Abstract
The authors describe an amperometric sensor for dopamine (DA) by employing olive-like Fe2O3 microspheres (OFMs) as the electrocatalyst for DA oxidization. The OFMs were prepared by using a protein templated method. The structure and properties of the OFMs were characterized by scanning electron microscopy, X-ray powder diffraction, energy dispersive x-ray spectroscopy, cyclic voltammetry and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. The OFMs possess excellent catalytic activity towards DA oxidization due to their unique morphology. The sensor responds to DA within less than 5 s. The sensor, best operated at a voltage of +0.2 V (vs. SCE) responds linearly in the 0.2 to 115 μM DA concentration range and has a 30 nM detection limit. The selectivity, reproducibility and long-term stability of the sensor are acceptable. It performs well when applied to spiked human urine samples.

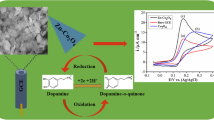
Olive-like Fe2O3 microspheres (OFMs), synthesized using egg white as template, display excellent catalytic activity towards dopamine (DA) oxidization due to their unique morphology. They were applied for DA detection using the amperometric technique. The electrochemical sensor exhibited a high sensitivity and a 30 nM detection limit. DAQ: dopaquinone.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rasheed PA, Lee J-S (2017) Recent advances in optical detection of dopamine using nanomaterials. Microchim Acta 184(5):1239–1266
Peltola E, Sainio S, Holt KB, Palomäki T, Koskinen J, Laurila TL (2018) Electrochemical fouling of dopamine and recovery of carbon electrodes. Anal Chem 90(2):1408–1416
Wightman R, May L, Michael A (1988) Detection of dopamine dynamics in the brain. Anal Chem 60(13):769–779
Li Y, Peng W, You X (2017) Determination of dopamine by exploiting the catalytic effect of hemoglobin–stabilized gold nanoclusters on the luminol–NaIO4 chemiluminescence system. Microchim Acta 184(9):3539–3545
Carrera V, Sabater E, Vilanova E, Sogorb MA (2007) A simple and rapid HPLC–MS method for the simultaneous determination of epinephrine, norepinephrine, dopamine and 5-hydroxytryptamine: application to the secretion of bovine chromaffin cell cultures. J Chromatogr B 847(2):88–94
Mamiński M, Olejniczak M, Chudy M, Dybko A, Brzózka Z (2005) Spectrophotometric determination of dopamine in microliter scale using microfluidic system based on polymeric technology. Anal Chim Acta 540(1):153–157
Wang D, Hu Y, Meng L, Wang X, Lu Q (2015) One-pot synthesis of fluorescent and cross-linked polyphosphazene nanoparticles for highly sensitive and selective detection of dopamine in body fluids. RSC Adv 5(112):92762–92768
Wen D, Liu W, Herrmann A, Haubold D, Holzschuh M, Simon F, Eychmüller A (2016) Simple and sensitive colorimetric detection of dopamine based on assembly of cyclodextrin-modified au nanoparticles. Small 12(18):2439–2442
Li H, Wang W, Lv Q, Xi G, Bai H, Zhang Q (2016) Disposable paper-based electrochemical sensor based on stacked gold nanoparticles supported carbon nanotubes for the determination of bisphenol a. Electrochem Commun 68:104–107
Zhong S, Zhuang J, Yang D-P, Tang D (2017) Eggshell membrane-templated synthesis of 3D hierarchical porous au networks for electrochemical nonenzymatic glucose sensor. Biosens Bioelectron 96:26–32
Hammami A, Sahli R, Raouafi N (2016) Indirect amperometric sensing of dopamine using a redox-switchable naphthoquinone-terminated self-assembled monolayer on gold electrode. Microchim Acta 183(3):1137–1144
Cheemalapati S, Palanisamy S, Mani V, Chen S-M (2013) Simultaneous electrochemical determination of dopamine and paracetamol on multiwalled carbon nanotubes/graphene oxide nanocomposite-modified glassy carbon electrode. Talanta 117:297–304
VanDersarl JJ, Mercanzini A, Renaud P (2015) Integration of 2D and 3D thin film glassy carbon electrode arrays for electrochemical dopamine sensing in flexible neuroelectronic implants. Adv Funct Mater 25(1):78–84
Kang M, Yoo SM, Gwak R, Eom G, Kim J, Lee SY, Kim B (2016) Electro-triggering and electrochemical monitoring of dopamine exocytosis from a single cell by using ultrathin electrodes based on au nanowires. Nanoscale 8(1):214–218
Anithaa AC, Lavanya N, Asokan K, Sekar C (2015) WO3 nanoparticles based direct electrochemical dopamine sensor in the presence of ascorbic acid. Electrochim Acta 167:294–302
Mercante LA, Pavinatto A, Iwaki LEO, Scagion VP, Zucolotto V, Oliveira ON, Mattoso LHC, Correa DS (2015) Electrospun polyamide 6/poly(allylamine hydrochloride) nanofibers functionalized with carbon nanotubes for electrochemical detection of dopamine. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7(8):4784–4790
Gao F, Cai X, Wang X, Gao C, Liu S, Gao F, Wang Q (2013) Highly sensitive and selective detection of dopamine in the presence of ascorbic acid at graphene oxide modified electrode. Sensors Actuators B Chem 186:380–387
Wang X, Wang Q, Wang Q, Gao F, Gao F, Yang Y, Guo H (2014) Highly dispersible and stable copper terephthalate metal–organic framework-graphene oxide nanocomposite for an electrochemical sensing application. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 6:11573–11580
Lin R, Lim TM, Tran T (2018) Carbon nanotube band electrodes for electrochemical sensors. Electrochem Commun 86:135–139
Corma A, Serna P (2006) Chemoselective hydrogenation of nitro compounds with supported gold catalysts. Science 313(5785):332–334
Adekunle AS, Agboola BO, Pillay J, Ozoemena KI (2010) Electrocatalytic detection of dopamine at single-walled carbon nanotubes–iron (III) oxide nanoparticles platform. Sensors Actuators B Chem 148(1):93–102
Cao X, Xu Y, Wang N (2012) Hollow Fe2O3 polyhedrons: one-pot synthesis and their use as electrochemical material for nitrite sensing. Electrochim Acta 59:81–85
Chen A, Xu L, Zhang X, Yang Z, Yang S (2016) Improving surface adsorption via shape control of hematite α-Fe2O3 nanoparticles for sensitive dopamine sensors. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8(49):33765–33774
Zhu M, Diao G (2011) Synthesis of porous Fe3O4 nanospheres and its application for the catalytic degradation of xylenol orange. J Phys Chem C 115(39):18923–18934
Rani GJ, Babu KJ, kumar GG, MAJ R (2016) Watsonia meriana flower like Fe3O4/reduced graphene oxide nanocomposite for the highly sensitive and selective electrochemical sensing of dopamine. Alloys Compd 688:500–512
Zen J-M, Chen P-J (1997) A selective voltammetric method for uric acid and dopamine detection using clay-modified electrodes. Anal Chem 69(24):5087–5093
Jie Y, Wang N, Cao X, Xu Y, Li T, Zhang X, Wang ZL (2015) Self-powered triboelectric nanosensor with poly(tetrafluoroethylene) nanoparticle arrays for dopamine detection. ACS Nano 9(8):8376–8383
Roychoudhury A, Basu S, Jha SK (2016) Dopamine biosensor based on surface functionalized nanostructured nickel oxide platform. Biosens Bioelectron 84:72–81
Qi S, Zhao B, Tang H, Jiang X (2015) Determination of ascorbic acid, dopamine, and uric acid by a novel electrochemical sensor based on pristine graphene. Electrochim Acta 161:395–402
Xu G, Jarjes Z, Desprez V, Kilmartin PA, Travas-Sejdic J (2018) Sensitive, selective, disposable electrochemical dopamine sensor based on PEDOT-modified laser scribed graphene. Biosens Bioelectron 107:184–191
Numan A, Shahid MM, Omar FS, Ramesh K, Ramesh S (2017) Facile fabrication of cobalt oxide nanograin-decorated reduced graphene oxide composite as ultrasensitive platform for dopamine detection. Sensors Actuators B Chem 238:1043–1051
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81472001, 31400851 & 21705092), Program of Science and Technology in Quanzhou City (2018Z132), the Minjiang Scholars Program of Fujian Province, the Tongjiang Scholars Program of Quanzhou City, the Fourth Health Education Joint Development Project of Fujian Province (WKJ-2016-2-36) and the Fujian Educational Committee (JAT170487).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 357 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, X., Liu, Q., Liu, M. et al. Protein-templated Fe2O3 microspheres for highly sensitive amperometric detection of dopamine. Microchim Acta 185, 340 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-2876-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-2876-5