Abstract
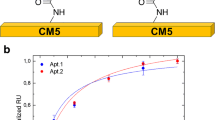
A group of aptamers possessing high specificity and affinity for creatine kinase MB (CKMB) was obtained by magnetic systematic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment. Two aptamers (referred to as C.Apt.21 and C.Apt.30) were found to possess adequately low Kd values. They form a well suited pair for CKMB binding. By using fluorescent microspheres, an aptamer-based lateral flow assay was developed. It is portable, economical, and sensitive. The limit of detection for CKMB is as low as 0.63 ng·mL-1, and the assay works in the 0.005 - 2 μg·mL-1 CKMB concentration range. The method is specific for CKMB, and biomarkers for AMI (such as cardiac troponin I and myoglobin) and serum do not interfere. The strip is highly accurate as shown by analysis of spiked serum samples which gave recoveries ranging between 88 and 117%.

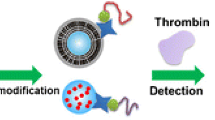
Schematic of the test strip and sandwich aptamer-based fluorometric lateral flow assay for creatine kinease. The detection is based on the specific affinity between CKMB and selected aptamers to form a sandwich structure.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
WHO (2014) Cardiovascular diseases. http://www.who.int/cardiovascular_diseases/en/
Thygesen K, Alpert JS, White HD (2007) Universal definition of myocardial infarction. Circulation 116(22):2634–2653. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.107.187397
Lai XH, Liang RL, Liu TC, Dong ZN, Wu YS, Li LH (2016) A fluorescence immunochromatographic assay using europium (III) chelate microparticles for rapid, quantitative and sensitive detection of creatine kinase MB. J Fluoresc 26(3):987–996. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10895-016-1786-3
Friess U, Stark M (2009) Cardiac markers: a clear cause for point-of-care testing. Anal Bioanal Chem 393(5):1453–1462. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-008-2573-z
Roberts R, Sobel BE, Parker CW (1976) Radioimmunoassay for creatine kinase isoenzymes. Science 194(4267):855–857
Hammerer-Lercher A, Erlacher P, Bittner R, Korinthenberg R, Skladal D, Sorichter S, Sperl W, Puschendorf B, Mair J (2001) Clinical and experimental results on cardiac troponin expression in Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Clin Chem 47(3):451–458
Zhang GJ, Ning Y (2012) Silicon nanowire biosensor and its applications in disease diagnostics: a review. Anal Chim Acta 749:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2012.08.035
Chou SF (2013) Development of a manual self-assembled colloidal gold nanoparticle-immunochromatographic strip for rapid determination of human interferon-gamma. Analyst 138(9):2620–2623. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3an36547f
Li X, Li W, Yang Q, Gong X, Guo W, Dong C, Liu J, Xuan L, Chang J (2014) Rapid and quantitative detection of prostate specific antigen with a quantum dot nanobeads-based immunochromatography test strip. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 6(9):6406–6414. https://doi.org/10.1021/am5012782
Mao X, Wang W, Du T-E (2013) Rapid quantitative immunochromatographic strip for multiple proteins test. Sensors Actuators B Chem 186:315–320. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2013.05.083
Ang SH, Rambeli M, Thevarajah TM, Alias YB, Khor SM (2016) Quantitative, single-step dual measurement of hemoglobin A1c and total hemoglobin in human whole blood using a gold sandwich immunochromatographic assay for personalized medicine. Biosens Bioelectron 78:187–193. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2015.11.045
Wang Z, Li H, Li C, Yu Q, Shen J, De Saeger S (2014) Development and application of a quantitative fluorescence-based immunochromatographic assay for fumonisin b1 in maize. J Agric Food Chem 62(27):6294–6298. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf5017219
Chen R, Li H, Zhang H, Zhang S, Shi W, Shen J, Wang Z (2013) Development of a lateral flow fluorescent microsphere immunoassay for the determination of sulfamethazine in milk. Anal Bioanal Chem 405(21):6783–6789. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-013-7150-4
Torabi F, Mobini Far HR, Danielsson B, Khayyami M (2007) Development of a plasma panel test for detection of human myocardial proteins by capillary immunoassay. Biosens Bioelectron 22(7):1218–1223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2006.04.030
Chen A, Yang S (2015) Replacing antibodies with aptamers in lateral flow immunoassay. Biosens Bioelectron 71:230–242. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2015.04.041
Wang L, Chen W, Ma W, Liu L, Ma W, Zhao Y, Zhu Y, Xu L, Kuang H, Xu C (2011) Fluorescent strip sensor for rapid determination of toxins. Chem Commun (Camb) 47(5):1574–1576. https://doi.org/10.1039/c0cc04032k
Mao X, Ma Y, Zhang A, Zhang L, Zeng L, Liu G (2009) Disposable nucleic acid biosensors based on gold nanoparticle probes and lateral flow strip. Anal Chem 81(4):1660–1668. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac8024653
Darwish NT, Sekaran SD, Khor SM (2018) Point-of-care tests: a review of advances in the emerging diagnostic tools for dengue virus infection. Sensors Actuators B Chem 255:3316–3331. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2017.09.159
Sajid M, Kawde A-N, Daud M (2015) Designs, formats and applications of lateral flow assay: a literature review. J Saudi Chem Soc 19(6):689–705. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jscs.2014.09.001
Cheng S, Yang Y, Ni X, Peng J, Lai W (2017) Fluorescent microspheres lateral flow assay for sensitive detection of the milk allergen casein. Food Agric Immunol 28(6):1017–1028. https://doi.org/10.1080/09540105.2017.1325841
Zhang X, Wen K, Wang Z, Jiang H, Beier RC, Shen J (2016) An ultra-sensitive monoclonal antibody-based fluorescent microsphere immunochromatographic test strip assay for detecting aflatoxin M 1 in milk. Food Control 60(2):588–595. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2015.08.040
Gui C, Wang K, Li C, Dai X, Cui D (2014) A CCD-based reader combined with CdS quantum dot-labeled lateral flow strips for ultrasensitive quantitative detection of CagA. Nanoscale Res Lett 9(1):1–8. https://doi.org/10.1186/1556-276X-9-57
Zeng N, You Y, Xie L, Zhang H, Ye L, Hong W, Li Y, Zeng N, You Y, Xie L (2017) A new imaged-based quantitative reader for the gold immunochromatographic assay. Optik 152:92–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2017.09.109
Hohenstein J, O’Dell D, Murnane EL, Lu Z, Erickson D, Gay G (2017) Enhancing the usability of an optical reader system to support point-of-care rapid diagnostic testing: an iterative design approach. JHF 4(4):e29. https://doi.org/10.2196/humanfactors.8621
Lee S, Kim G, Moon J (2013) Performance improvement of the one-dot lateral flow immunoassay for aflatoxin b1 by using a smartphone-based reading system. Sensors 13(4):5109–5116. https://doi.org/10.3390/s130405109
Sefah K, Shangguan D, Xiong X, O'Donoghue MB, Tan W (2010) Development of DNA aptamers using Cell-SELEX. Nat Protoc 5(6):1169–1185. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2010.66
Xiao P, Lv X, Wang S, Iqbal J, Qing H, Li Q, Deng Y (2013) An aptamer-based trypsin reactor for on-line protein digestion with electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry. Anal Biochem 441(2):123–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ab.2013.06.012
Fialová M, Kypr J, Vorlícková M (2006) The thrombin binding aptamer GGTTGGTGTGGTTGG forms a bimolecular guanine tetraplex. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 344(1):50–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2006.03.144
Vianini E, Palumbo M, Gatto B (2001) In vitro selection of DNA aptamers that bind L-tyrosinamide. Bioorg Med Chem 9(10):2543–2548. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0968-0896(01)00054-2
Li S, Huo Y, Tian H, Zhang Q, Lv Y, Hao Z (2015) Invitro selection and characterization of deoxyribonucleic acid aptamers against connective tissue growth factor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 457(4):640–646. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2015.01.041
Ha NR, Lee SC, Hyun JW, Yoon MY (2016) Development of inhibitory ssDNA aptamers for the FtsZ cell division protein from citrus canker phytopathogen. Process Biochem 51(1):24–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2015.11.008
Di Nardo F, Anfossi L, Giovannoli C, Passini C, Goftman VV, Goryacheva IY, Baggiani C (2016) A fluorescent immunochromatographic strip test using Quantum Dots for fumonisins detection. Talanta 150:463–468. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2015.12.072
Liu M, Zeng LF, Yang YJ, Hu LM, Lai WH (2017) Fluorescent microsphere immunochromatographic assays for detecting bone alkaline phosphatase based on biolayer interferometry-selected antibody. RSC Adv 7(52):32952–32959. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7RA03756B
Acknowledgement
This work was partly supported by the National Special R&D Programmer for Key Scientific Instruments and Equipment (2012YQ04014001) and the Beijing Institute of Technology Research Foundation (3160050321211).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 1278 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, J., Lv, X., Feng, W. et al. Aptamer-based fluorometric lateral flow assay for creatine kinase MB. Microchim Acta 185, 364 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-2905-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-2905-4