Abstract
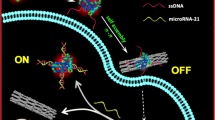
A dual-channel ratiometric nanoprobe is described for detection and imaging of microRNA. It was prepared from MoS2 quantum dots (QDs; with blue emission and excitation/emission peaks at 310/398 nm) which acts as both the gene carrier and as a donor in fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET). Molecular beacons containing loops for molecular recognition of microRNA and labeled with carboxyfluorescein (FAM) were covalently attached to the MoS2 QDs and serve as the FRET acceptor. In the absence of microRNA, the nanoprobe exhibits low FRET efficiency due to the close distance between the FAM tag and the QDs. Hybridization with microRNA enlarges the distance between QD and beacon. This results in an enhancement of the FRET efficiency of the nanoprobe. The ratio of green and blue fluorescence (I520/I398) increases linearly in the 5 to 150 nM microRNA concentration range in both aqueous solution and diluted artificial cerebrospinal fluid. The limit of detection (LOD) is as low as 0.38 nM and 0.52 nM, respectively. Other features of this nanoprobe include (a) excellent resistance to nuclease-induced false positive signals and (b) the option to use it for distinguishing different cell lines by in-situ imaging of intracellular microRNAs.

Schematic of a dual-channel photoluminescence nanoprobe for the determination of microRNA-21 (miR-21) by monitoring the microRNA-triggered enhancement of the fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) efficiency between MoS2 QDs and carboxyfluorescein-labeled molecular beacons.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lee J-S, Kim S, Na H-K, Min D-H (2016) MicroRNA-responsive drug release system for selective fluorescence imaging and photodynamic therapy in vivo. Adv Healthc Mater 5(18):2386–2395
Qian R-C, Cao Y, Long Y-T (2016) Binary system for MicroRNA-targeted imaging in single cells and Photothermal Cancer therapy. Anal Chem 88(17):8640–8647
Lin S, Gregory RI (2015) MicroRNA biogenesis pathways in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 15(6):321–333
Hébert SS, De SB (2009) Alterations of the microRNA network cause neurodegenerative disease. Trends Neurosci 32(4):199–206
Musilova K, Mraz M (2015) MicroRNAs in B-cell lymphomas: how a complex biology gets more complex. Leukemia 29(5):1004–1017
Liu R, Chen X, Du Y, Yao W, Shen L, Wang C, Hu Z, Zhuang R, Ning G, Zhang C (2012) Serum microRNA expression profile as a biomarker in the diagnosis and prognosis of pancreatic cancer. Clin Chem 58(3):610–618
Taylor DD, Gercel-Taylor C (2008) MicroRNA signatures of tumor-derived exosomes as diagnostic biomarkers of ovarian cancer. Gynecol Oncol 110(1):13–21
Joshi GK, Deitzmcelyea S, Liyanage T, Lawrence K, Mali S, Sardar R, Korc M (2015) Label-free Nanoplasmonic-based short noncoding RNA sensing at Attomolar concentrations allows for quantitative and highly specific assay of MicroRNA-10b in biological fluids and circulating exosomes. ACS Nano 9(11):11075–11089
Yuan Y-H, Wu Y-D, Chi B-Z, Wen S-H, Lian R-P, Qiu J-D (2017) Simultaneously electrochemical detection of microRNAs based on multifunctional magnetic nanoparticles probe coupling with hybridization chain reaction. Biosens Bioelectron 97:325–331
Guo Q, Bian F, Liu Y, Qu X, Hu X, Sun Q (2017) Hybridization chain reactions on silica coated Qbeads for the colorimetric detection of multiplex microRNAs. Chem Commun 53(36):4954–4957
Kim S, Park JE, Hwang W, Seo J, Lee YK, Hwang JH, Nam JM (2017) Optokinetically encoded Nanoprobe-based multiplexing strategy for MicroRNA profiling. J Am Chem Soc 139(9):3558–3566
Yin BC, Liu YQ, Ye BC (2012) One-step, multiplexed fluorescence detection of microRNAs based on duplex-specific nuclease signal amplification. J Am Chem Soc 134(11):5064–5067
Borghei YS, Hosseini M, Ganjali MR (2017) Fluorometric determination of microRNA via FRET between silver nanoclusters and CdTe quantum dots. Microchim Acta 184(12):1–9
Liu H, Bei X, Xia Q, Fu Y, Zhang S, Liu M, Fan K, Zhang M, Yang Y (2016) Enzyme-free electrochemical detection of microRNA-21 using immobilized hairpin probes and a target-triggered hybridization chain reaction amplification strategy. Microchim Acta 183(1):297–304
Yang JR, Tang M, Diao W, Cheng WB, Zhang Y, Yan YR (2016) Electrochemical strategy for ultrasensitive detection of microRNA based on MNAzyme-mediated rolling circle amplification on a gold electrode. Microchim Acta 183(11):3061–3067
Zeng K, Li HY, Peng YY (2017) Gold nanoparticle enhanced surface plasmon resonance imaging of microRNA-155 using a functional nucleic acid-based amplification machine. Microchim Acta 184(8):2637–2644
Lee J, Jin YA, Ko HY, Lee YS, Heo H, Cho S, Kim S (2015) Magnetic resonance beacon to detect intracellular microRNA during neurogenesis. Biomaterials 41:69–78
Zhao X, Xu L, Sun M, Ma W, Wu X, Kuang H, Wang L, Xu C (2016) Gold-quantum dot Core–satellite assemblies for lighting up MicroRNA in vitro and in vivo. Small 12(34):4662–4668
Ye S, Li X, Wang M, Tang B (2017) Fluorescence and SERS imaging for the simultaneous absolute quantification of multiple miRNAs in living cells. Anal Chem 89(9):5124–5130
Huang L, Chen Y, Chen L, Xiao X, Wang X, Li J, Zhang Y (2017) Photo-clickable microRNA for in situ fluorescence labeling and imaging of microRNA in living cells. Chem Commun 53(48):6452–6455
Ha HD, Han DJ, Choi JS, Park M, Seo TS (2014) Dual role of blue luminescent MoS2 quantum dots in fluorescence resonance energy transfer phenomenon. Small 10(19):3858–3862
Shi HY, Yang L, Zhou XY, Bai J, Gao J, Jia HX, Li QG (2017) A gold nanoparticle-based colorimetric strategy coupled to duplex-specific nuclease signal amplification for the determination of microRNA. Microchim Acta 184(2):525–531
Zhang H, Wang Y, Zhao D, Zeng D, Xia J, Aldalbahi A, Wang C, San L, Fan C, Zuo X (2015) Universal fluorescence biosensor platform based on graphene quantum dots and pyrene-functionalized molecular beacons for detection of MicroRNAs. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7(30):16152–16156
Li Y, Pu Q, Li J, Zhou L, Tao Y, Li Y, Yu W, Xie G (2017) An “off-on” fluorescent switch assay for microRNA using nonenzymatic ligation-rolling circle amplification. Microchim Acta 184(11):4323–4330
He L, Lu DQ, Liang H, Xie S, Luo C, Hu M, Xu L, Zhang X, Tan W (2017) Fluorescence resonance energy transfer-based DNA tetrahedron Nano-tweezer for highly reliable detection of tumor-related mRNA in living cells. ACS Nano 11(4):4060–4066
Fu Y, Chen T, Wang G, Gu T, Xie C, Huang J, Li X, Best S, Han G (2017) Production of a fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) biosensor membrane for microRNA detection. J Mater Chem B 5(34):7133–7139
Chen YX, Huang KJ, Niu KX (2018) Recent advances in signal amplification strategy based on oligonucleotide and nanomaterials for microRNA detection-a review. Biosens Bioelectron 99:612–624
Liu LZ, Jiang ST, Wang L, Zhang Z, Xie GM (2015) Direct detection of microRNA-126 at a femtomolar level using a glassy carbon electrode modified with chitosan, graphene sheets, and a poly(amidoamine) dendrimer composite with gold and silver nanoclusters. Microchim Acta 182(1–2):77–84
Zhou LL, Wang J, Chen ZP, Li JL, Wang T, Zhang Z, Xie GM (2017) A universal electrochemical biosensor for the highly sensitive determination of microRNAs based on isothermal target recycling amplification and a DNA signal transducer triggered reaction. Microchim Acta 184(5):1305–1313
Yi JT, Chen TT, Huo J, Chu X (2017) Nanoscale Zeolitic Imidazolate Framework-8 for Ratiometric fluorescence imaging of MicroRNA in living cells. Anal Chem 89(22):12351–12359
Li S, Xu L, Sun M, Wu X, Liu L, Kuang H, Xu C (2017) Hybrid nanoparticle pyramids for intracellular dual MicroRNAs Biosensing and Bioimaging. Adv Mater 29(19):1606086
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21705012, 21675016) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (106112017CDJXFLX0014).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 809 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, X., Hu, L., Zhang, F. et al. MoS2 quantum dots modified with a labeled molecular beacon as a ratiometric fluorescent gene probe for FRET based detection and imaging of microRNA. Microchim Acta 185, 239 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-2773-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-2773-y