., Zheng, C., Cui, M. et al. Graphene oxide wrapped with gold nanorods as a tag in a SERS based immunoassay for the hepatitis B surface antigen. Microchim Acta 185, 458 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-2989-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-2989-x