Abstract
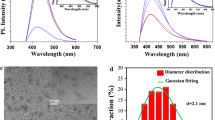
Hollow carbon dots (HCDs) were prepared by a solvothermal method and conjugated to either tetramethyl rhodamine isothiocyanate (TRITC) or fluorescein-5-isothiocyanate (FITC). This resulted in HCDs with bright red or green fluorescence, with excitation/emission peaks at 550/580 and 491/520 nm, respectively. The nanocomposites are well water-soluble, remarkably photostable and biocompatible. In addition, the fluorescence of the composites is more stable in a reactive oxygen environment than the free dyes. Confocal images indicate that the nanoparticles quickly enter A549 cells and mainly accumulate in the cytoplasm. The wavelength of functionalized HCDs can be regulating via coupling the HCDs to different dyes. These results demonstrate that these composite materials can be very promising reagents for biological labeling and imaging.

Schematic of the preparation of hollow carbon dots conjugated to tetramethyl rhodamine isothiocyanate (RHCDs) by solvothermal method. The material is water-soluble, remarkably photostable and biocompatible. It was applied to cellular labeling and imaging.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shen J, Zhu Y, Yang X, Li C (2012) Graphene quantum dots: emergent nanolights for bioimaging, sensors, catalysis and photovoltaic devices. Chem Commun 48:3686–3699
Baker SN, Baker GA (2010) Luminescent carbon nanodots: emergent nanolights. Angew Chem Int Ed 49:6726–6744
Zhou J, Zhou H, Tang J, Deng S, Yan F, Li W, Qu M (2017) Carbon dots doped with heteroatoms for fluorescent bioimaging: a review. Microchim Acta 184:343–368
Tang L, Ji R, Cao X, Lin J, Jiang H, Li X, Teng KS, Luk CM, Zeng S, Hao J, Lau SP (2012) Deep ultraviolet photoluminescence of water-soluble self-passivated graphene quantum dots. ACS Nano 6:5102–5110
Miao X, Qu D, Yang D, Nie B, Zhao Y, Fan H, Sun Z (2017) Synthesis of carbon dots with multiple color emission by controlled graphitization and surface functionalization. Adv Mater 30. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201704740
Wang W, Lu YC, Huang H, Feng JJ, Chen JR, Wang AJ (2014) Facile synthesis of water-soluble and biocompatible fluorescent nitrogen-doped carbon dots for cell imaging. Analyst 139:1692–1696
Bourlinos AB, Stassinopoulos A, Anglos D et al (2012) Surface functionalized carbogenic quantum dots. Small 4:455–458
Wu B, Zhu R, Wang M, Liang P, Qian Y, Wang S (2017) Fluorescent carbon dots from antineoplastic drug etoposide for bioimaging in vitro and in vivo. J Mater Chem B 5:7796–7800
Yang ST, Cao L, Sun YP et al (2009) Carbon dots for optical imaging in vivo. J Am Chem Soc 131:11308–11309
Li Q, Ohulchanskyy TY, Prasad PN et al (2010) Photoluminescent carbon dots as biocompatible Nanoprobes for targeting Cancer cells in vitro. J Phys Chem C 114:12062–12068
Huang H, Xu Y, Tang CJ, Chen JR, Wang AJ, Feng JJ (2014) Facile and green synthesis of photoluminescent carbon nanoparticles for cellular imaging. New J Chem 38:784–789
Pan DY, Guo L, Wu MH et al (2012) Cutting sp 2 clusters in graphene sheets into colloidal graphene quantum dots with strong green fluorescence. J Mater Chem 22:3314–3318
Luo PG, Yang F, Yang ST, Sonkar SK, Yang L, Broglie JJ, Liu Y, Sun YP (2014) Carbon-based quantum dots for fluorescence imaging of cells and tissues. RSC Adv 4:10791–10807
Lei Z, Xu S, Wan J et al (2016) Facile synthesis of N-rich carbon quantum dots by spontaneous polymerization and incision of solvents as efficient bioimaging probes and advanced electrocatalysts for oxygen reduction reaction. Nano 8:2219–2226
Sun YP, Zhou B, Lin Y, Wang W, Fernando KAS, Pathak P, Meziani MJ, Harruff BA, Wang X, Wang H, Luo PG, Yang H, Kose ME, Chen B, Veca LM, Xie SY (2006) Quantum-sized carbon dots for bright and colorful photoluminescence. J Am Chem Soc 128:7756–7757
Hu S, Dong Y, Cao S et al (2012) Simultaneous synthesis of luminescent carbon nanoparticles and carbon nanocages by laser ablation of carbon black suspension and their optical limiting properties. J Mater Chem 22:1957–1961
Li Y, Hu Y, Qu L et al (2011) An electrochemical avenue to green-luminescent graphene quantum dots as potential electron-acceptors for photovoltaics. Adv Mater 23:776–780
Wang F, Li Q, Liu C et al (2010) One-step synthesis of highly luminescent carbon dots in noncoordinating solvents. Chem Mater 22:4528–4530
Liu R, Wu D, Li Q et al (2009) An aqueous route to multicolor photoluminescent carbon dots using silica spheres as carriers. Angew Chem 121:4668–4671
Wang X, Cao L, Yang ST, Lu F, Meziani M J, Tian L, Sun K W, Bloodgood M A, Sun YP (2010) Bandgap-like strong fluorescence in functionalized carbon nanoparticles. Angew Chem 49:5310–5314
Liu C, Zhang P, Tian F, Li W, Li F, Liu W (2011) One-step synthesis of surface passivated carbon nanodots by microwave assisted pyrolysis for enhanced multicolor photoluminescence and bioimaging. J Mater Chem 21:13163–13167
Miao X, Yan X, Qu D, Li D, Tao FF, Sun Z (2017) Red emissive sulfur, nitrogen codoped carbon dots and their application in ion detection and theraonostics. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9:18549–18556
Qu D, Miao X, Wang X, Nie C, Li Y, Luo L, Sun Z (2017) Se & N co-doped carbon dots for high-performance fluorescence imaging agent of angiography. J Mater Chem B 5:4988–4992
Li H, Shao FQ, Zou SY, Yang QJ, Huang H, Feng JJ, Wang AJ (2016) Microwave-assisted synthesis of N, P-doped carbon dots for fluorescent cell imaging. Microchim Acta 183:821–826
Zheng H, Wang Q, Long Y, Zhang H, Huang X, Zhu R (2011) Enhancing the luminescence of carbon dots with a reduction pathway. Chem Commun 47:10650–10652
Li J, Jiao Y, Feng L, Zhong Y, Zuo G, Xie A, Dong W (2017) Highly N, P-doped carbon dots: rational design, photoluminescence and cellular imaging. Microchim Acta 184:2933–2940
Wang Q, Huang X, Zheng H et al (2013) Hollow luminescent carbon dots for drug delivery. Carbon 59:192–199
Das B, Dadhich P, Pal P, Srivas PK, Bankoti K, Dhara S (2014) Carbon nanodots from date molasses: new nanolights for the in vitro scavenging of reactive oxygen species. J Mater Chem B 2:6839–6684
Shi L, Li X, Li Y, Wen X, Li J, Choi MMF, Dong C, Shuang S (2015) Naked oats-derived dual-emission carbon nanodots for ratiometric sensing and cellular imaging. Sensors Actuators B Chem 210:533–541
Sachdev A, Matai I, Gopinath P (2015) Dual-functional carbon dots–silver@zinc oxide nanocomposite: in vitro evaluation of cellular uptake and induction of apoptosis. J Mater Chem B 3:1217–1229
Wang LL, Xue LX, Yan HX, Li J, Lu YC (2010) Effects of ROCK inhibitor, Y-27632, on adhesion and mobility in esophageal squamous cell cancer cells. Mol Biol Rep 37:1971–1977
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Key Scientific Program Nanoscience and Nanotechnology (No. 2011CB933600), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21405124).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOC 20947 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tang, M., Teng, P., Long, Y. et al. Hollow carbon dots labeled with FITC or TRITC for use in fluorescent cellular imaging. Microchim Acta 185, 223 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-2761-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-2761-2